Q641Y8
Gene name |
Ddx1 |
Protein name |
ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 |
Names |
DEAD box protein 1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:84474 |
EC number |
3.6.4.13: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
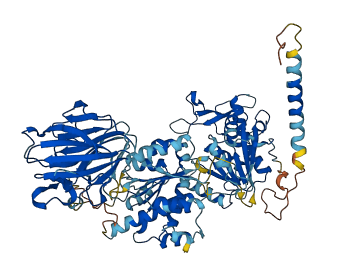
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q641Y8
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q641Y8-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q641Y8
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q641Y8 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q641Y8
6 regional properties for Q641Y8
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Helicase, C-terminal | 493 - 681 | IPR001650 |
| domain | B30.2/SPRY domain | 70 - 247 | IPR001870 |
| domain | SPRY domain | 130 - 246 | IPR003877 |
| domain | DEAD/DEAH box helicase domain | 26 - 418 | IPR011545 |
| domain | Helicase superfamily 1/2, ATP-binding domain | 21 - 444 | IPR014001 |
| domain | RNA helicase, DEAD-box type, Q motif | 2 - 30 | IPR014014 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.13 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cleavage body | A nuclear body that contains proteins involved in pre-mRNA 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation, such as DDX1, CSTF2 and CPSFs, as well as the transcription factors TFIIE and TFIIF. Cleavage bodies are localized adjacent to Cajal bodies and are involved in mRNA3'-end processing. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic stress granule | A dense aggregation in the cytosol composed of proteins and RNAs that appear when the cell is under stress. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| ribonucleoprotein complex | A macromolecular complex that contains both RNA and protein molecules. |
| tRNA-splicing ligase complex | A protein complex that catalyzes the ligation of cleaved pre-tRNAs by directly joining spliced tRNA halves to mature-sized tRNAs by incorporating the precursor-derived splice junction phosphate into the mature tRNA as a canonical 3',5'-phosphodiester. |
11 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA/RNA helicase activity | Unwinding of a DNA/RNA duplex, i.e. a double helix in which a strand of DNA pairs with a complementary strand of RNA, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| double-stranded RNA binding | Binding to double-stranded RNA. |
| exonuclease activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of ester linkages within nucleic acids by removing nucleotide residues from the 3' or 5' end. |
| nuclease activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of ester linkages within nucleic acids. |
| poly(A) binding | Binding to a sequence of adenylyl residues in an RNA molecule, such as the poly(A) tail, a sequence of adenylyl residues at the 3' end of eukaryotic mRNA. |
| RNA helicase activity | Unwinding of an RNA helix, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| transcription coregulator activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Coregulators often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| DNA duplex unwinding | The process in which interchain hydrogen bonds between two strands of DNA are broken or 'melted', generating a region of unpaired single strands. |
| double-strand break repair | The repair of double-strand breaks in DNA via homologous and nonhomologous mechanisms to reform a continuous DNA helix. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| mRNA processing | Any process involved in the conversion of a primary mRNA transcript into one or more mature mRNA(s) prior to translation into polypeptide. |
| nucleic acid phosphodiester bond hydrolysis | The nucleic acid metabolic process in which the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides are cleaved by hydrolysis. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production. |
| protein localization to cytoplasmic stress granule | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within a cytoplasmic stress granule. |
| response to exogenous dsRNA | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an exogenous double-stranded RNA stimulus. |
| response to virus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus. |
| tRNA splicing, via endonucleolytic cleavage and ligation | Splicing of tRNA substrates via recognition of the folded RNA structure that brings the 5' and 3' splice sites into proximity and cleavage of the RNA at both the 3' and 5' splice sites by an endonucleolytic mechanism, followed by ligation of the exons. |
7 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0IIK5 | DDX1 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q90WU3 | DDX1 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q92499 | DDX1 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q91VR5 | Ddx1 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5RKI1 | Eif4a2 | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-II | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q62780 | Ddx46 | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX46 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q5XH91 | ddx1 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAFSEMGVM | PEIAQAVEEM | DWLLPTDIQA | ESIPLILGGG | DVLMAAETGS | GKTGAFSIPV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IQIVYETLKD | QQEGKKGKAT | IKTGASVLNK | WQMNPYDRGS | AFAIGSDGLC | CQSREVKEWH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| GCRATRGLLR | GKHYYEVSCH | DQGLCRVGWS | TMQASLDLGT | DKFGFGFGGT | GKKSHNKQFD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| NYGEEFTMHD | TIGCYLDIDK | GHVKFSKNGK | DLGLAFEIPA | HIKNQALFPA | CVLKNAELKF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NFGEEEFKFP | PKDGFVALSK | APDSYVVKSQ | HTGNAQVSQT | KFLPNAPKAL | IVEPSRELAE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QTLNNVKQFK | KYIDNPKLRE | LLIIGGVAAR | DQLSVLDNGV | DIVVGTPGRL | DDLVSTGKLN |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LSQVRFLVLD | EADGLLSQGY | SDFINRMHNQ | IPQITSDGKR | LQVIVCSATL | HSFDVKKLSE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| KIMHFPTWVD | LKGEDSVPDT | VHHVVVPVNP | KTDRLWERLG | KNHIRTDDVH | AKDNTRPGAN |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SPEMWSEAIK | ILKGEYAVRA | IKEHKMDQAI | IFCRTKIDCD | NLEQYFMQQG | GGPDKKGHQF |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SCVCLHGDRK | PHERKQNLER | FKKGDVRFLI | CTDVAARGID | IHGVPYVINV | TLPDEKQNYV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| HRIGRVGRAE | RMGLAISLVA | TEKEKVWYHV | CSNRGKGCYN | TRLKEDGGCT | IWYNEMQLLS |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| EIEEHLNCTI | SQVEPDIKVP | VDEFDGKVTY | GQKRAAGGGN | YKGHVDILAP | TVQELAALEK |
| 730 | |||||
| EAQTSFLHLG | YLPNQLFRTF |