Q62101
Gene name |
Prkd1 (Pkcm, Pkd, Prkcm) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase D1 |
Names |
Protein kinase C mu type, Protein kinase D, nPKC-D1, nPKC-mu |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18760 |
EC number |
2.7.11.13: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
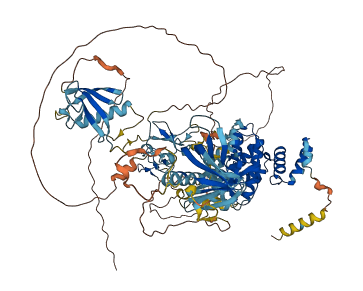
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
589-845 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
732-754 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
589-845 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q62101
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q62101-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
8 variants for Q62101
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs582508677 | 5 | P>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs240367187 | 233 | V>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs47851355 | 331 | T>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs227241661 | 379 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs48999653 | 384 | G>E | No | Ensembl | |
| rs245484345 | 514 | V>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs215597880 | 559 | G>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs264236950 | 892 | S>T | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q62101
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.13 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an autophagosome, a double-membrane-bounded vesicle in which endogenous cellular material is sequestered. |
| cell cortex | The region of a cell that lies just beneath the plasma membrane and often, but not always, contains a network of actin filaments and associated proteins. |
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity | Calcium-dependent catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein kinase C activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires diacylglycerol. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
41 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to amino acid starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of amino acids. |
| cellular response to hydroperoxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydroperoxide stimulus. Hydroperoxides are monosubstitution products of hydrogen peroxide, HOOH. |
| cellular response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus. |
| defense response to Gram-negative bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-negative bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| Golgi organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. |
| Golgi vesicle transport | The directed movement of substances into, out of or within the Golgi apparatus, mediated by vesicles. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of cell death | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that activates or increases angiogenesis. |
| positive regulation of autophagy | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor CREB. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell chemotaxis. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to its receptor on the surface of a cell, which activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell chemotaxis. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell migration | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of endothelial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of histone deacetylase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of histone deacetylase activity. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of protein import into nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of movement of proteins from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein kinase D signaling | A series of reactions, mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase D, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| Ras protein signal transduction | The series of molecular signals within the cell that are mediated by a member of the Ras superfamily of proteins switching to a GTP-bound active state. |
| regulation of keratinocyte proliferation | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of keratinocyte proliferation. Keratinocyte proliferation is the multiplication or reproduction of keratinocytes, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| regulation of protein stability | Any process that affects the structure and integrity of a protein, altering the likelihood of its degradation or aggregation. |
| regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) on the surface of the target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O94806 | PRKD3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BZL6 | PRKD2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15139 | PRKD1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8BZ03 | Prkd2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K1Y2 | Prkd3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q5XIS9 | Prkd2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WTQ1 | Prkd1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase D1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O45818 | dkf-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase dkf-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSVPPLLRPP | SPLLPAAAAV | AAAAAALVPG | SGPAPFPAPG | AAPAGGISFH | LQIGLSREPV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LLLQDSSGDY | SLAHVREMAC | SIVDQKFPEC | GFYGLYDKIL | LFRHDPASDN | ILQLVKIASD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IQEGDLIEVV | LSASATFEDF | QIRPHALFVH | SYRAPAFCDH | CGEMLWGLVR | QGLKCEGCGL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| NYHKRCAFKI | PNNCSGVRRR | RLSNVSLTGL | GTVRTASAEF | STSVPDEPLL | SPVSPGFEQK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SPSESFIGRE | KRSNSQSYIG | RPIQLDKLLM | SKVKVPHTFV | IHSYTRPTVC | QFCKKLLKGL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| FRQGLQCKDC | RFNCHKRCAP | KVPNNCLGEV | TINGELLSPG | AESDVVMEEG | SDDNDSERNS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| GLMDDMDEAM | VQDTEMALAE | GQSGGAEMQD | PDADQEDSNR | TISPSTSNNI | PLMRVVQSVK |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| HTKRRSSTVM | KEGWMVHYTS | KDTLRKRHYW | RLDSKCITLF | QNDTGSRYYK | EIPLSEILCL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EPAKPSALTP | VGATPHCFEI | TTANVVYYVG | ENVVNPSSSP | PNNSVLPSGI | GPDVARMWEV |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| AIQHALMPVI | PKGSSVGSGS | NSHKDISVSI | SVSNCQIQEN | VDISTVYQIF | PDEVLGSGQF |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GIVYGGKHRK | TGRDVAIKII | DKLRFPTKQE | SQLRNEVAIL | QNLHHPGVVN | LECMFETPER |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| VFVVMEKLHG | DMLEMILSSE | KGRLPEHITK | FLITQILVAL | RHLHFKNIVH | CDLKPENVLL |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ASADPFPQVK | LCDFGFARII | GEKSFRRSVV | GTPAYLAPEV | LRNKGYNRSL | DMWSVGVIIY |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| VSLSGTFPFN | EDEDIHDQIQ | NAAFMYPPNP | WKEISHEAID | LINNLLQVKM | RKRYSVDKTL |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| SHPWLQDYQT | WLDLRELECR | IGERYITHES | DDSRWEQYAG | EQGLQYPAHL | ISLSASHSDS |
| 910 | |||||
| PEAEEREMKA | LSERVSIL |