Q62862
Gene name |
Map2k5 (Mek5, Mkk5, Prkmk5) |
Protein name |
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 |
Names |
MAP kinase kinase 5, MAPKK 5, MAPK/ERK kinase 5, MEK 5 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:29568 |
EC number |
2.7.12.2: Dual-specificity kinases (those acting on Ser/Thr and Tyr residues) |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
300-321 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
166-419 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
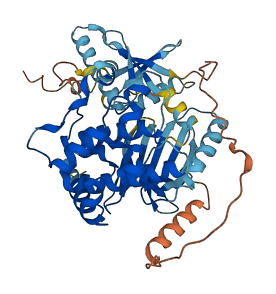
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q62862
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q62862-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for Q62862
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3321290903 | 89 | V>A | No | EVA |
1 associated diseases with Q62862
Without disease ID
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.12.2 | Dual-specificity kinases (those acting on Ser/Thr and Tyr residues) |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| spindle | The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| MAP kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: protein + ATP = protein phosphate + ADP. This reaction is the phosphorylation of proteins. Mitogen-activated protein kinase; a family of protein kinases that perform a crucial step in relaying signals from the plasma membrane to the nucleus. They are activated by a wide range of proliferation- or differentiation-inducing signals; activation is strong with agonists such as polypeptide growth factors and tumor-promoting phorbol esters, but weak (in most cell backgrounds) by stress stimuli. |
| MAP kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the concomitant phosphorylation of threonine (T) and tyrosine (Y) residues in a Thr-Glu-Tyr (TEY) thiolester sequence in a MAP kinase (MAPK) substrate. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
19 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a growth factor stimulus. |
| ERK5 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK5 (also called BMK1; a MAPK), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis. Cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis is the orderly movement of endothelial cells into the extracellular matrix in order to form new blood vessels contributing to the process of sprouting angiogenesis. |
| negative regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production. |
| negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in the apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand. |
| negative regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion. |
| negative regulation of interleukin-8 production | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-8 production. |
| negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| negative regulation of response to cytokine stimulus | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of a response to cytokine stimulus. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| positive regulation of cell growth | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, extent or direction of cell growth. |
| positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of epithelial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of protein metabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways involving a protein. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
19 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P32491 | MKK2 | MAP kinase kinase MKK2/SSP33 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P32490 | MKK1 | MAP kinase kinase MKK1/SSP32 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q90891 | MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q9XT09 | MAP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q24324 | Dsor1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase dSOR1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P36507 | MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q02750 | MAP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13163 | MAP2K5 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P31938 | Map2k1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q63932 | Map2k2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WVS7 | Map2k5 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q4KSH7 | Map2k7 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P36506 | Map2k2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01986 | Map2k1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q5QN75 | MKK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q10664 | mek-2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase mek-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9FJV0 | MKK6 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9S7U9 | MKK2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94A06 | MKK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MLWLALGPFR | AMENQVLVIR | IKIPNSGAVD | WTVHSGPQLL | FRDVLDVIGQ | VLPEATTTAF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EYEDEDGDRI | TVRSDEEMKA | MLSYYYSTVM | EQQVNGQLIE | PLQIFPRACK | PPGERNIHGL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KVNTRAGPSQ | HTSPVVSDSL | PSNSLKKSSA | ELRKILANGQ | MNEQDIRYRD | TLGHGNGGTV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| YKAYHVPSGK | ILAVKVILLD | ITLELQKQIM | SELEILYKCD | SSYIIGFYGA | FFVENRISIC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TEFMDGGSLD | VYRKIPEHVL | GRIAVAVVKG | LTYLWSLKIL | HRDVKPSNML | VNTSGQVKLC |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DFGVSTQLVN | SIAKTYVGTN | AYMAPERISG | EQYGIHSDVW | SLGISFMELA | LGRFPYPQIQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KNQGSLMPLQ | LLQCIVDEDS | PVLPLGEFSE | PFVHFITQCM | RKQPKERPAP | EELMGHPFIV |
| 430 | 440 | ||||
| QFNDGNATVV | SMWVCRALEE | RRSQQGPP |