Q61194
Gene name |
Pik3c2a (Cpk) |
Protein name |
Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing subunit alpha |
Names |
PI3K-C2-alpha, PtdIns-3-kinase C2 subunit alpha, Cpk-m, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-C2-alpha, p170 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18704 |
EC number |
2.7.1.137: Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
Protein Class |
|
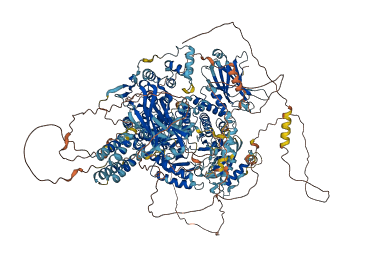
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
1268-1292 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
1043-1395 (Catalytic domain of Class II Phosphoinositide 3-kinase alpha) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

No variants for Q61194
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q61194 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q61194
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.1.137 | Phosphotransferases with an alcohol group as acceptor |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| clathrin-coated vesicle | A vesicle with a coat formed of clathrin connected to the membrane via one of the clathrin adaptor complexes. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex | A protein complex capable of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and containing subunits of any phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) enzyme. These complexes are divided in three classes (called I, II and III) that differ for their presence across taxonomic groups and for the type of their constituents. Catalytic subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enzymes are present in all 3 classes; regulatory subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enzymes are present in classes I and III; adaptor proteins have been observed in class II complexes and may be present in other classes too. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
| vesicle | Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol + ATP = a 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate + ADP + 2 H(+). |
| 1-phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4-phosphate + ATP = 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4-bisphosphate + ADP + 2 H(+). |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| clathrin binding | Binding to a clathrin heavy or light chain, the main components of the coat of coated vesicles and coated pits, and which also occurs in synaptic vesicles. |
| phosphatidylinositol binding | Binding to an inositol-containing glycerophospholipid, i.e. phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| phosphatidylinositol kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a phosphatidylinositol = ADP + a phosphatidylinositol phosphate. |
| phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate 5-kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4-bisphosphate + ATP = a 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate + ADP + 2 H(+). |
| phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate + ATP = a 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate + ADP + 2 H(+). |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an autophagosome. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of nourishment. |
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| macroautophagy | The major inducible pathway for the general turnover of cytoplasmic constituents in eukaryotic cells, it is also responsible for the degradation of active cytoplasmic enzymes and organelles during nutrient starvation. Macroautophagy involves the formation of double-membrane-bounded autophagosomes which enclose the cytoplasmic constituent targeted for degradation in a membrane-bounded structure. Autophagosomes then fuse with a lysosome (or vacuole) releasing single-membrane-bounded autophagic bodies that are then degraded within the lysosome (or vacuole). Some types of macroautophagy, e.g. pexophagy, mitophagy, involve selective targeting of the targets to be degraded. |
| negative regulation of zinc ion transmembrane transport | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of zinc ions (Zn2+) from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling | A series of reactions within the signal-receiving cell, mediated by the intracellular phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Many cell surface receptor linked signaling pathways signal through PI3K to regulate numerous cellular functions. |
| phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol phosphate. |
| phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate, a phosphatidylinositol monophosphate carrying the phosphate group at the 3-position. |
| phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling | The series of molecular signals in which a cell uses a phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling to convert a signal into a response. Phosphatidylinositols include phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| positive regulation of autophagy | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis. Cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis is the orderly movement of endothelial cells into the extracellular matrix in order to form new blood vessels contributing to the process of sprouting angiogenesis. |
10 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1X283 | SH3PXD2B | SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 2B | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q5TCZ1 | SH3PXD2A | SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 2A | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O00443 | PIK3C2A | Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing subunit alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| A2AAY5 | Sh3pxd2b | SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 2B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O89032 | Sh3pxd2a | SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 2A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BKC8 | Pi4kb | Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JHG7 | Pik3cg | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P42337 | Pik3ca | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BTI9 | Pik3cb | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit beta isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O35904 | Pik3cd | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit delta isoform | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAQISNNSEF | KQCSSSHPEP | IRTKDVNKAE | ALQMEAEALA | KLQKDRQMTD | SPRGFELSSS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TRQRTQGFNK | QDYDLMVFPE | LDSQKRAVDI | DVEKLTQAEL | EKILLDDNFE | TRKPPALPVT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PVLSPSFSTQ | LYLRPSGQRG | QWPPGLCGPS | TYTLPSTYPS | AYSKQATFQN | GFSPRMPTFP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| STESVYLRLP | GQSPYFSYPL | TPATPFHPQG | SLPVYRPLVS | PDMAKLFEKI | ASTSEFLKNG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KARTDLEIAN | SKASVCNLQI | SPKSEDINKF | DWLDLDPLSK | PKVDYVEVLE | HEEEKKDPVL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LAEDPWDAVL | LEERSPSCHL | ERKVNGKSLS | GATVTRSQSL | IIRTAQFTKA | QGQVSQKDPN |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| GTSSLPTGSS | LLQEFEVQND | EVAAFCQSIM | KLKTKFPYTD | HCTNPGYLLS | PVTVQRNMCG |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| ENASVKVSIE | IEGLQLPVTF | TCDVSSTVEI | IIMQALCWVH | DDLNQVDVGS | YILKVCGQEE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VLQNNHCLGS | HEHIQNCRKW | DTEIKLQLLT | LSAMCQNLAR | TAEDDEAPVD | LNKYLYQIEK |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| PYKEVMTRHP | VEELLDSYHY | QVELALQTEN | QHRAVDQVIK | AVRKICSALD | GVETPSVTEA |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| VKKLKRAVNL | PRNKSADVTS | LSGSDTRKNS | TKGSLNPENP | VQVSMDHLTT | AIYDLLRLHA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| NSSRCSTACP | RGSRNIKEAW | TATEQLQFTV | YAAHGISSNW | VSNYEKYYLI | CSLSHNGKDL |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| FKPIQSKKVG | TYKNFFYLIK | WDELIIFPIQ | ISQLPLESVL | HLTLFGVLNQ | SSGSSPDSNK |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| QRKGPEALGK | VSLTLFDFKR | FLTCGTKLLY | LWTSSHTNSI | PGAIPKKSYV | MERIVLQVDF |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| PSPAFDIIYT | SPQIDRNIIQ | QDKLETLESD | IKGKLLDIIH | RDSSFGLSKE | DKVFLWENRY |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| YCLKHPNCLP | KILASAPNWK | WANLAKTYSL | LHQWPPLCPL | AALELLDAKF | ADQEVRSLAV |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| SWMEAISDDE | LADLLPQFVQ | ALKYEIYLNS | SLVRFLLSRA | LGNIQIAHSL | YWLLKDALHD |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| THFGSRYEHV | LGALLSVGGK | GLREELSKQM | KLVQLLGGVA | EKVRQASGST | RQVVLQKSME |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| RVQSFFLRNK | CRLPLKPSLV | AKELNIKSCS | FFSSNAMPLK | VTMVNADPLG | EEINVMFKVG |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| EDLRQDMLAL | QMIKIMDKIW | LKEGLDLRMV | IFRCLSTGRD | RGMVELVPAS | DTLRKIQVEY |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| GVTGSFKDKP | LAEWLRKYNP | SEEEYEKASE | NFIYSCAGCC | VATYVLGICD | RHNDNIMLRS |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| TGHMFHIDFG | KFLGHAQMFG | SFKRDRAPFV | LTSDMAYVIN | GGEKPTIRFQ | LFVDLCCQAY |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| NLIRKQTNLF | LNLLSLMIPS | GLPELTSIQD | LKYVRDALQP | QTTDAEATIF | FTRLIESSLG |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| SIATKFNFFI | HNLAQLRFSG | LPSNDEPILS | FSPKTYSFRQ | DGRIKEVSVF | TYHKKYNPDK |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| HYIYVVRILR | EGHLEPSFVF | RTFDEFQELH | NKLSIIFPLW | KLPGFPNRMV | LGRTHIKDVA |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| AKRKIELNSY | LQSLMNASTD | VAECDLVCTF | FHPLLRDEKA | EGIARSAGAV | PFSPTLGQIG |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| GAVKLSVSYR | NGTLFIMVMH | IKDLVTEDGA | DPNPYVKTYL | LPDTHKTSKR | KTKISRKTRN |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | 1660 | 1670 | 1680 |
| PTFNEMLVYS | GYSKETLRQR | ELQLSVLSAE | SLRENFFLGG | ITLPLKDFNL | SKETVKWYQL |
| TAATYL |