Q62833
Gene name |
Grk5 (Gprk5) |
Protein name |
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 |
Names |
EC 2.7.11.16 , G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK5 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:59075 |
EC number |
2.7.11.16: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
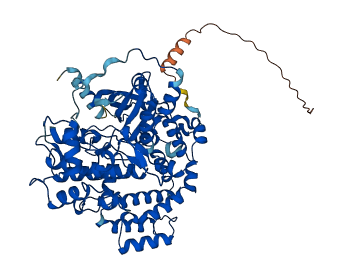
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
186-448 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
328-350 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
186-448 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
328-350 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
186-448 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Pronin AN et al. (1998) "Structure-function analysis of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5. Role of the carboxyl terminus in kinase regulation", The Journal of biological chemistry, 273, 31510-8
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q62833
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q62833-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q62833
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q62833 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q62833
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.16 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| beta-adrenergic receptor kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| G protein-coupled receptor kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| lipid binding | Binding to a lipid. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway after prolonged stimulation with an agonist of the pathway. |
| fat cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of an adipocyte, an animal connective tissue cell specialized for the synthesis and storage of fat. |
| negative regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of an adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| oligodendrocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an oligodendrocyte. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons of neurons in the central nervous system. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle. |
| regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. |
| regulation of signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction. |
| response to cocaine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cocaine stimulus. Cocaine is a crystalline alkaloid obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. |
| tachykinin receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by tachykinin binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process. Tachykinin is a short peptide with the terminal sequence (Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2). |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
20 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P26818 | GRK3 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P21146 | GRK2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P43249 | GRK5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P32865 | Gprk1 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P25098 | GRK2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P35626 | GRK3 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q15835 | GRK1 | Rhodopsin kinase GRK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P32298 | GRK4 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P43250 | GRK6 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P34947 | GRK5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O70293 | Grk6 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99MK8 | Grk2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WVL4 | Grk1 | Rhodopsin kinase GRK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q3UYH7 | Adrbk2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VEB1 | Grk5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26817 | Grk2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P26819 | Grk3 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P97711 | Grk6 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q09639 | grk-2 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| O48963 | PHOT1 | Phototropin-1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MELENIVANT | VLLKAREGGG | GKRKGKSKKW | KEILKFPHIN | QCEDLRRTID | RDYYSLCDKQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PIGRLLFRQF | CETRPGLECY | IQFLDLVAEY | EITPDENLGA | KGKEIMTKYL | SPKSPVFIAQ |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VGQDLVSQTE | KKLLQSPCKE | LFSACAQSVH | DYLKGDPFHE | YLDSMYFDRF | LQWKWLERQP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VTKNTFRQYR | VLGKGGFGEV | CACQVRATGK | MYACKRLEKK | RIKKRKGESM | ALNEKQILEK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VNSQFVVNLA | YAYETKDALC | LVLTIMNGGD | LKFHIYNMGN | PGFEEERALF | YAAEILCGLE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DLHRENTVYR | DLKPENILLD | DYGHIRISDL | GLAVKIPEGD | LIRGRVGTVG | YMAPEVLNNQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| RYGLSPDYWG | LGCLIYEMIE | GQSPFRGRKE | KVKREEVDRR | VLETEEVYSP | KFSEEAKSIC |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| NMLLTKDSKQ | RLGCQEEGAA | EVKRHPFFRN | MNFKRLEAGM | LDPPFVPDPR | AVYCKDVLDI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EQFSTVKGVN | LDHTDDDFYS | KFSTGSVPIP | WQNEMIETEC | FKELNVFGPN | GTLSPDLNRS |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | ||
| QPPEPPKKGL | FHRLFRRQHQ | NNSKSSPTPK | TSCNHRINSN | HINSNSTGSS |