Q63622
Gene name |
Dlg2 (Dlgh2) |
Protein name |
Disks large homolog 2 |
Names |
Channel-associated protein of synapse-110, Chapsyn-110, Postsynaptic density protein PSD-93 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:64053 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
DISCS LARGE (PTHR23119) |
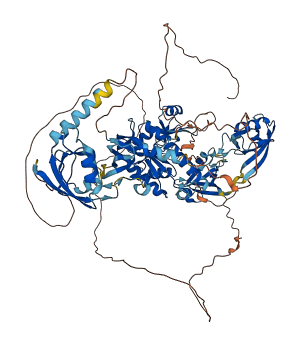
Descriptions
Dlg2 is a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family of PDZ domain-containing proteins and regulates surface expression of NMDA receptors. The activity of Dlg2 (GK domain) is autoinhibited by the PDZ domains (PDZ2 and PDZ3). In rat Dlg4 (P31016), SH3 domain also interacts with GK domain for regulation.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
503-724 (GK domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Others |
Assay |
Split protein assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
503-724 (GK domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
Split protein assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Brenman JE et al. (1998) "Localization of postsynaptic density-93 to dendritic microtubules and interaction with microtubule-associated protein 1A", The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 18, 8805-13
- McGee AW et al. (1999) "Identification of an intramolecular interaction between the SH3 and guanylate kinase domains of PSD-95", The Journal of biological chemistry, 274, 17431-6
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q63622
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4H11 | X-ray | 167 A | A/B | 93-188 | PDB |
| AF-Q63622-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q63622
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q63622 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q63622
10 regional properties for Q63622
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SH3 domain | 536 - 606 | IPR001452 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 98 - 185 | IPR001478-1 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 193 - 280 | IPR001478-2 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 421 - 502 | IPR001478-3 |
| domain | Guanylate kinase-like domain | 662 - 837 | IPR008144 |
| domain | Guanylate kinase/L-type calcium channel beta subunit | 661 - 840 | IPR008145 |
| domain | Disks large homolog 1-4, PDZ-associated domain | 278 - 345 | IPR019583 |
| domain | Disks large homologue 1, N-terminal PEST domain | 14 - 97 | IPR019590 |
| conserved_site | Guanylate kinase, conserved site | 694 - 711 | IPR020590 |
| domain | Disks Large homologue 2, SH3 domain | 534 - 607 | IPR035759 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR23119 | DISCS LARGE |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR23119:SF6 | DISKS LARGE HOMOLOG 2 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | scaffold/adaptor protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
17 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchored component of postsynaptic density membrane | The component of the postsynaptic density membrane consisting of the gene products that are tethered to the membrane only by a covalently attached anchor, such as a lipid group that is embedded in the membrane. Gene products with peptide sequences that are embedded in the membrane are excluded from this grouping. |
| axon cytoplasm | Any cytoplasm that is part of a axon. |
| basolateral plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| juxtaparanode region of axon | A region of an axon near a node of Ranvier that is between the paranode and internode regions. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| neuromuscular junction | The junction between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. In response to the arrival of action potentials, the presynaptic button releases molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle fiber, leading to a change in post-synaptic potential. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic density membrane | The membrane component of the postsynaptic density. This is the region of the postsynaptic membrane in which the population of neurotransmitter receptors involved in synaptic transmission are concentrated. |
| postsynaptic membrane | A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
| synaptic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| kinase binding | Binding to a kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| protein phosphatase binding | Binding to a protein phosphatase. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| structural constituent of postsynaptic density | The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a postsynaptic density. |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anterograde axonal protein transport | The directed movement of proteins along microtubules from the cell body toward the cell periphery in nerve cell axons. |
| cell-cell adhesion | The attachment of one cell to another cell via adhesion molecules. |
| cellular response to potassium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a potassium ion stimulus. |
| chemical synaptic transmission | The vesicular release of classical neurotransmitter molecules from a presynapse, across a chemical synapse, the subsequent activation of neurotransmitter receptors at the postsynapse of a target cell (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) and the effects of this activation on the postsynaptic membrane potential and ionic composition of the postsynaptic cytosol. This process encompasses both spontaneous and evoked release of neurotransmitter and all parts of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Evoked transmission starts with the arrival of an action potential at the presynapse. |
| establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of the apicobasal polarity of an epithelial cell. |
| neuronal ion channel clustering | The process in which voltage-gated ion channels become localized to distinct subcellular domains in the neuron. Specific targeting, clustering, and maintenance of these channels in their respective domains are essential to achieve high conduction velocities of action potential propagation. |
| neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane | A process in which a neurotransmitter is transported to, or maintained in, a location within the membrane adjacent to a postsynaptic specialization (e.g. postsynaptic density). |
| receptor clustering | The receptor metabolic process that results in grouping of a set of receptors at a cellular location, often to amplify the sensitivity of a signaling response. |
| receptor localization to synapse | Any process in which a receptor is transported to, and/or maintained at the synapse, the junction between a nerve fiber of one neuron and another neuron or muscle fiber or glial cell. |
| retrograde axonal protein transport | The directed movement of proteins along microtubules from the cell periphery toward the cell body in nerve cell axons. |
| sensory perception of pain | The series of events required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Pain is medically defined as the physical sensation of discomfort or distress caused by injury or illness, so can hence be described as a harmful stimulus which signals current (or impending) tissue damage. Pain may come from extremes of temperature, mechanical damage, electricity or from noxious chemical substances. This is a neurological process. |
21 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P31007 | dlg1 | Disks large 1 tumor suppressor protein | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| Q12959 | DLG1 | Disks large homolog 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q92796 | DLG3 | Disks large homolog 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BXL7 | CARD11 | Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P78352 | DLG4 | Disks large homolog 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15700 | DLG2 | Disks large homolog 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q62108 | Dlg4 | Disks large homolog 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q811D0 | Dlg1 | Disks large homolog 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CIS0 | Card11 | Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70175 | Dlg3 | Disks large homolog 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99KF0 | Card14 | Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 14 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91XM9 | Dlg2 | Disks large homolog 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70587 | Lrrc7 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q62936 | Dlg3 | Disks large homolog 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62696 | Dlg1 | Disks large homolog 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P31016 | Dlg4 | Disks large homolog 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5ECY0 | dlg-1 | Disks large homolog 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q28C55 | dlg1 | Disks large homolog 1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q6R005 | dlg4 | Disks large homolog 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5PYH5 | dlg1l | Discs large homolog 1-like protein | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5PYH7 | dlg2 | Disks large homolog 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MFFACYCALR | TNVKKYRYQD | EDGPHDHSLP | RLTHEVRGPE | LVHVSEKNLS | QIENVHGYVL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QSHISPLKAS | PAPIIVNTDT | LDTIPYVNGT | EIEYEFEEIT | LERGNSGLGF | SIAGGTDNPH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IGDDPGIFIT | KIIPGGAAAE | DGRLRVNDCI | LRVNEVDVSE | VSHSKAVEAL | KEAGSIVRLY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VRRRRPILET | VVEIKLFKGP | KGLGFSIAGG | VGNQHIPGDN | SIYVTKIIDG | GAAQKDGRLQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VGDRLLMVNN | YSLEEVTHEE | AVAILKNTSD | VVYLKVGKPT | TIYMTDPYGP | PDITHSYSPP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MENHLLSGNN | GTLEYKTSLP | PISPGRYSPI | PKHMLVEDDY | TRPPEPVYST | VNKLCDKPAS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| PRHYSPVECD | KSFLLSTPYP | HYHLGLLPDS | DMTSHSQHST | ATRQPSVTLQ | RAISLEGEPR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| KVVLHKGSTG | LGFNIVGGED | GEGIFVSFIL | AGGPADLSGE | LQRGDQILSV | NGIDLRGASH |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EQAAAALKGA | GQTVTIIAQY | QPEDYARFEA | KIHDLREQMM | NHSMSSGSGS | LRTNQKRSLY |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VRAMFDYDKS | KDSGLPSQGL | SFKYGDILHV | INASDDEWWQ | ARRVILDGDS | EEMGVIPSKR |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| RVERKERARL | KTVKFNAKPG | VIDSKGDIPG | LGDDGYGTKT | LRGQEDLILS | YEPVTRQEIN |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| YTRPVIILGP | MKDRINDDLI | SEFPDKFGSC | VPHTTRPKRD | YEVDGRDYHF | VISREQMEKD |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| IQEHKFIEAG | QYNDNLYGTS | VQSVRFVAER | GKHCILDVSG | NAIKRLQVAQ | LYPIAIFIKP |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| KSLEPLMEMN | KRLTEEQAKK | TYDRAIKLEQ | EFGEYFTAIV | QGDTLEDIYN | QCKLVIEEQS |
| 850 | |||||
| GPFIWIPSKE | KL |