Q63120
Gene name |
Abcc2 |
Protein name |
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 |
Names |
Canalicular multidrug resistance protein, Canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 1, Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:25303 |
EC number |
7.6.2.2: Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
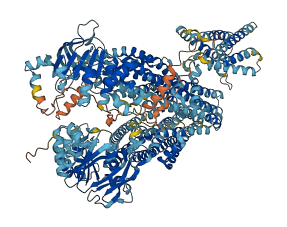
MRP2 (Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2) is an efflux transporter for organic anions, expressed in hepatocyte canalicular membranes. It plays a role in exporting bilirubin glucuronide, a breakdown product of heme. The structural analysis of rat Mrp2 (rMrp2) reveals an autoinhibited state where the regulatory domain (R-domain) is folded within the transmembrane domain cavity, preventing substrate binding and NBD:NBD interface formation. Phosphorylation of the R-domain by intracellular kinases relieves autoinhibition, enhancing rMrp2 transport activity. The drug-bound state of rMrp2 shows two probenecid binding sites, suggesting a dynamic interplay with autoinhibition and providing insights into drug modulation of MRP2 activity.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
320-601 (Transmembrane domain 1); 976-1260 (Transmembrane domain 2) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for Q63120
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8RQ3 | EM | 321 A | A | 1-1541 | PDB |
| 8RQ4 | EM | 345 A | A | 1-1541 | PDB |
| AF-Q63120-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for Q63120
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3319258154 | 91 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3319262337 | 611 | R>G | No | EVA |
1 associated diseases with Q63120
Without disease ID
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 7.6.2.2 | Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| brush border membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding the brush border. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| intercellular canaliculus | An extremely narrow tubular channel located between adjacent cells. An instance of this is the secretory canaliculi occurring between adjacent parietal cells in the gastric mucosa of vertebrates. |
| intracellular canaliculus | An apical plasma membrane part that forms a narrow enfolded luminal membrane channel, lined with numerous microvilli, that appears to extend into the cytoplasm of the cell. A specialized network of intracellular canaliculi is a characteristic feature of parietal cells of the gastric mucosa in vertebrates. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + glutathione S-conjugate(in) -> ADP + phosphate + glutathione S-conjugate(out). |
| ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + xenobiotic(in) = ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic(out). |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity | Primary active transporter of a solute across a membrane, via the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate, to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. The transport protein may be transiently phosphorylated (P-type transporters), or not (ABC-type transporters and other families of transporters). Primary active transport occurs up the solute's concentration gradient and is driven by a primary energy source. |
| bilirubin transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of bilirubin from one side of a membrane to the other. Bilirubin is a linear tetrapyrrole produced in the reticuloendothelial system from biliverdin and transported to the liver as a complex with serum albumin. In the liver, bilirubin is converted to bilirubin bisglucuronide, which is excreted in the bile. |
| organic anion transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of organic anions from one side of a membrane to the other. Organic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which contain carbon in covalent linkage. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the directed movement of a xenobiotic from one side of a membrane to the other. A xenobiotic is a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
43 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| antibiotic metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving an antibiotic, a substance produced by or derived from certain fungi, bacteria, and other organisms, that can destroy or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms. |
| benzylpenicillin metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving benzylpenicillin. |
| bile acid and bile salt transport | The directed movement of bile acid and bile salts into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| bile acid signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by bile acid binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| bilirubin transport | The directed movement of bilirubin into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| canalicular bile acid transport | Enables the transfer of bile acid from one side of a hepatocyte plasma membrane into a bile canaliculus. Bile canaliculi are the thin tubes formed by hepatocyte membranes. Bile acids are any of a group of steroid carboxylic acids occurring in bile, where they are present as the sodium salts of their amides with glycine or taurine. |
| cellular chloride ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of chloride ions at the level of a cell. |
| cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a dexamethasone stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| cellular response to interleukin-6 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-6 stimulus. |
| cellular response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| cellular response to tumor necrosis factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a tumor necrosis factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organism exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| detoxification of mercury ion | Any process that reduce or remove the toxicity of mercuric ion. These include transport of mercury away from sensitive areas and to compartments or complexes whose purpose is sequestration of mercury ion and/or reduction of mercury ion (Hg) to metallic mercury (Hg). |
| female pregnancy | The set of physiological processes that allow an embryo or foetus to develop within the body of a female animal. It covers the time from fertilization of a female ovum by a male spermatozoon until birth. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| leukotriene transport | The directed movement of leukotrienes into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. Leukotrienes are linear C20 endogenous metabolites of arachidonic acid (icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid) containing a terminal carboxy function and four or more double bonds (three or more of which are conjugated) as well as other functional groups. |
| mercury ion transport | The directed movement of mercury (Hg) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| organic anion transport | The directed movement of organic anions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. Organic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which contain carbon in covalent linkage. |
| prostaglandin transport | The directed movement of prostaglandins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of bile acid secretion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of bile acid from a cell or a tissue. |
| regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| response to 17alpha-ethynylestradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a 17alpha-ethynylestradiol stimulus. |
| response to antineoplastic agent | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an antineoplastic agent stimulus. An antineoplastic agent is a substance that inhibits or prevents the proliferation of neoplasms. |
| response to arsenic-containing substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an arsenic stimulus from compounds containing arsenic, including arsenates, arsenites, and arsenides. |
| response to estradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by estradiol, a C18 steroid hormone hydroxylated at C3 and C17 that acts as a potent estrogen. |
| response to estrogen | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of stimulus by an estrogen, C18 steroid hormones that can stimulate the development of female sexual characteristics. |
| response to glucagon | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucagon stimulus. |
| response to heat | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a heat stimulus, a temperature stimulus above the optimal temperature for that organism. |
| response to lipopolysaccharide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipopolysaccharide stimulus; lipopolysaccharide is a major component of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| response to steroid hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a steroid hormone stimulus. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| thyroid hormone transport | The directed movement of thyroid hormone into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| transepithelial transport | The directed movement of a substance from one side of an epithelium to the other. |
| transmembrane transport | The process in which a solute is transported across a lipid bilayer, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| xenobiotic catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a xenobiotic compound, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the plasma membrane | A process that reduces or removes the toxicity of a xenobiotic by exporting it outside the cell. |
| xenobiotic export from cell | The directed movement of a xenobiotic from a cell, into the extracellular region. A xenobiotic is a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| xenobiotic transmembrane transport | The process in which a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it, is transported across a membrane. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier | The directed movement of a xenobiotic through the blood-brain barrier. |
25 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P14772 | BPT1 | Bile pigment transporter 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q8HXQ5 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2QLE5 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| P91660 | Rh5 | Probable multidrug resistance-associated protein lethal(2)03659 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P13569 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95255 | ABCC6 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O15438 | ABCC3 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O15439 | ABCC4 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96J66 | ABCC11 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P33527 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92887 | ABCC2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| B2RX12 | Abcc3 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P26361 | Cftr | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O35379 | Abcc1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80WJ6 | Abcc12 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VI47 | Abcc2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6PQZ2 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q8CG09 | Abcc1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q6Y306 | Abcc12 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q00553 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | PR |
| Q9SKX0 | ABCC13 | ABC transporter C family member 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8VZZ4 | ABCC6 | ABC transporter C family member 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M1C7 | ABCC9 | ABC transporter C family member 9 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C8G9 | ABCC1 | ABC transporter C family member 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C8H0 | ABCC12 | ABC transporter C family member 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDKFCNSTFW | DLSLLESPEA | DLPLCFEQTV | LVWIPLGFLW | LLAPWQLYSV | YRSRTKRSSI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TKFYLAKQVF | VVFLLILAAI | DLSLALTEDT | GQATVPPVRY | TNPILYLCTW | LLVLAVQHSR |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QWCVRKNSWF | LSLFWILSVL | CGVFQFQTLI | RALLKDSKSN | MAYSYLFFVS | YGFQIVLLIL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TAFSGPSDST | QTPSVTASFL | SSITFSWYDR | TVLKGYKHPL | TLEDVWDIDE | GFKTRSVTSK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| FEAAMTKDLQ | KARQAFQRRL | QKSQRKPEAT | LHGLNKKQSQ | SQDVLVLEEA | KKKSEKTTKD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| YPKSWLIKSL | FKTFHVVILK | SFILKLIHDL | LVFLNPQLLK | LLIGFVKSSN | SYVWFGYICA |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ILMFAVTLIQ | SFCLQSYFQH | CFVLGMCVRT | TVMSSIYKKA | LTLSNLARKQ | YTIGETVNLM |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SVDSQKLMDA | TNYMQLVWSS | VIQITLSIFF | LWRELGPSIL | AGVGVMVLLI | PVNGVLATKI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RNIQVQNMKN | KDKRLKIMNE | ILSGIKILKY | FAWEPSFQEQ | VQGIRKKELK | NLLRFGQLQS |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LLIFILQITP | ILVSVVTFSV | YVLVDSANVL | NAEKAFTSIT | LFNILRFPLS | MLPMVTSSIL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| QASVSVDRLE | RYLGGDDLDT | SAIRRVSNFD | KAVKFSEASF | TWDPDLEATI | QDVNLDIKPG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| QLVAVVGTVG | SGKSSLVSAM | LGEMENVHGH | ITIQGSTAYV | PQQSWIQNGT | IKDNILFGSE |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| YNEKKYQQVL | KACALLPDLE | ILPGGDMAEI | GEKGINLSGG | QKQRVSLARA | AYQDADIYIL |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| DDPLSAVDAH | VGKHIFNKVV | GPNGLLAGKT | RIFVTHGIHF | LPQVDEIVVL | GKGTILEKGS |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| YRDLLDKKGV | FARNWKTFMK | HSGPEGEATV | NNDSEAEDDD | DGLIPTMEEI | PEDAASLAMR |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| RENSLRRTLS | RSSRSSSRRG | KSLKNSLKIK | NVNVLKEKEK | EVEGQKLIKK | EFVETGKVKF |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| SIYLKYLQAV | GWWSILFIIL | FYGLNNVAFI | GSNLWLSAWT | SDSDNLNGTN | NSSSHRDMRI |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| GVFGALGLAQ | GICLLISTLW | SIYACRNASK | ALHGQLLTNI | LRAPMRFFDT | TPTGRIVNRF |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| SGDISTVDDL | LPQTLRSWMM | CFFGIAGTLV | MICMATPVFA | IIIIPLSILY | ISVQVFYVAT |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| SRQLRRLDSV | TKSPIYSHFS | ETVTGLPIIR | AFEHQQRFLA | WNEKQIDINQ | KCVFSWITSN |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| RWLAIRLELV | GNLVVFCSAL | LLVIYRKTLT | GDVVGFVLSN | ALNITQTLNW | LVRMTSEAET |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| NIVAVERISE | YINVENEAPW | VTDKRPPADW | PRHGEIQFNN | YQVRYRPELD | LVLKGITCNI |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| KSGEKVGVVG | RTGAGKSSLT | NCLFRILESA | GGQIIIDGID | VASIGLHDLR | ERLTIIPQDP |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| ILFSGSLRMN | LDPFNKYSDE | EVWRALELAH | LRSFVSGLQL | GLLSEVTEGG | DNLSIGQRQL |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| LCLGRAVLRK | SKILVLDEAT | AAVDLETDSL | IQTTIRKEFS | QCTVITIAHR | LHTIMDSDKI |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | ||
| MVLDNGKIVE | YGSPEELLSN | RGSFYLMAKE | AGIENVNHTE | L |