Q6F353
Gene name |
Os05g0235800 (LOC_Os05g14590, OJ1384_A02.2, OsJ_17726, OSJNBa0093E24.13) |
Protein name |
DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 |
Names |
Minichromosome maintenance protein 6, OsMCM6 |
Species |
Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) |
KEGG Pathway |
osa:4338176 |
EC number |
3.6.4.12: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
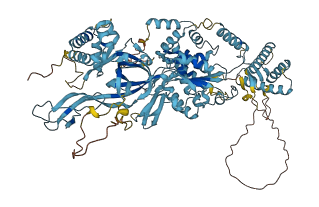
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q6F353
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q6F353-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q6F353
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q6F353 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q6F353
7 regional properties for Q6F353
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 656 - 912 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 773 - 785 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 662 - 685 | IPR017441 |
| domain | MAP3K, TRAFs-binding domain | 140 - 518 | IPR025136 |
| domain | MAP3K, PH domain | 531 - 627 | IPR043969 |
| domain | MAP3K, deoxyribohydrolase domain | 90 - 125 | IPR046872 |
| domain | MAP3K, HisK-N-like globin domain | 1009 - 1140 | IPR046873 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.12 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| MCM complex | A hexameric protein complex required for the initiation and regulation of DNA replication. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| DNA helicase activity | Unwinding of a DNA helix, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| single-stranded DNA binding | Binding to single-stranded DNA. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA replication initiation | The process in which DNA-dependent DNA replication is started; this begins with the ATP dependent loading of an initiator complex onto the DNA, this is followed by DNA melting and helicase activity. In bacteria, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are loaded after the initial melting and in archaea and eukaryotes, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are inactive when they are loaded and subsequently activate. |
| DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication | The process in which interchain hydrogen bonds between two strands of DNA are broken or 'melted', generating unpaired template strands for DNA replication. |
| double-strand break repair via break-induced replication | The error-free repair of a double-strand break in DNA in which the centromere-proximal end of a broken chromosome searches for a homologous region in an intact chromosome. DNA synthesis initiates from the 3' end of the invading DNA strand, using the intact chromosome as the template, and progresses to the end of the chromosome. |
| mitotic DNA replication | Any nuclear DNA replication that is involved in a mitotic cell cycle. |
10 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2KIZ8 | MCM6 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9V461 | Mcm6 | DNA replication licensing factor Mcm6 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q14566 | MCM6 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P97311 | Mcm6 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62724 | Mcm6 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q69QA6 | MCM9 | Probable DNA helicase MCM9 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| P34647 | mcm-6 | DNA replication licensing factor mcm-6 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9SF37 | MCM8 | Probable DNA helicase MCM8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q28CM3 | mmcm6 | Maternal DNA replication licensing factor mcm6 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q6P1V8 | zmcm6 | Zygotic DNA replication licensing factor mcm6 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEAFGGFFVD | EKAARVENIF | LEFLRRFKEA | DAAEAFYETE | LEAMRSREST | TMYVDFAHVM |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RFNDVLQKAI | SEEYLRFEPY | LRNACKRFVM | EQRTGENRAP | IISDDSPNKD | INIAFYNIPM |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LKRLRELGTA | EIGKLTAVMG | VVTRTSEVRP | ELLQGTFKCL | DCGNVVKNVE | QQFKYTEPII |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| CVNATCQNRS | KWALLRQESK | FTDWQRVRMQ | ETSKEIPAGS | LPRSLDVILR | HEIVEKARAG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DTVIFTGTVV | AVPDVMALTS | PGERAECRRE | APQRKNGSGV | QEGVKGLKSL | GVRDLSYRLA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| FVANSVQVAD | GRREVDIRDR | DIDGDDSERQ | KFTEEEEDEV | VRMRNVPDFF | NKIVDSICPT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VFGHQEIKRA | ILLMLLGGVH | KITHEGINLR | GDINVCIVGD | PSCAKSQFLK | YTAGIVPRSV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YTSGKSSSAA | GLTATVAKEP | ETGEFCIEAG | ALMLADNGIC | CIDEFDKMDI | KDQVAIHEAM |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EQQTISITKA | GIQATLNART | SILAAANPTG | GRYDKSKPLK | YNVALPPAIL | SRFDLVYIMI |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| DEPDENTDYH | IAHHIVRVHQ | KREEALAPAF | STAELKRYIA | FAKSLKPQLS | SEAKKVLVES |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| YVTLRRGDST | PGTRVAYRMT | VRQLEALIRL | SEAIARSHLE | RVVLPAHVRM | AVKLLKTSII |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| SVESSEVDLS | DFQDADDGTN | VPADNDAGQP | TEMDAAPQQD | GPENEQAADT | GKKKLVITEE |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| HFQRVTQALV | MRLRQHEESV | TKDGDGLAGM | KQGDLIIWYV | EQQNAQGAYS | STAEVKEEVK |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | ||
| CIKAIIERLI | QRDGHLIVID | EGAAPAADDG | AARRTSESRI | LAVNPNYVID |