Q62838
Gene name |
Musk |
Protein name |
Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase |
Names |
EC 2.7.10.1 , Muscle-specific tyrosine protein kinase receptor , MuSK , Muscle-specific kinase receptor |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:81725 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
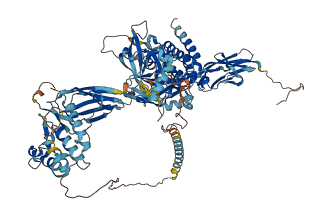
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
574-855 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
741-766 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
574-855 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
741-766 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
574-855 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Juxtamembrane autoinhibition in receptor tyrosine kinases", Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 5, 464-71
- Artim SC et al. (2012) "Assessing the range of kinase autoinhibition mechanisms in the insulin receptor family", The Biochemical journal, 448, 213-20
- Uchikawa E et al. (2019) "Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex", eLife, 8,
- Nielsen J et al. (2022) "Structural Investigations of Full-Length Insulin Receptor Dynamics and Signalling", Journal of molecular biology, 434, 167458
- Chen YS et al. (2021) "Insertion of a synthetic switch into insulin provides metabolite-dependent regulation of hormone-receptor activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118,
- Craddock BP et al. (2007) "Autoinhibition of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor by the juxtamembrane region", FEBS letters, 581, 3235-40
- Huang X et al. (2009) "Structural insights into the inhibited states of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase", Journal of structural biology, 165, 88-96
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

4 structures for Q62838
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1LUF | X-ray | 205 A | A | 529-868 | PDB |
| 2IEP | X-ray | 221 A | A/B | 22-212 | PDB |
| 3HKL | X-ray | 210 A | A/B | 313-494 | PDB |
| AF-Q62838-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q62838
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q62838 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q62838
18 regional properties for Q62838
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 574 - 855 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 575 - 855 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 40 - 106 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 133 - 197 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 224 - 289 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 34 - 118 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 127 - 209 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 218 - 300 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 28 - 116 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 121 - 205 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 212 - 302 | IPR007110-3 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 720 - 732 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 28 - 110 | IPR013098-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 121 - 202 | IPR013098-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 213 - 296 | IPR013098-3 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 580 - 608 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Frizzled domain | 312 - 450 | IPR020067 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 574 - 855 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| external side of plasma membrane | The leaflet of the plasma membrane that faces away from the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| neuromuscular junction | The junction between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. In response to the arrival of action potentials, the presynaptic button releases molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle fiber, leading to a change in post-synaptic potential. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic membrane | A specialized area of membrane facing the presynaptic membrane on the tip of the nerve ending and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft). Neurotransmitters cross the synaptic cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction |
| Wnt-protein binding | Binding to a Wnt-protein, a secreted growth factor involved in signaling. |
28 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell differentiation | The cellular developmental process in which a relatively unspecialized cell, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cell, acquires specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize a specific cell. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cochlea development | The progression of the cochlea over time from its formation to the mature structure. The cochlea is the snail-shaped portion of the inner ear that is responsible for the detection of sound. |
| enzyme-linked receptor protein signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell, where the receptor possesses catalytic activity or is closely associated with an enzyme such as a protein kinase, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| long-term synaptic potentiation | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity such that synapses are changed resulting in the increase in the rate, or frequency of synaptic transmission at the synapse. |
| memory | The activities involved in the mental information processing system that receives (registers), modifies, stores, and retrieves informational stimuli. The main stages involved in the formation and retrieval of memory are encoding (processing of received information by acquisition), storage (building a permanent record of received information as a result of consolidation) and retrieval (calling back the stored information and use it in a suitable way to execute a given task). |
| motor neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a motor neuron, an efferent neuron that passes from the central nervous system or a ganglion toward or to a muscle and conducts an impulse that causes movement. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| neuromuscular junction development | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a neuromuscular junction. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of motor neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of motor neuron apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of protein geranylgeranylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein geranylgeranylation. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of Rac protein signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of Rac protein signal transduction. |
| positive regulation of skeletal muscle acetylcholine-gated channel clustering | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of skeletal muscle acetylcholine-gated channel clustering. |
| positive regulation of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction. |
| positive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cholinergic synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse using the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. |
| receptor clustering | The receptor metabolic process that results in grouping of a set of receptors at a cellular location, often to amplify the sensitivity of a signaling response. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junctions. |
| response to axon injury | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an axon injury stimulus. |
| response to electrical stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an electrical stimulus. |
| response to muscle activity | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a muscle activity stimulus. |
| retina development in camera-type eye | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the retina over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The retina is the innermost layer or coating at the back of the eyeball, which is sensitive to light and in which the optic nerve terminates. |
| skeletal muscle acetylcholine-gated channel clustering | The accumulation of acetylcholine-gated cation channels in a narrow, central region of muscle fibers, in apposition to nerve terminals. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
61 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q91044 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q91987 | NTRK2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q91009 | NTRK1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8AXY6 | MUSK | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q5IS37 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| Q24488 | Ror | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor Ror | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V6K3 | Nrk | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor Ror2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q16620 | NTRK2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q16288 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q01973 | ROR1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q01974 | ROR2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P04629 | NTRK1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O15146 | MUSK | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9Z138 | Ror2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24786 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63604 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35739 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q03351 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64716 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P24062 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P57097 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P97523 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q62956 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62799 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P15127 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63474 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P06494 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q00495 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| G5EGK5 | cam-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor cam-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O64770 | At1g61490 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61490 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64783 | At1g61370 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61370 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O81833 | SD11 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWZ5 | SD25 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD2-5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LPZ9 | SD113 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SXB5 | At1g11303 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11303 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SYA0 | At1g61500 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61500 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SXB4 | At1g11300 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11300 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64778 | At1g61420 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61420 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64776 | At1g61440 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61440 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64780 | At1g61400 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61400 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SY95 | At1g61550 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61550 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64782 | SD129 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-29 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64774 | At1g61460 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61460 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64477 | At2g19130 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g19130 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64793 | At1g67520 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67520 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SXB8 | At1g11330 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11330 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64784 | At1g61360 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61360 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39203 | SD22 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD2-2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MRELVNIPLL | QMLTLVAFSG | TEKLPKAPVI | TTPLETVDAL | VEEVATFMCA | VESYPQPEIS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| WTRNKILIKL | FDTRYSIREN | GQLLTILSVE | DSDDGIYCCT | ANNGVGGAVE | SCGALQVKMK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PKITRPPINV | KIIEGLKAVL | PCTTMGNPKP | SVSWIKGDSA | LRENSRIAVL | ESGSLRIHNV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| QKEDAGQYRC | VAKNSLGTAY | SKLVKLEVEV | FARILRAPES | HNVTFGSFVT | LRCTAIGMPV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PTISWIENGN | AVSSGSIQEN | VKDRVIDSRL | QLFITKPGLY | TCIATNKHGE | KFSTAKAAAT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| VSIAEWSKSQ | KESKGYCAQY | RGEVCDAVLV | KDSLVFFNTS | YPDPEEAQEL | LIHTAWNELK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| AVSPLCRPAA | EALLCNHLFQ | ECSPGVLPTP | MPICREYCLA | VKELFCAKEW | LAMEGKTHRG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LYRSGMHFLP | VPECSKLPSM | HQDPTACTRL | PYLDYKKENI | TTFPSITSSK | PSVDIPNLPA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| STSSFAVSPA | YSMTVIISIM | SCFAVFALLT | ITTLYCCRRR | REWKNKKRES | AAVTLTTLPS |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| ELLLDRLHPN | PMYQRMPLLL | NPKLLSLEYP | RNNIEYVRDI | GEGAFGRVFQ | ARAPGLLPYE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| PFTMVAVKML | KEEASADMQA | DFQREAALMA | EFDNPNIVKL | LGVCAVGKPM | CLLFEYMAYG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| DLNEFLRSMS | PHTVCSLSHS | DLSTRARVSS | PGPPPLSCAE | QLCIARQVAA | GMAYLSERKF |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| VHRDLATRNC | LVGENMVVKI | ADFGLSRNIY | SADYYKADGN | DAIPIRWMPP | ESIFYNRYTT |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| ESDVWAYGVV | LWEIFSYGLQ | PYYGMAHEEV | IYYVRDGNIL | ACPENCPLEL | YNLMRLCWSK |
| 850 | 860 | ||||
| LPADRPSFCS | IHRILQRMCE | RAEGTVGV |