Q62159
Gene name |
Rhoc (Arhc) |
Protein name |
Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC |
Names |
Silica-induced gene 61 protein, SIG-61 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:11853 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
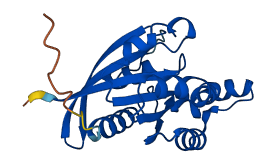
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q62159
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q62159-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
5 variants for Q62159
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388654682 | 3 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388650061 | 14 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388648513 | 109 | N>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388648511 | 144 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388658698 | 193 | L>F | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q62159
6 regional properties for Q62159
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 277 - 304 | IPR013087-1 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 305 - 332 | IPR013087-2 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 333 - 360 | IPR013087-3 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 361 - 388 | IPR013087-4 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 389 - 416 | IPR013087-5 |
| domain | Zinc finger C2H2-type | 417 - 445 | IPR013087-6 |
Functions
11 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cortex | The region of a cell that lies just beneath the plasma membrane and often, but not always, contains a network of actin filaments and associated proteins. |
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| stereocilium | An actin-based protrusion from the apical surface of auditory and vestibular hair cells and of neuromast cells. These protrusions are supported by a bundle of cross-linked actin filaments (an actin cable), oriented such that the plus (barbed) ends are at the tip of the protrusion, capped by a tip complex which bridges to the plasma. Bundles of stereocilia act as mechanosensory organelles. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments. Includes processes that control the spatial distribution of actin filaments, such as organizing filaments into meshworks, bundles, or other structures, as by cross-linking. |
| apical junction assembly | The formation of an apical junction, a functional unit located near the cell apex at the points of contact between epithelial cells composed of the tight junction, the zonula adherens junction and the desmosomes, by the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of its constituents. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cortical cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures in the cell cortex, i.e. just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| establishment or maintenance of cell polarity | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| mitotic cytokinesis | A cell cycle process that results in the division of the cytoplasm of a cell after mitosis, resulting in the separation of the original cell into two daughter cells. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of lipase activity | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of lipase activity, the hydrolysis of a lipid or phospholipid. |
| positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein complex assembly. |
| positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| skeletal muscle satellite cell migration | The orderly movement of a skeletal muscle satellite cell from one site to another. Migration of these cells is a key step in the process of growth and repair of skeletal muscle cells. |
| small GTPase mediated signal transduction | The series of molecular signals in which a small monomeric GTPase relays a signal. |
| wound healing, spreading of cells | The migration of a cell along or through a wound gap that contributes to the reestablishment of a continuous surface. |
36 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q17QI8 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2HJ68 | RND1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P61585 | RHOA | Transforming protein RhoA | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q3ZBW5 | RHOB | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1RMJ6 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9PSX7 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P48148 | Rho1 | Ras-like GTP-binding protein Rho1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q96L33 | RHOV | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92730 | RND1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O94844 | RHOBTB1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61587 | RND3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O94955 | RHOBTB3 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P61586 | RHOA | Transforming protein RhoA | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P62745 | RHOB | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P08134 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9CTN4 | Rhobtb3 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P61588 | Rnd3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P62746 | Rhob | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VDU1 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DAK3 | Rhobtb1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9QUI0 | Rhoa | Transforming protein RhoA | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BLR7 | Rnd1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O77683 | RND3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q6SA80 | Rnd3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9Z1Y0 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P61589 | Rhoa | Transforming protein RhoA | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P62747 | Rhob | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9SSX0 | RAC1 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 1 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6Z808 | RAC3 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q68Y52 | RAC2 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q67VP4 | RAC4 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 4 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q22038 | rho-1 | Ras-like GTP-binding protein rhoA | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9SU67 | ARAC8 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O82480 | ARAC7 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q38903 | ARAC2 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O82481 | ARAC10 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAIRKKLVI | VGDGACGKTC | LLIVFSKDQF | PEVYVPTVFE | NYIADIEVDG | KQVELALWDT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AGQEDYDRLR | PLSYPDTDVI | LMCFSIDSPD | SLENIPEKWT | PEVKHFCPNV | PIILVGNKKD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LRQDEHTRRE | LAKMKQEPVR | SEEGRDMANR | ISAFGYLECS | AKTKEGVREV | FEMATRAGLQ |
| 190 | |||||
| VRKNKRRRGC | PIL |