Q60848
Gene name |
Hells |
Protein name |
Lymphocyte-specific helicase |
Names |
CD30L receptor, Lymphocyte activation antigen CD30, Proliferation-associated SNF2-like protein |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:15201 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
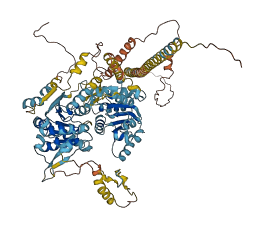
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q60848
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q60848-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
43 variants for Q60848
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs234655880 | 3 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs261920883 | 27 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389543404 | 42 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530867 | 70 | M>L | No | EVA | |
| rs252358692 | 93 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389538315 | 98 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530907 | 99 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs237574890 | 106 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs228554628 | 150 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs248788832 | 156 | I>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389550357 | 181 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389538281 | 197 | Q>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389547221 | 228 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530861 | 302 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs225234699 | 313 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3408840769 | 317 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530828 | 318 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389538304 | 325 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389538336 | 353 | L>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389516345 | 363 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530838 | 428 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389538286 | 448 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389539191 | 528 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs214483846 | 544 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3389484816 | 594 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3389533077 | 604 | F>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3389503587 | 608 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389516362 | 641 | I>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389493883 | 646 | T>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389484772 | 657 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530874 | 668 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389484795 | 679 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530293 | 687 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389503592 | 701 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530905 | 714 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389530286 | 723 | R>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389538284 | 729 | I>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3409164869 | 742 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs213521724 | 778 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs48707868 | 801 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs251082573 | 811 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs257457302 | 815 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389446254 | 822 | F>Y | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q60848
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromosome, centromeric region | The region of a chromosome that includes the centromeric DNA and associated proteins. In monocentric chromosomes, this region corresponds to a single area of the chromosome, whereas in holocentric chromosomes, it is evenly distributed along the chromosome. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| pericentric heterochromatin | Heterochromatin that is located adjacent to the CENP-A rich centromere 'central core' and characterized by methylated H3 histone at lysine 9 (H3K9me2/H3K9me3). |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity | An activity, driven by ATP hydrolysis, that modulates the contacts between histones and DNA, resulting in a change in chromosome architecture within the nucleosomal array, leading to chromatin remodeling. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| helicase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate, to drive the unwinding of a DNA or RNA helix. |
| hydrolase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a leukemia inhibitory factor stimulus. |
| DNA methylation | The covalent transfer of a methyl group to either N-6 of adenine or C-5 or N-4 of cytosine. |
| DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin assembly | Repression of transcription by methylation of DNA, leading to the formation of heterochromatin. |
| heterochromatin assembly | An epigenetic gene silencing mechanism in which chromatin is compacted into heterochromatin, resulting in a chromatin conformation refractory to transcription. This process starts with heterochromatin nucleation, its spreading, and ends with heterochromatin boundary formation. |
| kidney development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the kidney over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The kidney is an organ that filters the blood and/or excretes the end products of body metabolism in the form of urine. |
| lymphocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized precursor cell acquires specialized features of a lymphocyte. A lymphocyte is a leukocyte commonly found in the blood and lymph that has the characteristics of a large nucleus, a neutral staining cytoplasm, and prominent heterochromatin. |
| lymphocyte proliferation | The expansion of a lymphocyte population by cell division. |
| maintenance of DNA methylation | Any process involved in maintaining the methylation state of a nucleotide sequence. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| pericentric heterochromatin assembly | The compaction of chromatin located adjacent to the CENP-A rich centromere 'central core' and characterized by methylation of histone H3K9, into heterochromatin, resulting in the repression of transcription at pericentric DNA. |
| urogenital system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the urogenital system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3B7N1 | CHD1L | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q24368 | Iswi | Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain Iswi | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| O60264 | SMARCA5 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q86WJ1 | CHD1L | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P28370 | SMARCA1 | Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9NRZ9 | HELLS | Lymphoid-specific helicase | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9CXF7 | Chd1l | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q91ZW3 | Smarca5 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6PGB8 | Smarca1 | Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q7G8Y3 | Os01g0367900 | Probable chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| P41877 | isw-1 | Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain isw-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q8RWY3 | CHR11 | ISWI chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase CHR11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9XFH4 | DDM1 | ATP-dependent DNA helicase DDM1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAEQTEPAVI | TPAMLEEEEQ | LEAAGLEKER | KMLEEAQKSW | DRESTEIRYR | RLQHLLEKSN |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IYSKFLLTKM | EQQQLEEQKK | KEKLEKKKRS | LKLTEGKSLV | DGNGEKPVMK | KKRGREDESY |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NISEVMSKEE | ILSVAKKHKD | NEDESSSTTS | LCVEDIQKNK | DSNSMIKDRL | SQTVRQNSKF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| FFDPVRKCNG | QPVPFQQPKH | FTGGVMRWYQ | VEGMEWLRML | WENGINGILA | DEMGLGKTVQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CIATIALMIQ | RGVPGPFLVC | GPLSTLPNWM | AEFKRFTPEI | PTLLYHGTRE | DRRKLVKNIH |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KRQGTLQIHP | VVVTSFEIAM | RDQNALQHCY | WKYLIVDEGH | RIKNMKCRLI | RELKRFNADN |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KLLLTGTPLQ | NNLSELWSLL | NFLLPDVFDD | LKSFESWFDI | TSLSETAEDI | IAKEREQNVL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| HMLHQILTPF | LLRRLKSDVA | LEVPPKREVV | VYAPLCNKQE | IFYTAIVNRT | IANMFGSCEK |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| ETVELSPTGR | PKRRSRKSIN | YSELDQFPSE | LEKLISQIQP | EVNRERTVVE | GNIPIESEVN |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LKLRNIMMLL | RKCCNHPYMI | EYPIDPVTQE | FKIDEELVTN | SGKFLILDRM | LPELKKRGHK |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| VLVFSQMTSM | LDILMDYCHL | RNFIFSRLDG | SMSYSEREKN | IYSFNTDPDV | FLFLVSTRAG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| GLGINLTAAD | TVIIYDSDWN | PQSDLQAQDR | CHRIGQTKPV | VVYRLVTANT | IDQKIVERAA |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| AKRKLEKLII | HKNHFKGGQS | GLSQSKNFLD | AKELMELLKS | RDYEREVKGS | REKVISDEDL |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | ||
| ELLLDRSDLI | DQMKASRPIK | GKTGIFKILE | NSEDSSAECL | F |