Q61458
Gene name |
Ccnh |
Protein name |
Cyclin-H |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:66671 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
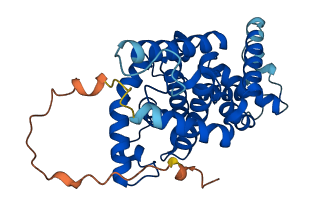
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q61458
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q61458-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
7 variants for Q61458
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389223394 | 95 | S>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389293435 | 194 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs235911340 | 268 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs235943668 | 289 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389291213 | 293 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389291212 | 299 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs246305315 | 320 | V>I | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q61458
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| CAK-ERCC2 complex | A protein complex formed by the association of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase activating kinase (CAK) holoenzyme complex with ERCC2. |
| cyclin-dependent protein kinase activating kinase holoenzyme complex | A cyclin-dependent kinase activating kinase complex capable of activating cyclin-dependent kinases by threonine phosphorylation, thus regulating cell cycle progression. consists of a kinase, cyclin and optional assembly factors, in human CDK7, CCNH and MNAT1. CAK activity is itself regulated throughout the cell cycle by T-loop phosphorylation of its kinase component (CDK7 in human). Phosphorylation of serine residues during mitosis inactivates the enzyme. Also capable of CAK phosphorylating the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II and other transcription activating proteins, as part of the general transcription factor TFIIH. |
| male germ cell nucleus | The nucleus of a male germ cell, a reproductive cell in males. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| transcription factor TFIIH core complex | The 7 subunit core of TFIIH that is a part of either the general transcription factor holo-TFIIH or the nucleotide-excision repair factor 3 complex. In S. cerevisiae/humans the complex is composed of: Ssl2/XPB, Tfb1/p62, Tfb2/p52, Ssl1/p44, Tfb4/p34, Tfb5/p8 and Rad3/XPD. |
| transcription factor TFIIH holo complex | A complex that is capable of kinase activity directed towards the C-terminal Domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II and is essential for initiation at RNA polymerase II promoters in vitro. It is composed of the core TFIIH complex and the TFIIK complex. |
| transcription factor TFIIK complex | A transcription factor complex that forms part of the holo TFIIH complex. In Saccharomyces/human, TFIIK contains Ccl1p/Cyclin H, Tfb3p/MAT1 and Kin28p/CDK7. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Cyclin-dependent catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity | Modulates the activity of a cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase, enzymes of the protein kinase family that are regulated through association with cyclins and other proteins. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity | A general transcription initiation factor activity that contributes to transcription start site selection and transcription initiation of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II. The general transcription factors for RNA polymerase II include TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH and TATA-binding protein (TBP). In most species, RNA polymerase II transcribes all messenger RNAs (mRNAs), most untranslated regulatory RNAs, the majority of the snoRNAs, four of the five snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, and U5), and other small noncoding RNAs. For some small RNAs there is variability between species as to whether it is transcribed by RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. However there are also rare exceptions, such as Trypanosoma brucei, where RNA polymerase I transcribes certain mRNAs in addition to its normal role in rRNA transcription. |
8 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to an amino acid residue in the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Typically, this occurs during the transcription cycle and results in production of an RNA polymerase II enzyme where the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit is extensively phosphorylated, often referred to as hyperphosphorylated or the II(0) form. Specific types of phosphorylation within the CTD are usually associated with specific regions of genes, though there are exceptions. The phosphorylation state regulates the association of specific complexes such as the capping enzyme or 3'-RNA processing machinery to the elongating RNA polymerase complex. |
| protein stabilization | Any process involved in maintaining the structure and integrity of a protein and preventing it from degradation or aggregation. |
| regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity. |
| regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle | Any signalling pathway that modulates the activity of a cell cycle cyclin-dependent protein kinase to modulate the switch from G1 phase to S phase of the mitotic cell cycle. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| transcription by RNA polymerase II | The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II), originating at an RNA polymerase II promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). |
| transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter | A transcription initiation process that takes place at a RNA polymerase II gene promoter. Messenger RNAs (mRNA) genes, as well as some non-coding RNAs, are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3ZBL9 | CCNH | Cyclin-H | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P51946 | CCNH | Cyclin-H | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q62447 | Ccnc | Cyclin-C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9QWV9 | Ccnt1 | Cyclin-T1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O88874 | Ccnk | Cyclin-K | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9R1A0 | Ccnh | Cyclin-H | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MYHSSSQKRH | WTFASEEQLA | RLRADANRKF | KCKAVANGKV | LPNDPVFLEP | HEELTLCKYY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EKRLLEFCSV | FKPAMPRSVV | GTACMYFKRF | YLNNSVMEYH | PRIIMLTCAF | LACKVDEFNV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SSPQFVGNLR | ESPLGQERAL | EQILEYELLL | IQQLNFHLIV | HNPYRPFEGF | LIDIKTRYPM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LENPEILRKT | ADDFLSRIAL | TDAYLLYTPS | QIALTAILSS | ASRAGITMES | YLSESLMLKE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NRTCLSQLLD | IMKSMRNLVK | KYEPPRSDEV | AVLKQKLERC | HSSDLALNAV | TKKRKGYEDD |
| 310 | 320 | ||||
| DYVSKKPKQE | EEEWTDDDLV | DSL |