Q62420
Gene name |
Sh3gl2 (Een1) |
Protein name |
Endophilin-A1 |
Names |
Endophilin-1, SH3 domain protein 2A, SH3 domain-containing GRB2-like protein 2, SH3p4 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:20404 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
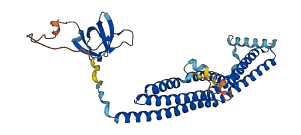
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q62420
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1ZWW | X-ray | 230 A | A/B | 1-256 | PDB |
| AF-Q62420-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
11 variants for Q62420
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388696974 | 17 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388672393 | 21 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388693724 | 34 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388692434 | 68 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388689981 | 136 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388690686 | 146 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388697005 | 217 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388691064 | 258 | K>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388680033 | 264 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388690754 | 274 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388696979 | 338 | F>L | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q62420
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchoring junction | A cell junction that mechanically attaches a cell (and its cytoskeleton) to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix. |
| basal dendrite | A dendrite that emerges near the basal pole of a neuron. In bipolar neurons, basal dendrites are either on the same side of the soma as the axon, or project toward the axon. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse | One of the giant synapses that form between the mossy fiber axons of dentate gyrus granule cells and the large complex spines of CA3 pyramidal cells. It consists of a giant bouton known as the mossy fiber expansion, synapsed to the complex, multiheaded spine (thorny excresence) of a CA3 pyramidal cell. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| photoreceptor ribbon synapse | A ribbon synapse between a retinal photoreceptor cell (rod or cone) and a retinal bipolar cell. These contain a plate-like synaptic ribbon. |
| presynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the presynaptic cell. |
| presynaptic cytosol | The region of the cytosol consisting of all cytosol that is part of the presynapse. |
| Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse | A synapse between the Schaffer collateral axon of a CA3 pyramidal cell and a CA1 pyramidal cell. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
| synaptic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| lipid binding | Binding to a lipid. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus | A process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus. |
| dendrite extension | Long distance growth of a single dendrite involved in cellular development. |
| lipid tube assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of macromolecules to form a macromolecular complex that contains a tube of lipid surrounded by a protein coat involved in membrane shaping of vesicle membranes as they fuse or undergo fission. |
| membrane bending | A membrane organization process resulting in the bending of a membrane. |
| membrane tubulation | A membrane organization process resulting in the formation of a tubular projection. This may face inwardly (as in tubular membrane invaginations) or outwardly (as in endosomal tubules). |
| negative regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability | Any process that decreases blood-brain barrier permeability, the quality of the blood-brain barrier that allows for a controlled passage of substances (e.g. macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into and out of the brain. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of membrane tubulation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of membrane tubulation. |
| regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. |
| regulation of receptor internalization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of receptor internalization. |
| synaptic vesicle endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process, in which the synaptic vesicle membrane constituents are retrieved from the presynaptic membrane on the axon terminal after neurotransmitter secretion by exocytosis. Synaptic vesicle endocytosis can occur via clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent mechanisms. |
| synaptic vesicle uncoating | The removal of the protein coat on a synaptic vesicle following the pinching step at the end of budding from the presynaptic membrane. |
| vesicle scission | The membrane scission process that is the final step in the formation of a vesicle, leading to separation from its parent membrane. Vesicle scission involves the constriction of a neck-forming protein complex, consisting e.g. of dynamin, around the budded membrane, leading to vesicle closure during its separation from the parent membrane. |
15 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2KJA1 | SH3GL1 | Endophilin-A2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q8AXU9 | SH3GL3 | Endophilin-A3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q8AXV1 | SH3GL2 | Endophilin-A1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q99961 | SH3GL1 | Endophilin-A2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99963 | SH3GL3 | Endophilin-A3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q99962 | SH3GL2 | Endophilin-A1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Y371 | SH3GLB1 | Endophilin-B1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q62419 | Sh3gl1 | Endophilin-A2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BZT2 | Sh3rf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SH3RF2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JK48 | Sh3glb1 | Endophilin-B1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62421 | Sh3gl3 | Endophilin-A3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JLQ0 | Cd2ap | CD2-associated protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8R550 | Sh3kbp1 | SH3 domain-containing kinase-binding protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O35180 | Sh3gl3 | Endophilin-A3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O35179 | Sh3gl2 | Endophilin-A1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSVAGLKKQF | HKATQKVSEK | VGGAEGTKLD | DDFKEMERKV | DVTSRAVMEI | MTKTIEYLQP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NPASRAKLSM | INTMSKIRGQ | EKGPGYPQAE | ALLAEAMLKF | GRELGDDCNF | GPALGEVGEA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| MRELSEVKDS | LDMEVKQNFI | DPLQNLHDKD | LREIQHHLKK | LEGRRLDFDY | KKKRQGKIPD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EELRQALEKF | DESKEIAESS | MFNLLEMDIE | QVSQLSALVQ | AQLEYHKQAV | QILQQVTVRL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EERIRQASSQ | PRREYQPKPR | MSLEFATGDS | TQPNGGLSHT | GTPKPPGVQM | DQPCCRALYD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| FEPENEGELG | FKEGDIITLT | NQIDENWYEG | MLHGQSGFFP | INYVEILVAL | PH |