Q64434
Gene name |
Ptk6 (Sik) |
Protein name |
Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 |
Names |
EC 2.7.10.2 , SRC-related intestinal kinase |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:20459 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
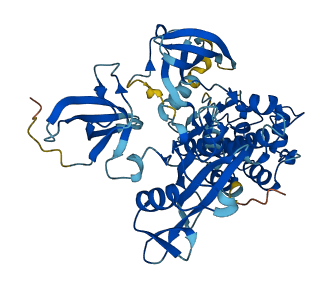
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
171-191 (Linker region between the SH2 domain and the catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Hong E et al. (2004) "Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase-6 Src homology 2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 29700-8
- Ko S et al. (2009) "Structural basis of the auto-inhibition mechanism of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase PTK6", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 384, 236-42
- Qiu H et al. (2002) "Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 34634-41
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q64434
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q64434-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
28 variants for Q64434
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3392450467 | 36 | H>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3392679958 | 37 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3392662756 | 38 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3392633417 | 39 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3392450497 | 40 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388621194 | 67 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388621372 | 76 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs236335379 | 134 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs225430192 | 134 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs258692683 | 136 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs243119845 | 147 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs252077467 | 215 | H>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388604499 | 220 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388618977 | 225 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388622753 | 227 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388622716 | 243 | R>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3388617210 | 248 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs1134443262 | 264 | T>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388621136 | 267 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388611405 | 280 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388623589 | 296 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs27693077 | 343 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388618951 | 361 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388621359 | 375 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388613171 | 383 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs240962005 | 407 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388623586 | 428 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs215183312 | 447 | Y>* | No | EVA |
15 associated diseases with Q64434
[MIM: 100800]: Achondroplasia (ACH)
A frequent form of short-limb dwarfism. It is characterized by a long, narrow trunk, short extremities, particularly in the proximal (rhizomelic) segments, a large head with frontal bossing, hypoplasia of the midface and a trident configuration of the hands. ACH is an autosomal dominant disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10611230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7758520, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7847369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8078586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8599935}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 612247]: Crouzon syndrome with acanthosis nigricans (CAN)
Classic Crouzon disease which is caused by mutations in the FGFR2 gene is characterized by craniosynostosis (premature fusion of the skull sutures), and facial hypoplasia. Crouzon syndrome with acanthosis nigricans (a skin disorder characterized by pigmentation anomalies), CAN, is considered to be an independent disorder from classic Crouzon syndrome. CAN is characterized by additional more severe physical manifestation, such as Chiari malformation, hydrocephalus, and atresia or stenosis of the choanas, and is caused by a specific mutation (Ala-391 to Glu) in the transmembrane domain of FGFR3. It is proposed to have an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17935505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7493034}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 187600]: Thanatophoric dysplasia 1 (TD1)
A neonatal lethal skeletal dysplasia. Affected individuals manifest severe shortening of the limbs with macrocephaly, narrow thorax, short ribs, and curved femurs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10360402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10671061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7773297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8589699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8845844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9790257}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 187601]: Thanatophoric dysplasia 2 (TD2)
A neonatal lethal skeletal dysplasia causing severe shortening of the limbs, narrow thorax and short ribs. Patients with thanatophoric dysplasia type 2 have straight femurs and cloverleaf skull. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7773297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8754806}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 146000]: Hypochondroplasia (HCH)
Autosomal dominant disease and is characterized by disproportionate short stature. It resembles achondroplasia, but with a less severe phenotype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10215410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10777366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11055896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7670477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452043}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 109800]: Bladder cancer (BLC)
A malignancy originating in tissues of the urinary bladder. It often presents with multiple tumors appearing at different times and at different sites in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas that begin in cells that normally make up the inner lining of the bladder. Other types of bladder cancer include squamous cell carcinoma (cancer that begins in thin, flat cells) and adenocarcinoma (cancer that begins in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids). Bladder cancer is a complex disorder with both genetic and environmental influences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10471491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11314002}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Somatic mutations can constitutively activate FGFR3.
[MIM: 603956]: Cervical cancer (CERCA)
A malignant neoplasm of the cervix, typically originating from a dysplastic or premalignant lesion previously present at the active squamocolumnar junction. The transformation from mild dysplastic to invasive carcinoma generally occurs slowly within several years, although the rate of this process varies widely. Carcinoma in situ is particularly known to precede invasive cervical cancer in most cases. Cervical cancer is strongly associated with infection by oncogenic types of human papillomavirus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10471491}. Note=The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.
[MIM: 610474]: Camptodactyly, tall stature, and hearing loss syndrome (CATSHLS)
An autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by permanent and irreducible flexion of one or more fingers of the hand and/or feet, tall stature, scoliosis and/or a pectus excavatum, and hearing loss. Affected individuals have developmental delay and/or intellectual disability, and several of these have microcephaly. Radiographic findings included tall vertebral bodies with irregular borders and broad femoral metaphyses with long tubular shafts. On audiological exam, each tested member have bilateral sensorineural hearing loss and absent otoacoustic emissions. The hearing loss was congenital or developed in early infancy, progressed variably in early childhood, and range from mild to severe. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging reveal that the brain, middle ear, and inner ear are structurally normal. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17033969}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 254500]: Multiple myeloma (MM)
A malignant tumor of plasma cells usually arising in the bone marrow and characterized by diffuse involvement of the skeletal system, hyperglobulinemia, Bence-Jones proteinuria and anemia. Complications of multiple myeloma are bone pain, hypercalcemia, renal failure and spinal cord compression. The aberrant antibodies that are produced lead to impaired humoral immunity and patients have a high prevalence of infection. Amyloidosis may develop in some patients. Multiple myeloma is part of a spectrum of diseases ranging from monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS) to plasma cell leukemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11529856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9207791}. Note=The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis. A chromosomal aberration involving FGFR3 is found in multiple myeloma. Translocation t(4;14)(p16.3;q32.3) with the IgH locus.
[MIM: 149730]: Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome (LADDS)
An autosomal dominant ectodermal dysplasia, a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome is characterized by aplastic/hypoplastic lacrimal and salivary glands and ducts, cup-shaped ears, hearing loss, hypodontia and enamel hypoplasia, and distal limb segments anomalies. In addition to these cardinal features, facial dysmorphism, malformations of the kidney and respiratory system and abnormal genitalia have been reported. Craniosynostosis and severe syndactyly are not observed. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16501574}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 162900]: Keratinocytic non-epidermolytic nevus (KNEN)
Epidermal nevi of the common, non-organoid and non-epidermolytic type are benign skin lesions and may vary in their extent from a single (usually linear) lesion to widespread and systematized involvement. They may be present at birth or develop early during childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16841094}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 602849]: Muenke syndrome (MNKS)
A condition characterized by premature closure of coronal suture of skull during development (coronal craniosynostosis), which affects the shape of the head and face. It may be uni- or bilateral. When bilateral, it is characterized by a skull with a small antero-posterior diameter (brachycephaly), often with a decrease in the depth of the orbits and hypoplasia of the maxillae. Unilateral closure of the coronal sutures leads to flattening of the orbit on the involved side (plagiocephaly). The intellect is normal. In addition to coronal craniosynostosis some affected individuals show skeletal abnormalities of hands and feet, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disability and respiratory insufficiency. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11746040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9950359}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 182000]: Keratosis, seborrheic (KERSEB)
A common benign skin tumor. Seborrheic keratoses usually begin with the appearance of one or more sharply defined, light brown, flat macules. The lesions may be sparse or numerous. As they initially grow, they develop a velvety to finely verrucous surface, followed by an uneven warty surface with multiple plugged follicles and a dull or lackluster appearance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15772091}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 273300]: Testicular germ cell tumor (TGCT)
A common malignancy in males representing 95% of all testicular neoplasms. TGCTs have various pathologic subtypes including
[MIM: 616482]: Achondroplasia, severe, with developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans (SADDAN)
A severe form of achondroplasia associated with developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans. Patients manifest short-limb dwarfism, with a long, narrow trunk, short extremities, particularly in the proximal (rhizomelic) segments, a large head with frontal bossing, hypoplasia of the midface and a trident configuration of the hands. Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition characterized by brown-pigmented, velvety verrucosities in body folds and creases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10053006}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- A frequent form of short-limb dwarfism. It is characterized by a long, narrow trunk, short extremities, particularly in the proximal (rhizomelic) segments, a large head with frontal bossing, hypoplasia of the midface and a trident configuration of the hands. ACH is an autosomal dominant disease. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10611230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7758520, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7847369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8078586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8599935}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- Classic Crouzon disease which is caused by mutations in the FGFR2 gene is characterized by craniosynostosis (premature fusion of the skull sutures), and facial hypoplasia. Crouzon syndrome with acanthosis nigricans (a skin disorder characterized by pigmentation anomalies), CAN, is considered to be an independent disorder from classic Crouzon syndrome. CAN is characterized by additional more severe physical manifestation, such as Chiari malformation, hydrocephalus, and atresia or stenosis of the choanas, and is caused by a specific mutation (Ala-391 to Glu) in the transmembrane domain of FGFR3. It is proposed to have an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17935505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7493034}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A neonatal lethal skeletal dysplasia. Affected individuals manifest severe shortening of the limbs with macrocephaly, narrow thorax, short ribs, and curved femurs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10360402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10671061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7773297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8589699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8845844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9790257}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A neonatal lethal skeletal dysplasia causing severe shortening of the limbs, narrow thorax and short ribs. Patients with thanatophoric dysplasia type 2 have straight femurs and cloverleaf skull. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7773297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8754806}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- Autosomal dominant disease and is characterized by disproportionate short stature. It resembles achondroplasia, but with a less severe phenotype. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10215410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10777366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11055896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7670477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9452043}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A malignancy originating in tissues of the urinary bladder. It often presents with multiple tumors appearing at different times and at different sites in the bladder. Most bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas that begin in cells that normally make up the inner lining of the bladder. Other types of bladder cancer include squamous cell carcinoma (cancer that begins in thin, flat cells) and adenocarcinoma (cancer that begins in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids). Bladder cancer is a complex disorder with both genetic and environmental influences. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10471491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11314002}. Note=Disease susceptibility is associated with variants affecting the gene represented in this entry. Somatic mutations can constitutively activate FGFR3.
- A malignant neoplasm of the cervix, typically originating from a dysplastic or premalignant lesion previously present at the active squamocolumnar junction. The transformation from mild dysplastic to invasive carcinoma generally occurs slowly within several years, although the rate of this process varies widely. Carcinoma in situ is particularly known to precede invasive cervical cancer in most cases. Cervical cancer is strongly associated with infection by oncogenic types of human papillomavirus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10471491}. Note=The gene represented in this entry is involved in disease pathogenesis.
- An autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by permanent and irreducible flexion of one or more fingers of the hand and/or feet, tall stature, scoliosis and/or a pectus excavatum, and hearing loss. Affected individuals have developmental delay and/or intellectual disability, and several of these have microcephaly. Radiographic findings included tall vertebral bodies with irregular borders and broad femoral metaphyses with long tubular shafts. On audiological exam, each tested member have bilateral sensorineural hearing loss and absent otoacoustic emissions. The hearing loss was congenital or developed in early infancy, progressed variably in early childhood, and range from mild to severe. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging reveal that the brain, middle ear, and inner ear are structurally normal. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17033969}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A malignant tumor of plasma cells usually arising in the bone marrow and characterized by diffuse involvement of the skeletal system, hyperglobulinemia, Bence-Jones proteinuria and anemia. Complications of multiple myeloma are bone pain, hypercalcemia, renal failure and spinal cord compression. The aberrant antibodies that are produced lead to impaired humoral immunity and patients have a high prevalence of infection. Amyloidosis may develop in some patients. Multiple myeloma is part of a spectrum of diseases ranging from monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS) to plasma cell leukemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11529856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9207791}. Note=The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis. A chromosomal aberration involving FGFR3 is found in multiple myeloma. Translocation t(4;14)(p16.3;q32.3) with the IgH locus.
- An autosomal dominant ectodermal dysplasia, a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. Lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome is characterized by aplastic/hypoplastic lacrimal and salivary glands and ducts, cup-shaped ears, hearing loss, hypodontia and enamel hypoplasia, and distal limb segments anomalies. In addition to these cardinal features, facial dysmorphism, malformations of the kidney and respiratory system and abnormal genitalia have been reported. Craniosynostosis and severe syndactyly are not observed. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16501574}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- Epidermal nevi of the common, non-organoid and non-epidermolytic type are benign skin lesions and may vary in their extent from a single (usually linear) lesion to widespread and systematized involvement. They may be present at birth or develop early during childhood. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16841094}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A condition characterized by premature closure of coronal suture of skull during development (coronal craniosynostosis), which affects the shape of the head and face. It may be uni- or bilateral. When bilateral, it is characterized by a skull with a small antero-posterior diameter (brachycephaly), often with a decrease in the depth of the orbits and hypoplasia of the maxillae. Unilateral closure of the coronal sutures leads to flattening of the orbit on the involved side (plagiocephaly). The intellect is normal. In addition to coronal craniosynostosis some affected individuals show skeletal abnormalities of hands and feet, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disability and respiratory insufficiency. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11746040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9042914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9950359}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A common benign skin tumor. Seborrheic keratoses usually begin with the appearance of one or more sharply defined, light brown, flat macules. The lesions may be sparse or numerous. As they initially grow, they develop a velvety to finely verrucous surface, followed by an uneven warty surface with multiple plugged follicles and a dull or lackluster appearance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15772091}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A common malignancy in males representing 95% of all testicular neoplasms. TGCTs have various pathologic subtypes including
- A severe form of achondroplasia associated with developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans. Patients manifest short-limb dwarfism, with a long, narrow trunk, short extremities, particularly in the proximal (rhizomelic) segments, a large head with frontal bossing, hypoplasia of the midface and a trident configuration of the hands. Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition characterized by brown-pigmented, velvety verrucosities in body folds and creases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10053006}. Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
15 regional properties for Q64434
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 472 - 761 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 472 - 748 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 52 - 116 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 167 - 235 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 266 - 346 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 46 - 126 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 161 - 246 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 260 - 357 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 39 - 110 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 151 - 244 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 253 - 355 | IPR007110-3 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 613 - 625 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 166 - 245 | IPR013098 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 478 - 508 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 472 - 748 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nuclear body | Extra-nucleolar nuclear domains usually visualized by confocal microscopy and fluorescent antibodies to specific proteins. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| ruffle | Projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell; the protrusions are supported by a microfilament meshwork. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell differentiation | The cellular developmental process in which a relatively unspecialized cell, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cell, acquires specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize a specific cell. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. |
| cellular response to retinoic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a retinoic acid stimulus. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intestinal epithelial cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a columnar/cuboidal epithelial cell of the intestine. |
| negative regulation of growth | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of growth, the increase in size or mass of all or part of an organism. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | The process of introducing a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
90 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P48025 | Syk | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P43404 | Zap70 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ZAP-70 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9QVP9 | Ptk2b | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P34152 | Ptk2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99ML2 | Tnk1 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TNK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O54967 | Tnk2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70451 | Fer | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P00520 | Abl1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q4JIM5 | Abl2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MVSWDKAHLG | PKYVGLWDFK | ARTDEELSFQ | AGDLLHVTKK | EELWWWATLL | DAEGKALAEG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YVPHNYLAEK | ETVESEPWFF | GCISRSEAMH | RLQAEDNSKG | AFLIRVSQKP | GADYVLSVRD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AQAVRHYRIW | KNNEGRLHLN | EAVSFSNLSE | LVDYHKTQSL | SHGLQLSMPC | WKHKTEPLPH |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| WDDWERPREE | FTLCKKLGAG | YFGEVFEALW | KGQVHVAVKV | ISRDNLLHQH | TFQAEIQAMK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KLRHKHILSL | YAVATAGDPV | YIITELMPKG | NLLQLLRDSD | EKALPILELV | DFASQVAEGM |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| CYLESQNYIH | RDLAARNVLV | TENNLCKVGD | FGLARLVKED | IYLSHEHNVP | YKWTAPEALS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| RGHYSIKSDV | WSFGVLLHEI | FSRGQMPYPG | MSNHETFLRV | DAGYRMPCPL | ECPPNIHKLM |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | |||
| LSCWSRDPKQ | RPCFKDLCEK | LTGITRYENL | V |