Q63474
Gene name |
Ddr1 (Eddr1, Ptk3) |
Protein name |
Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 |
Names |
Epithelial discoidin domain receptor 1 , EC 2.7.10.1 , CD167 antigen-like family member A , Cell adhesion kinase , Discoidin receptor tyrosine kinase , Protein-tyrosine kinase 3 , Tyrosine kinase DDR , Tyrosine-protein kinase CAK , CD antigen CD167a |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
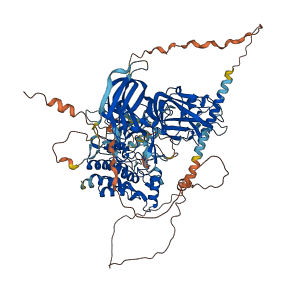
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
607-902 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Sammon D et al. (2020) "Two-step release of kinase autoinhibition in discoidin domain receptor 1", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117, 22051-22060
- Fu HL et al. (2014) "Glycosylation at Asn211 regulates the activation state of the discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1)", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 9275-87
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q63474
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q63474-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q63474
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q63474 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q63474
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| basolateral plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| brush border | The dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of an epithelial cell in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| collagen binding | Binding to collagen, a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. Collagen is highly enriched in glycine (some regions are 33% glycine) and proline, occurring predominantly as 3-hydroxyproline (about 20%). |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein tyrosine kinase collagen receptor activity | Combining with collagen and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction |
20 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| animal organ regeneration | The regrowth of a lost or destroyed animal organ. |
| axon development | The progression of an axon over time. Covers axonogenesis (de novo generation of an axon) and axon regeneration (regrowth), as well as processes pertaining to the progression of the axon over time (fasciculation and defasciculation). |
| branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis | The process in which the branching structure of the mammary gland duct is generated and organized. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| collagen-activated tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by collagen binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| ear development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The ear is the sense organ in vertebrates that is specialized for the detection of sound, and the maintenance of balance. Includes the outer ear and middle ear, which collect and transmit sound waves; and the inner ear, which contains the organs of balance and (except in fish) hearing. Also includes the pinna, the visible part of the outer ear, present in some mammals. |
| embryo implantation | Attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine lining. |
| lactation | The regulated release of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. |
| mammary gland alveolus development | The progression of the mammary gland alveolus over time, from its formation to its mature state. The mammary gland alveolus is a sac-like structure that is found in the mature gland. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| neuron projection extension | Long distance growth of a single neuron projection involved in cellular development. A neuron projection is a prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own tyrosine amino acid residues, or a tyrosine residue on an identical protein. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| regulation of cell growth | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| regulation of cell-matrix adhesion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of attachment of a cell to the extracellular matrix. |
| regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of extracellular matrix disassembly. Extracellular matrix disassembly is a process that results in the breakdown of the extracellular matrix. |
| skin development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skin over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skin is the external membranous integument of an animal. In vertebrates the skin generally consists of two layers, an outer nonsensitive and nonvascular epidermis (cuticle or skarfskin) composed of cells which are constantly growing and multiplying in the deeper, and being thrown off in the superficial layers, as well as an inner vascular dermis (cutis, corium or true skin) composed mostly of connective tissue. |
| smooth muscle cell migration | The orderly movement of a smooth muscle cell from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism. |
| smooth muscle cell-matrix adhesion | The binding of a smooth muscle cell to the extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules. |
| wound healing, spreading of cells | The migration of a cell along or through a wound gap that contributes to the reestablishment of a continuous surface. |
29 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5F3X2 | DDR1 | receptor protein-tyrosine kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q7YR43 | DDR1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| Q16832 | DDR2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08345 | DDR1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62838 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63604 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35739 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q03351 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64716 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P24062 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P15127 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P57097 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P97523 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P06494 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62956 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62799 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q00495 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q95ZV7 | ddr-2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor tyrosine kinase B | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| E7F3X9 | ddr1 | receptor protein-tyrosine kinase | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGTGTLSSLL | LLLLLVTIGD | ADMKGHFDPA | KCRYALGMQD | RTIPDSDISV | SSSWSDSTAA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RHSRLESSDG | DGAWCPAGPV | FPKEEEYLQV | DLRRLHLVAL | VGTQGRHAGG | LGKEFSRSYR |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LRYSRDGRRW | MDWKDRWGQE | VISGNEDPGG | VVLKDLGPPM | VARLVRFYPR | ADRVMSVCLR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VELYGCLWRD | GLLSYTAPVG | QTMQLSEMVY | LNDSTYDGYT | AGGLQYGGLG | QLADGVVGLD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DFRQSQELRV | WPGYDYVGWS | NHSFPSGYVE | MEFEFDRLRS | FQTMQVHCNN | MHTLGARLPG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GVECRFKRGP | AMAWEGEPVH | HALGGSLGDP | RARAISVPLG | GHVGRFLQCR | FLFAGPWLLF |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SEISFISDVV | NDSSDTFPPA | PWWPPGPPPT | NFSSLELEPR | GQQPVAKAEG | SPTAILIGCL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VAIILLLLLI | IALMLWRLHW | RRLLSKAERR | VLEEELTVHL | SVPGDTILIN | NRPGPREPPP |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| YQEPRPRGTP | THSAPCVPNG | SALLLSNPAY | RLLLATYARP | PRGPGPPTPA | WAKPTNTQAC |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SGDYMEPEKP | GAPLLPPPPQ | NSVPHYAEAD | IVTLQGVTGG | NTYAVPALPP | GAVGDGPPRV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| DFPRSRLRFK | EKLGEGQFGE | VHLCEVEDPQ | DLVTSDFPIS | VQKGHPLLVA | VKILRPDATK |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| NARNDFLKEV | KIMSRLKDLN | IIRLLGVCVQ | DDPLCMITDY | MENGDLNQFL | SAHQLENKVT |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| QGLPGDRESD | QGPTISYPML | LHVGAQIASG | MRYLATLNFV | HRDLATRNCL | VGENFTIKIA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| DFGMSRNLYA | GDYYRVQGRA | VLPIRWMAWE | CILMGKFTTA | SDVWAFGVTL | WEVLMLCRSQ |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| PFGQLTDEQV | IENAGEFFRD | QGRQVYLSRP | PACPQTLYEL | MLRCWSREPE | QRPPFSQLHR |
| FLADDALNTV |