Q5ZJJ5
Gene name |
AKTIP (FTS, RCJMB04_17k13) |
Protein name |
AKT-interacting protein |
Names |
Fused toes protein homolog |
Species |
Gallus gallus (Chicken) |
KEGG Pathway |
gga:415720 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
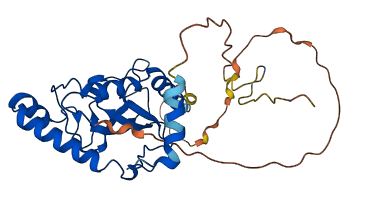
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q5ZJJ5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q5ZJJ5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q5ZJJ5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q5ZJJ5 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q5ZJJ5
1 regional properties for Q5ZJJ5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 | 74 - 222 | IPR000608 |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| FHF complex | A protein complex that is composed of AKTIP/FTS, FAM160A2/p107FHIP, and one or more members of the Hook family of proteins, HOOK1, HOOK2, and HOOK3. The complex is thought to promote vesicle trafficking and/or fusion, and associates with the homotypic vesicular sorting complex (the HOPS complex). |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity | Isoenergetic transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-ubiquitin + Y -> Y-ubiquitin + X, where both the X-ubiquitin and Y-ubiquitin linkages are thioester bonds between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and a sulfhydryl side group of a cysteine residue. |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| early endosome to late endosome transport | The directed movement of substances, in membrane-bounded vesicles, from the early sorting endosomes to the late sorting endosomes; transport occurs along microtubules and can be experimentally blocked with microtubule-depolymerizing drugs. |
| endosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of endosomes. |
| endosome to lysosome transport | The directed movement of substances from endosomes to lysosomes. |
| lysosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a lysosome. A lysosome is a cytoplasmic, membrane-bounded organelle that is found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q7K4V4 | CG46338 | Protein crossbronx | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P25867 | eff | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-17 kDa | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q9H8T0 | AKTIP | AKT-interacting protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q64362 | Aktip | AKT-interacting protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5FVH4 | Aktip | AKT-interacting protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35129 | let-70 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9SLE4 | UBC29 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 29 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C8X7 | UBC31 | Probable ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 31 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNPFWSMSAA | SGRKRPEADE | KTLSGELRTS | PPRASAKKQL | PSVPKNAVPV | TKPASPAMSS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QSTNGTHASY | GPFYLEYSLL | AEFTLVVKQK | LPGVYVQPSY | RSALMWFGVI | FIRHGLYQDG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VFKFTVYIPD | NYPDGDCPRL | VFDLPVFHPL | VDPLSGELDV | KRAFAKWRRN | HNHIWQVLMY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ARRVFYKIDT | TSPLNPEAAV | LYEKDIQLFK | SKVVDSVKLC | SSHLFDQPKI | EDPYAIVFSP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | |
| WNPAIHDEAR | EKMLTQKKKP | EDQHCKSMHV | SGLSWVKPGS | VQPFSKEEKT | MPT |