Q64287
Gene name |
Irf4 (Spip) |
Protein name |
Interferon regulatory factor 4 |
Names |
IRF-4, Lymphocyte-specific interferon regulatory factor, LSIRF, NF-EM5, PU.1 interaction partner, Transcriptional activator PIP |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:16364 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
INTERFERON REGULATORY FACTOR (PTHR11949) |
Descriptions
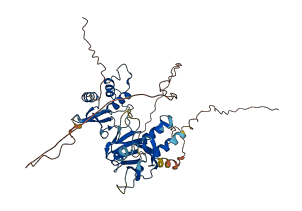
IRF4 is a transcription factor regulating immune cell development, obesity-induced inflammation, and so forth. The low DNA binding affinity of IRF4 has been attributed to the presence of an C-terminal autoinhibitory region residing in the last 30 residues of the C-terminal interferon activation domain (IAD). It has been suggested that this region physically interacts with the N-terminal helix-turn-helix DNA-binding domain and maintains the protein in an autoinhibited state. Upon interaction with a binding partner, the inhibitory mechanism is relieved, allowing IRF4 to bind its recognition DNA sequence.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
20-139 (DNA-binding domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Remesh SG et al. (2015) "Structural Studies of IRF4 Reveal a Flexible Autoinhibitory Region and a Compact Linker Domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 290, 27779-90
- Brass AL et al. (1999) "Assembly requirements of PU.1-Pip (IRF-4) activator complexes: inhibiting function in vivo using fused dimers", The EMBO journal, 18, 977-91
- Brass AL et al. (1996) "Pip, a lymphoid-restricted IRF, contains a regulatory domain that is important for autoinhibition and ternary complex formation with the Ets factor PU.1", Genes & development, 10, 2335-47
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

2 structures for Q64287
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5BVI | X-ray | 260 A | A/B | 238-420 | PDB |
| AF-Q64287-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for Q64287
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs265187539 | 186 | S>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs217122175 | 269 | T>S | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q64287
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR11949 | INTERFERON REGULATORY FACTOR |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR11949:SF6 | INTERFERON REGULATORY FACTOR 4 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
DNA-binding transcription factor
helix-turn-helix transcription factor winged helix/forkhead transcription factor |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleosome | A complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by some RNA polymerase. The proximal promoter is in cis with and relatively close to the core promoter. |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| transcription coactivator activity | A transcription coregulator activity that activates or increases the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Coactivators often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription coactivators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. A fourth class of coactivator activity is the bridging of a DNA-binding transcription factor to the general (basal) transcription machinery. The Mediator complex, which bridges sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factors and RNA polymerase, is also a transcription coactivator. |
16 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| defense response to protozoan | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a protozoan that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| histone H3 acetylation | The modification of histone H3 by the addition of an acetyl group. |
| histone H4 acetylation | The modification of histone H4 by the addition of an acetyl group. |
| immune system process | Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats. |
| myeloid dendritic cell differentiation | The process in which a monocyte acquires the specialized features of a dendritic cell, an immunocompetent cell of the lymphoid and hemopoietic systems and skin. |
| negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of toll-like receptor signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cold-induced thermogenesis. |
| positive regulation of DNA binding | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA binding. DNA binding is any process in which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| positive regulation of interleukin-10 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-10 production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-13 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-13 production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-2 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-2 production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-4 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-4 production. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment | The process in which a CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell becomes committed to becoming a T-helper 17 cell, a CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell with the phenotype RORgamma-t-positive that produces IL-17. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q15306 | IRF4 | Interferon regulatory factor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q61179 | Irf9 | Interferon regulatory factor 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P56477 | Irf5 | Interferon regulatory factor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70671 | Irf3 | Interferon regulatory factor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70434 | Irf7 | Interferon regulatory factor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P23611 | Irf8 | Interferon regulatory factor 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNLETGSRGS | EFGMSAVSCG | NGKLRQWLID | QIDSGKYPGL | VWENEEKSVF | RIPWKHAGKQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DYNREEDAAL | FKAWALFKGK | FREGIDKPDP | PTWKTRLRCA | LNKSNDFEEL | VERSQLDISD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PYKVYRIVPE | GAKKGAKQLT | LDDTQMAMGH | PYPMTAPYGS | LPAQQVHNYM | MPPHDRSWRD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| YAPDQSHPEI | PYQCPVTFGP | RGHHWQGPSC | ENGCQVTGTF | YACAPPESQA | PGIPIEPSIR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SAEALALSDC | RLHICLYYRD | ILVKELTTTS | PEGCRISHGH | TYDVSNLDQV | LFPYPDDNGQ |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RKNIEKLLSH | LERGLVLWMA | PDGLYAKRLC | QSRIYWDGPL | ALCSDRPNKL | ERDQTCKLFD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TQQFLSELQV | FAHHGRPAPR | FQVTLCFGEE | FPDPQRQRKL | ITAHVEPLLA | RQLYYFAQQN |
| 430 | 440 | ||||
| TGHFLRGYEL | PEHVTTPDYH | RSLRHSSIQE |