Q6I750
Gene name |
HAI-1 |
Protein name |
Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor-1 |
Names |
|
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
KUNITZ-TYPE PROTEASE INHIBITOR 1 (PTHR46750) |
Descriptions
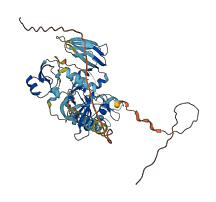
Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 1 (HAI-1) is important in the integrity of the basement membrane during placental development and maintaining postnatal tissue homeostasis including keratinization of the epidermis, hair development, colonic epithelium integrity, proliferation and cell fate of neural progenitor cells, and tissue injury and repair. HAI-1 is a membrane-bound multidomain protein containing an extracellular region that consists of a MANEC (motif at N terminus with eight cysteines, or MANSC) PAN-apple-like domain, an internal PKD-like domain, a Kunitz domain 1, a low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLRA) domain, and a Kunitz domain 2 followed by a C-terminal single-span transmembrane region.
HAI-1 inhibits a number of serine proteases, including matriptase, HGFA, hepsin, trypsin, and prostasin. The full-length extracellular portion of HAI-1 (sHAI-1) shows weaker inhibitory activity toward target proteases than the smaller fragments, suggesting autoinhibition of HAI-1. The full-length extracellular domain of HAI-1 (sHAI-1) has a compact conformation mediated by the MANEC domain and a long but well-ordered linker (365-linker), which sterically blocks the active site in Kunitz domain 1. Kunitz domain 2 also slightly inhibits the inhibitory activity of sHAI-1 in synergy with MANEC domain.
Also, an N-linked glycan moiety in the MANEC domain (Asn66) can block an additionally larger surrounding area from protease accessibility and the deglycosylation of Asn66 leads to stronger protease suppressive activity by releasing the autoinhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
241-295 (Kunitz domain 1) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay |
Target domain |
241-295 (Kunitz domain 1) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay |
Target domain |
241-295 (Kunitz domain 1) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Liu M et al. (2017) "The crystal structure of a multidomain protease inhibitor (HAI-1) reveals the mechanism of its auto-inhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 292, 8412-8423
- Kojima K et al. (2008) "Roles of functional and structural domains of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 in the inhibition of matriptase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 283, 2478-87
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q6I750
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q6I750-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q6I750
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q6I750 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q6I750
9 regional properties for Q6I750
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | FERM domain | 86 - 403 | IPR000299 |
| domain | I/LWEQ domain | 2293 - 2533 | IPR002558 |
| domain | Talin, central | 491 - 652 | IPR015224 |
| conserved_site | FERM conserved site | 173 - 201 | IPR019747-1 |
| conserved_site | FERM conserved site | 283 - 312 | IPR019747-2 |
| domain | FERM central domain | 202 - 313 | IPR019748 |
| domain | Band 4.1 domain | 82 - 313 | IPR019749 |
| domain | Talin, N-terminal F0 domain | 4 - 83 | IPR032425 |
| domain | Talin-1/2, rod-segment | 1654 - 1826 | IPR037438 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR46750 | KUNITZ-TYPE PROTEASE INHIBITOR 1 |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR46750:SF1 | KUNITZ-TYPE PROTEASE INHIBITOR 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | protease inhibitor | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a serine-type endopeptidase. |
No GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for biological process |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAARRLAQAS | ISTACVWLLC | ALGLQGTETE | LPSAPPEFSG | GAACLNRFTS | GVPAFVLDTE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ASVSNGATFL | GSPTVHRGWD | CVRACCTTQN | CNLALVELQP | DGGEDAISAC | FLMNCLYEQN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FVCKFAPKDG | FINYLTQDLY | NSYRELRTRG | FGGSRIPRIW | MGIDLKVQLQ | KPLVLRDADN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TDWHLLQGDQ | DVSVKRNHPE | EVELWGLKEG | TYLFQLTRTD | SDQLEETVNL | TITVLTAEQT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EDYCLASYKV | GRCRGSFPRW | YYDPKEQICK | SFTFGGCLGN | KNNYLREEEC | MLACKDVKGI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SPKRHHPVCT | GSCHSTQFQC | SNGCCIDGFL | ECDDTPDCPD | GSDEATCEKY | SSGFDELQSI |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| HFLSDKGYCA | ELPDTGFCKE | NIPRWYYNPF | SERCARFTYG | GCYGNKNNFE | KEQQCLESCR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GISKKDVFGL | RRESSVPSAG | SVEVAIAVLL | AVCIIVVLTI | LGYCFFKNQK | KNFHSPLHQP |
| 490 | 500 | ||||
| PPTPASSTVS | TTEDTEHLVY | NHTTQPL |