Q60875
Gene name |
Arhgef2 (Kiaa0651, Lbcl1, Lfc) |
Protein name |
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 |
Names |
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor H1, GEF-H1, LBC'S first cousin, Lymphoid blast crisis-like 1, Oncogene LFC, Rhobin |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:16800 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
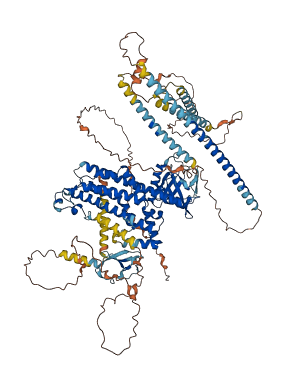
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q60875
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5WI4 | X-ray | 200 A | A/B/C | 139-164 | PDB |
| AF-Q60875-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
45 variants for Q60875
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388640077 | 8 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388634896 | 36 | Y>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640466 | 41 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388641308 | 49 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640516 | 91 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640140 | 94 | Q>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388634858 | 134 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640522 | 148 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388635708 | 200 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388634914 | 224 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388638137 | 235 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388639913 | 237 | K>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388643758 | 279 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388635712 | 313 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640497 | 369 | K>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388643809 | 377 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388643795 | 379 | H>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388638199 | 380 | G>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388638172 | 404 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388632358 | 432 | Q>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388635711 | 465 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388634906 | 502 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388629340 | 505 | Q>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640484 | 508 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3393371537 | 514 | T>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3393326581 | 516 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388634882 | 575 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388640115 | 601 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389584693 | 619 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388638154 | 649 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388638169 | 654 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388634824 | 675 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs32897383 | 676 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs32898156 | 679 | M>T | No | EVA | |
| rs242818936 | 679 | M>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388641266 | 739 | Q>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388637371 | 776 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388641248 | 778 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388629339 | 831 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3393362844 | 895 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3393117778 | 896 | F>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388629327 | 919 | R>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388641582 | 939 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388637822 | 948 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388643247 | 950 | V>A | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q60875
Functions
16 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bicellular tight junction | An occluding cell-cell junction that is composed of a branching network of sealing strands that completely encircles the apical end of each cell in an epithelial sheet; the outer leaflets of the two interacting plasma membranes are seen to be tightly apposed where sealing strands are present. Each sealing strand is composed of a long row of transmembrane adhesion proteins embedded in each of the two interacting plasma membranes. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| dendritic shaft | Cylindric portion of the dendrite, directly stemming from the perikaryon, and carrying the dendritic spines. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| podosome | An actin-rich adhesion structure characterized by formation upon cell substrate contact and localization at the substrate-attached part of the cell, contain an F-actin-rich core surrounded by a ring structure containing proteins such as vinculin and talin, and have a diameter of 0.5 mm. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic density, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane forming an electron dense disc. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
| spindle | The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart. |
| vesicle | Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity | Stimulates the exchange of GDP to GTP on a signaling GTPase, changing its conformation to its active form. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) act by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is more abundant in the cell under normal cellular physiological conditions. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| microtubule binding | Binding to a microtubule, a filament composed of tubulin monomers. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments. Includes processes that control the spatial distribution of actin filaments, such as organizing filaments into meshworks, bundles, or other structures, as by cross-linking. |
| asymmetric neuroblast division | The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a neuroblast into two daughter cells with different developmental potentials. |
| cell morphogenesis | The developmental process in which the size or shape of a cell is generated and organized. |
| cellular response to muramyl dipeptide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a muramyl dipeptide stimulus. Muramyl dipeptide is derived from peptidoglycan. |
| establishment of mitotic spindle orientation | A cell cycle process that sets the alignment of mitotic spindle relative to other cellular structures. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of microtubule depolymerization; prevention of depolymerization of a microtubule can result from binding by 'capping' at the plus end (e.g. by interaction with another cellular protein of structure) or by exposing microtubules to a stabilizing drug such as taxol. |
| negative regulation of neurogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neurogenesis, the generation of cells within the nervous system. |
| negative regulation of podosome assembly | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of podosome assembly. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-6 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-6 production. |
| positive regulation of neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron differentiation. |
| positive regulation of neuron migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of neuron migration. |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of tumor necrosis factor production. |
| regulation of Rho protein signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of Rho protein signal transduction. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O15085 | ARHGEF11 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NZN5 | ARHGEF12 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q92974 | ARHGEF2 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8R4H2 | Arhgef12 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9ES67 | Arhgef11 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSRIESLTRA | RIDRSKEQAT | KTREKEKMKE | AKDARYTNGH | LFTTISVSGM | TMCYACNKSI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TAKEALICPT | CNVTIHNRCK | DTLANCTKVK | QKQQKAALLR | NNTALQSVSL | RSKTTTRERP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TSAIYPSDSF | RQSLLGSRRG | LSSLSLAKSV | STTNIAGHFN | DESPLGLRQI | LSQSTDSLNM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RNRTLSVESL | IDEGVEVFYN | ELMSDFEMDE | KDFEADSWSL | AVDSSFLQQH | KKEVMKKQDV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IYELIQTELH | HVRTLKIMTR | LFRTGMLEEL | QMEPEVVQGL | FPCVDELSDI | HTRFLNQLLE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| RRRQALCPGS | TRNFVIHRLG | DLLISQFSGS | NAEQMRKTYS | EFCSRHTKAL | KLYKELYARD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KRFQQFIRKM | TRSAVLKRHG | VQECILLVTQ | RITKYPVLIN | RILQNSHGVE | EEYQDLASAL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GLVKELLSNV | DQDVHELEKE | ARLQEIYNRM | DPRAQTPVPG | KGPFGRDELL | RRKLIHEGCL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LWKTATGRFK | DVLLLLMTDV | LVFLQEKDQK | YIFTSLDKPS | VVSLQNLIVR | DIANQAKGMF |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LISSGPPEMY | EVHAASRDDR | TTWIRVIQQS | VRLCPSREDF | PLIETEDKAY | LRRIKTKLQQ |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KNQALVELLQ | KNVELFAEMV | HFQALKAGFV | GMPPPALPRG | LFRLESFESL | RGERLLKDAL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| REVEGLKDLL | LGPCVDLPMT | SREPALPLDS | DSGSCPGVTA | NGEARTFNGS | IELCRADSDS |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| SQKDRNGNQL | RSPQEEVLQP | LINLYGLLHG | LQAVVVQQER | LMEALFPEGP | ERWEKLSRAN |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SRDGEAGRAA | VASVTPEKQA | TELALLQRQH | TLLQEELRRC | QRLGEERATE | AGSLEARLRE |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| SEQARALLER | EAEEIRRQLA | ALGQNEPLPA | EAPWARRPLD | PRRRSLPAGD | ALYLSFNPPQ |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| PSRGHDRLDL | PVTVRSLHRP | FDDREAQELG | SPEDRLQDSS | DPDTGSEEEV | SSRLSPPHSP |
| 970 | 980 | ||||
| RDFTRMQDIP | EETESRDGEP | TASES |