Q61851
Gene name |
Fgfr3 (Mfr3, Sam3) |
Protein name |
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
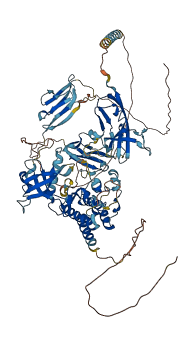
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P22607)
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) is one of the members of FGFR family belonging to the receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and maintenance of cellular homeostasis. FGFR3 consists of the ligand-binding region (immunoglobulin (Ig) domain 1-like domains) designated D1, D2, and D3, and a kinase domain. The D1 domain and the acid box (AB)-containing linker between D1 and D2 are involved in autoinhibition. Loss of D1 or the linker enhances the affinity of FGFR for FGF and HS and increases the signaling capacity of FGFR. Specifically, the AB region blocks the heparan sulfate (HS)-binding site on the D2 domain in cis to suppress HS-binding affinity of EGFR. D1 is dispensable for autoinhibition but plays a minor role in autoinhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q61851
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q61851-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q61851
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q61851 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q61851
15 regional properties for Q61851
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 466 - 756 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 466 - 743 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 50 - 114 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 161 - 229 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 260 - 340 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 44 - 124 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 155 - 240 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 254 - 351 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 39 - 108 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 145 - 238 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 247 - 349 | IPR007110-3 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 607 - 619 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 160 - 239 | IPR013098 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 472 - 502 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 466 - 743 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The leaflet the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| lysosome | A small lytic vacuole that has cell cycle-independent morphology found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases, most of which have their maximal activities in the pH range 5-6. The contained enzymes display latency if properly isolated. About 40 different lysosomal hydrolases are known and lysosomes have a great variety of morphologies and functions. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| transport vesicle | Any of the vesicles of the constitutive secretory pathway, which carry cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi, between Golgi cisternae, from the Golgi to the ER (retrograde transport) or to destinations within or outside the cell. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| fibroblast growth factor binding | Binding to a fibroblast growth factor. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor activity | Combining with a fibroblast growth factor receptor ligand and transmitting the signal across the plasma membrane to initiate a change in cell activity. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| miRNA binding | Binding to a microRNA, a 21-23 nucleotide RNA that is processed from a stem-loop RNA precursor (pre-miRNA) that is encoded within plant and animal genomes. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
71 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| alveolar secondary septum development | The progression of a secondary alveolar septum over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A secondary alveolar septum is a specialized epithelium that subdivides the initial saccule. |
| astrocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an astrocyte. An astrocyte is the most abundant type of glial cell. Astrocytes provide support for neurons and regulate the environment in which they function. |
| axonogenesis involved in innervation | The neurite development process that generates a long process of a neuron, as it invades a target tissue. |
| bone development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of bone over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Bone is the hard skeletal connective tissue consisting of both mineral and cellular components. |
| bone maturation | A developmental process, independent of morphogenetic (shape) change, that is required for bone to attain its fully functional state. |
| bone mineralization | The deposition of hydroxyapatite, a form of calcium phosphate with the formula Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, in bone tissue. |
| bone morphogenesis | The process in which bones are generated and organized. |
| bone trabecula morphogenesis | The process of shaping a trabecula in bone. A trabecula is a tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod. |
| calcium ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of calcium ions within an organism or cell. |
| cartilage development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cartilage element over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cartilage elements are skeletal elements that consist of connective tissue dominated by extracellular matrix containing collagen type II and large amounts of proteoglycan, particularly chondroitin sulfate. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| cell-cell signaling | Any process that mediates the transfer of information from one cell to another. This process includes signal transduction in the receiving cell and, where applicable, release of a ligand and any processes that actively facilitate its transport and presentation to the receiving cell. Examples include signaling via soluble ligands, via cell adhesion molecules and via gap junctions. |
| central nervous system myelination | The process in which neuronal axons and dendrites become coated with a segmented lipid-rich sheath (myelin) to enable faster and more energetically efficient conduction of electrical impulses. The sheath is formed by the cell membranes of oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system. Adjacent myelin segments are separated by a non-myelinated stretch of axon called a node of Ranvier. |
| cochlea development | The progression of the cochlea over time from its formation to the mature structure. The cochlea is the snail-shaped portion of the inner ear that is responsible for the detection of sound. |
| digestive tract morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the digestive tract are generated and organized. The digestive tract is the anatomical structure through which food passes and is processed. |
| endothelial cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of endothelial cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. Endothelial cells are thin flattened cells which line the inside surfaces of body cavities, blood vessels, and lymph vessels, making up the endothelium. |
| epithelial cell fate commitment | The process in which the developmental fate of a cell becomes restricted such that it will develop into an epithelial cell. |
| epithelial cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of epithelial cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. Epithelial cells make up the epithelium, the covering of internal and external surfaces of the body, including the lining of vessels and other small cavities. It consists of cells joined by small amounts of cementing substances. |
| ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK1 or ERK2 (MAPKs), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade may involve 4 different kinases, as it can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor apoptotic signaling pathway | An apoptotic signaling pathway that starts with a ligand binding to, or being withdrawn from, a fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR). |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| forebrain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions). |
| inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized inner cell acquires specialized features of an auditory hair cell. |
| inner ear development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the inner ear over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| lens fiber cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a lens fiber cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Cell development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a lens fiber cell fate. A lens fiber cell is any of the elongated, tightly packed cells that make up the bulk of the mature lens in a camera-type eye. |
| lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye | The process in which the anatomical structures of the lens are generated and organized. The lens is a transparent structure in the eye through which light is focused onto the retina. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus. |
| MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tiers: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| mitotic nuclear division | A mitotic cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell. |
| morphogenesis of an epithelium | The process in which the anatomical structures of epithelia are generated and organized. An epithelium consists of closely packed cells arranged in one or more layers, that covers the outer surfaces of the body or lines any internal cavity or tube. |
| negative regulation of astrocyte differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of astrocyte differentiation. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of developmental growth | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of developmental growth. |
| negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of epithelial cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of auditory hair cell differentiation. |
| negative regulation of mitotic nuclear division | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of mitosis. Mitosis is the division of the eukaryotic cell nucleus to produce two daughter nuclei that, usually, contain the identical chromosome complement to their mother. |
| negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of smoothened signaling. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| neuroepithelial cell differentiation | The process in which epiblast cells acquire specialized features of neuroepithelial cells. |
| neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a neuron, the basic cellular unit of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. |
| oligodendrocyte development | The process aimed at the progression of an oligodendrocyte over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons in the central nervous system. |
| p38MAPK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a p38 MAPK, a MAPKK and a MAP3K. The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of bone mineralization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of bone mineralization. |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cell proliferation in bone marrow | A process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell proliferation in the bone marrow. |
| positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of endothelial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade by fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands resulting in an increase in the rate or frequency of a MAPKKK cascade. |
| positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death of neurons by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of phospholipase activity | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipase activity, the hydrolysis of a phospholipid. |
| positive regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| post-anal tail morphogenesis | The process in which a post-anal tail is generated and organized. A post-anal tail is a muscular region of the body that extends posterior to the anus. The post-anal tail may aid locomotion and balance. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein ubiquitination | The process in which one or more ubiquitin groups are added to a protein. |
| regulation of bone remodeling | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of bone remodeling, the processes of bone formation and resorption that combine to maintain skeletal integrity. |
| regulation of collagen metabolic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the metabolism of collagen, any of a group of fibrous proteins of very high tensile strength that form the main component of connective tissue in animals. |
| regulation of ossification | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of ossification, the formation of bone or of a bony substance or the conversion of fibrous tissue or of cartilage into bone or a bony substance. |
| regulation of osteoclast differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoclast differentiation. |
| response to axon injury | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an axon injury stimulus. |
| response to sodium phosphate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a sodium phosphate stimulus. |
| somatic stem cell population maintenance | Any process by which an organism retains a population of somatic stem cells, undifferentiated cells in the embryo or adult which can undergo unlimited division and give rise to cell types of the body other than those of the germ-line. |
| substantia nigra development | The progression of the substantia nigra over time from its initial formation until its mature state. The substantia nigra is the layer of gray substance that separates the posterior parts of the cerebral peduncles (tegmentum mesencephali) from the anterior parts; it normally includes a posterior compact part with many pigmented cells (pars compacta) and an anterior reticular part whose cells contain little pigment (pars reticularis). |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
113 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q28889 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P21804 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9PUF6 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q08156 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QHL3 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18461 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18460 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07407 | htl | Fibroblast growth factor receptor homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P36888 | FLT3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16234 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09619 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35916 | FLT4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35968 | KDR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P17948 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10721 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P22455 | FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07949 | RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35590 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02763 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P11362 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P21802 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P22607 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q91V87 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z138 | Ror2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P97793 | Alk | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60805 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00993 | Axl | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55144 | Tyro3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70424 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61527 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61526 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01279 | Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01887 | Ryk | Tyrosine-protein kinase RYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q2HWD6 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q7TQM3 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17833 | old-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor old-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q19238 | F09A5.2 | Putative tyrosine-protein kinase F09A5.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P34892 | kin-16 | Receptor-like tyrosine-protein kinase kin-16 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5ED65 | ver-1 | Protein ver-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q10656 | egl-15 | Myoblast growth factor receptor egl-15 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| O64556 | At2g19230 | Putative leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g19230 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGI2 | At1g67720 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67720 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q6XAT2 | ERL2 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase ERL2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q3E991 | PRK6 | Pollen receptor-like kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LFG1 | At3g53590 | Putative leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At3g53590 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q0WR59 | At5g10020 | Probable inactive receptor kinase At5g10020 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94C77 | At4g34220 | Receptor protein kinase-like protein At4g34220 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94AG2 | SERK1 | Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8LPS5 | SERK5 | Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9XIC7 | SERK2 | Somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGX1 | At5g65240 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At5g65240 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGJ1 | At1g74360 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g74360 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q93ZS4 | NIK3 | Protein NSP-INTERACTING KINASE 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FXF2 | RKF1 | Probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase RFK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P43298 | TMK1 | Receptor protein kinase TMK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LRP3 | At3g17420 | Probable receptor-like protein kinase At3g17420 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| C0LGQ4 | MDIS2 | Protein MALE DISCOVERER 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8AXB3 | kdrl | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor kdr-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5GIT4 | kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73791 | tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90Z00 | fgfr1a | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JG38 | fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90413 | fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9DE49 | pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JFR5 | kita | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kita | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5MD89 | flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8X3 | fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MVVPACVLVF | CVAVVAGATS | EPPGPEQRVV | RRAAEVPGPE | PSQQEQVAFG | SGDTVELSCH |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PPGGAPTGPT | VWAKDGTGLV | ASHRILVGPQ | RLQVLNASHE | DAGVYSCQHR | LTRRVLCHFS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VRVTDAPSSG | DDEDGEDVAE | DTGAPYWTRP | ERMDKKLLAV | PAANTVRFRC | PAAGNPTPSI |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SWLKNGKEFR | GEHRIGGIKL | RHQQWSLVME | SVVPSDRGNY | TCVVENKFGS | IRQTYTLDVL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ERSPHRPILQ | AGLPANQTAI | LGSDVEFHCK | VYSDAQPHIQ | WLKHVEVNGS | KVGPDGTPYV |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TVLKTAGANT | TDKELEVLSL | HNVTFEDAGE | YTCLAGNSIG | FSHHSAWLVV | LPAEEELMET |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DEAGSVYAGV | LSYGVVFFLF | ILVVAAVILC | RLRSPPKKGL | GSPTVHKVSR | FPLKRQVSLE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SNSSMNSNTP | LVRIARLSSG | EGPVLANVSE | LELPADPKWE | LSRTRLTLGK | PLGEGCFGQV |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VMAEAIGIDK | DRTAKPVTVA | VKMLKDDATD | KDLSDLVSEM | EMMKMIGKHK | NIINLLGACT |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| QGGPLYVLVE | YAAKGNLREF | LRARRPPGMD | YSFDACRLPE | EQLTCKDLVS | CAYQVARGME |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| YLASQKCIHR | DLAARNVLVT | EDNVMKIADF | GLARDVHNLD | YYKKTTNGRL | PVKWMAPEAL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| FDRVYTHQSD | VWSFGVLLWE | IFTPGGPSPY | PGIPVEELFK | LLKEGHRMDK | PASCTHDLYM |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| IMRECWHAVP | SQRPTFKQLV | EDLDRILTVT | STDEYLDLSV | PFEQYSPGGQ | DTPSSSSSGD |
| 790 | 800 | ||||
| DSVFTHDLLP | PGPPSNGGPR | T |