Q62421
Gene name |
Sh3gl3 (Sh3d2c, Sh3d2c2) |
Protein name |
Endophilin-A3 |
Names |
Endophilin-3, SH3 domain protein 2C, SH3 domain-containing GRB2-like protein 3, SH3p13 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:20408 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
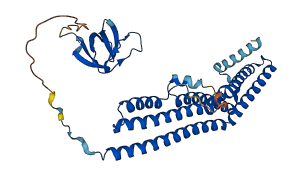
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q62421
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q62421-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q62421
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q62421 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q62421
Functions
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| acrosomal vesicle | A structure in the head of a spermatozoon that contains acid hydrolases, and is concerned with the breakdown of the outer membrane of the ovum during fertilization. It lies just beneath the plasma membrane and is derived from the lysosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| early endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an early endosome. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| postsynaptic density, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane forming an electron dense disc. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic endosome | An endosomal compartment that is part of the post-synapse. Only early and recycling endosomes are typically present in the postsynapse. |
| presynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the presynaptic cell. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| lipid binding | Binding to a lipid. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| negative regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. |
| positive regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. |
| synaptic vesicle uncoating | The removal of the protein coat on a synaptic vesicle following the pinching step at the end of budding from the presynaptic membrane. |
14 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2KJA1 | SH3GL1 | Endophilin-A2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q8AXV1 | SH3GL2 | Endophilin-A1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q8AXU9 | SH3GL3 | Endophilin-A3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q99961 | SH3GL1 | Endophilin-A2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99962 | SH3GL2 | Endophilin-A1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99963 | SH3GL3 | Endophilin-A3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8BZT2 | Sh3rf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SH3RF2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JK48 | Sh3glb1 | Endophilin-B1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62420 | Sh3gl2 | Endophilin-A1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62419 | Sh3gl1 | Endophilin-A2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JLQ0 | Cd2ap | CD2-associated protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8R550 | Sh3kbp1 | SH3 domain-containing kinase-binding protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O35179 | Sh3gl2 | Endophilin-A1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O35180 | Sh3gl3 | Endophilin-A3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSVAGLKKQF | HKASQLFSEK | ISGAEGTKLD | EEFLNMEKKI | DITSKAVAEI | LSKATEYLQP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NPAYRAKLGM | LNTVSKLRGQ | VKATGYPQTE | GLLGDCMLKY | GKELGEDSAF | GNSLVDVGEA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LKLMAEVKDS | LDINVKQTFI | DPLQLLQDKD | LKEIGHHLRK | LEGRRLDYDY | KKRRVGKIPE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EEIRQAVEKF | EESKELAERS | MFNFLENDVE | QVSQLAVFVE | AALDYHRQST | EILQELQSKL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ELRISLASKV | PKREFMPKPV | NMSSTDANGV | GPSSSSKTPG | TDTPADQPCC | RGLYDFEPEN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | ||
| EGELGFKEGD | IITLTNQIDE | NWYEGMLRGE | SGFFPINYVE | VIVPLPP |