Q63648
Gene name |
Nf2 |
Protein name |
Merlin |
Names |
Moesin-ezrin-radixin-like protein , Neurofibromin-2 , Schwannomin |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:25744 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
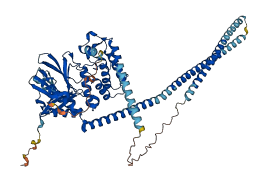
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
15-309 (FERM domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q63648
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q63648-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q63648
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q63648 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q63648
10 regional properties for Q63648
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | FERM domain | 18 - 307 | IPR000299 |
| domain | Ezrin/radixin/moesin, C-terminal | 515 - 576 | IPR011259 |
| domain | FERM, N-terminal | 24 - 82 | IPR018979 |
| domain | FERM, C-terminal PH-like domain | 222 - 311 | IPR018980 |
| conserved_site | FERM conserved site | 70 - 100 | IPR019747-1 |
| conserved_site | FERM conserved site | 188 - 217 | IPR019747-2 |
| domain | FERM central domain | 102 - 218 | IPR019748 |
| domain | Band 4.1 domain | 14 - 218 | IPR019749 |
| domain | ERM family, FERM domain C-lobe | 212 - 308 | IPR041789 |
| domain | Ezrin/radixin/moesin, alpha-helical domain | 342 - 461 | IPR046810 |
Functions
17 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction | A cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex. The epithelial cadherins, or E-cadherins, of each interacting cell extend through the plasma membrane into the extracellular space and bind to each other. The E-cadherins bind to catenins on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, where the E-cadherin-catenin complex binds to cytoskeletal components and regulatory and signaling molecules. |
| apical part of cell | The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| cell body | The portion of a cell bearing surface projections such as axons, dendrites, cilia, or flagella that includes the nucleus, but excludes all cell projections. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| cortical actin cytoskeleton | The portion of the actin cytoskeleton, comprising filamentous actin and associated proteins, that lies just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| filopodium | Thin, stiff, actin-based protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal or dendritic growth cone, or a dendritic shaft. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| ruffle | Projection at the leading edge of a crawling cell; the protrusions are supported by a microfilament meshwork. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| beta-catenin binding | Binding to a catenin beta subunit. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
35 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| cell-cell junction organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cell-cell junction. A cell-cell junction is a specialized region of connection between two cells. |
| ectoderm development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the ectoderm over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In animal embryos, the ectoderm is the outer germ layer of the embryo, formed during gastrulation. |
| hippocampus development | The progression of the hippocampus over time from its initial formation until its mature state. |
| lens fiber cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a lens fiber cell, any of the elongated, tightly packed cells that make up the bulk of the mature lens in the camera-type eye. The cytoplasm of a lens fiber cell is devoid of most intracellular organelles including the cell nucleus, and contains primarily crystallins, a group of water-soluble proteins expressed in vary large quantities. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers |
| mesoderm formation | The process that gives rise to the mesoderm. This process pertains to the initial formation of the structure from unspecified parts. |
| negative regulation of cell growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell adhesion to another cell. |
| negative regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPKKK cascade. |
| negative regulation of osteoblast proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of osteoblast proliferation. |
| negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT. |
| negative regulation of Schwann cell proliferation | Any process that decreases the frequency or extent of the multiplication or reproduction of Schwann cells, resulting in the expansion of their population. Schwann cells are a type of glial cell in the peripheral nervous system. |
| negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a dentin-containing tooth over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dentin-containing tooth is a hard, bony organ borne on the jaw or other bone of a vertebrate, and is composed mainly of dentin, a dense calcified substance, covered by a layer of enamel. |
| osteoblast proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of osteoblasts, resulting in the expansion of an osteoblast cell population. An osteoblast is a bone-forming cell which secretes an extracellular matrix. Hydroxyapatite crystals are then deposited into the matrix to form bone. |
| positive regulation of cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of early endosome to late endosome transport. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to early endosome | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to early endosome. |
| positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| regulation of cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle. |
| regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| regulation of gliogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gliogenesis, the formation of mature glia. |
| regulation of hippo signaling | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of hippo signaling. |
| regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neural precursor cell proliferation. |
| regulation of neurogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the generation of cells in the nervous system. |
| regulation of organelle assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of organelle assembly. |
| regulation of protein localization to nucleus | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to nucleus. |
| regulation of protein stability | Any process that affects the structure and integrity of a protein, altering the likelihood of its degradation or aggregation. |
| regulation of stem cell proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of stem cell proliferation. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
| Schwann cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of Schwann cells, resulting in the expansion of their population. Schwann cells are a type of glial cell in the peripheral nervous system. |
21 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q32LP2 | RDX | Radixin | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P31976 | EZR | Ezrin | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2HJ49 | MSN | Moesin | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9PU45 | RDX | Radixin | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P46150 | Moe | Moesin/ezrin/radixin homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q24564 | Mer | Moesin/ezrin/radixin homolog 2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P26038 | MSN | Moesin | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P15311 | EZR | Ezrin | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35241 | RDX | Radixin | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q3KP66 | INAVA | Innate immunity activator protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P35240 | NF2 | Merlin | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P26043 | Rdx | Radixin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A2AD83 | Frmd7 | FERM domain-containing protein 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P26040 | Ezr | Ezrin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26041 | Msn | Moesin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P46662 | Nf2 | Merlin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26042 | MSN | Moesin | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P26044 | RDX | Radixin | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O35763 | Msn | Moesin | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P31977 | Ezr | Ezrin | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6Q413 | nf2b | NF2, moesin-ezrin-radixin-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| IASRMSFSSL | KRKQPKTFTV | RIVTMDAEME | FNCEMKWKGK | DLFDLVCRTL | GLRETWFFGL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QYTIKDTVAW | LKMDKKVLDH | DVSKEEPVTF | HFLAKFYPEN | AEEELVQEIT | QHLFFLQVKK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QILDEKVYCP | PEASVLLASY | AVQAKYGDYD | PSVHKRGFLA | QEELLPKRVI | NLYQMTPEMW |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EERITAWYAE | HRGRARDEAE | MEYLKIAQDL | EMYGVNYFTI | RNKKGTELLL | GVDALGLHIY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DPENRLTPKI | SFPWNEIRNI | SYSDKEFTIK | PLDKKIDVFK | FNSSKLRVNK | LILQLCIGNH |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DLFMRRRKAD | SLEVQQMKAQ | AREEKARKQM | ERQRLAREKQ | MREEAERSRD | EPERRVLHMK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EEATMANEAL | MRSEETADLL | AEKAQITEEE | AKLLAQKAAE | AEQEMQRIKA | TAIRTEEEKR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LMEQKVLEAE | VLALKMAEES | ERRAKEADQL | KQDLQEAREA | ERRAKQKLLE | IATKPTYPPM |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NPIPAPLPPD | IPSFDIIGDS | LSFDFKDTDM | KRLSMEIEKE | KVEYMEKSKH | LQEQLNELKT |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | ||
| EIEALKLKER | ETALDILHSE | HSDSGTSSKH | NTIKKPQAQG | RRPICI |