Q5Y4Y6
Gene name |
Gsdma3 |
Protein name |
Gasdermin-A3 |
Names |
Gasdermin-3 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:450219 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
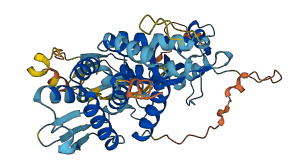
Descriptions
GSDMA3 is a member of the gasdermin family, which plays a role in pyroptosis, a form of cell death involved in immunity and diseases. It contains a gasdermin-N domain that can bind lipids and disrupt membranes, leading to cell lysis. GSDMA3 has a two-domain architecture with an autoinhibited state. The gasdermin-N domain is inhibited by the gasdermin-C domain, preventing unintended cell death. Mutations or cleavage by inflammatory caspases can release the gasdermin-N domain from autoinhibition, enabling it to induce pyroptosis by forming pores in cell membranes. Mutations in GSDMA3 are linked to skin and hair disorders in mice, and its mechanism of action provides insights into potential treatments for inflammation-related diseases.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-284 (GSDMA3-N domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Mutagenesis experiment, Split protein assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

3 structures for Q5Y4Y6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5B5R | X-ray | 190 A | A | 1-464 | PDB |
| 6CB8 | EM | 380 A | A | 1-262 | PDB |
| AF-Q5Y4Y6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
15 variants for Q5Y4Y6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs27059467 | 55 | R>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs27059466 | 88 | Q>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs259329858 | 142 | N>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs217001761 | 195 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs251612558 | 214 | F>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs265676256 | 237 | R>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs259765251 | 253 | E>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs584606067 | 268 | K>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs260508600 | 353 | T>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs27059447 | 382 | Q>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs27059446 | 387 | D>E | No | Ensembl | |
| rs241335410 | 429 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs578621326 | 431 | D>N | No | Ensembl | |
| rs585587845 | 447 | L>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs220354528 | 449 | H>Q | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q5Y4Y6
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| mitochondrial membrane | Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cardiolipin binding | Binding to cardiolipin. |
| phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 4' and 5' positions. |
| phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 4' position. |
| phosphatidylserine binding | Binding to phosphatidylserine, a class of glycophospholipids in which a phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of L-serine. |
| phospholipid binding | Binding to a phospholipid, a class of lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
| wide pore channel activity | Enables the transport of a solute across a membrane via a large pore, un-gated channel. Examples include gap junctions, which transport substances from one cell to another; and porins which transport substances in and out of bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| avascular cornea development in camera-type eye | The progression of an avascular cornea over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Corneal avascularity (the absence of blood vessels in the cornea) is required for optical clarity and optimal vision. Avascular corneas are present in most animals, except Manatees. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| hair cycle | The cyclical phases of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), quiescence (telogen), and shedding (exogen) in the life of a hair; one of the collection or mass of filaments growing from the skin of an animal, and forming a covering for a part of the head or for any part or the whole of the body. |
| hair follicle development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the hair follicle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A hair follicle is a tube-like opening in the epidermis where the hair shaft develops and into which the sebaceous glands open. |
| hair follicle morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the hair follicle are generated and organized. |
| mammary gland development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the mammary gland over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The mammary gland is a large compound sebaceous gland that in female mammals is modified to secrete milk. Its development starts with the formation of the mammary line and ends as the mature gland cycles between nursing and weaning stages. |
| negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| negative regulation of timing of anagen | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of timing of anagen, the growth phase of the hair cycle. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| programmed cell death | A process which begins when a cell receives an internal or external signal and activates a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway). The process ends with the death of the cell. |
| protein complex oligomerization | The process of creating protein oligomers, compounds composed of a small number, usually between three and ten, of component monomers; protein oligomers may be composed of different or identical monomers. Oligomers may be formed by the polymerization of a number of monomers or the depolymerization of a large protein polymer. |
| pyroptosis | A caspase-1-dependent cell death subroutine that is associated with the generation of pyrogenic mediators such as IL-1beta and IL-18. |
| sebaceous gland cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized epidermal cell acquires the specialized features of a sebaceous gland cell. |
| skin development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skin over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skin is the external membranous integument of an animal. In vertebrates the skin generally consists of two layers, an outer nonsensitive and nonvascular epidermis (cuticle or skarfskin) composed of cells which are constantly growing and multiplying in the deeper, and being thrown off in the superficial layers, as well as an inner vascular dermis (cutis, corium or true skin) composed mostly of connective tissue. |
| somatic stem cell population maintenance | Any process by which an organism retains a population of somatic stem cells, undifferentiated cells in the embryo or adult which can undergo unlimited division and give rise to cell types of the body other than those of the germ-line. |
12 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P57764 | GSDMD | Gasdermin-D | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9BYG8 | GSDMC | Gasdermin-C | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96QA5 | GSDMA | Gasdermin-A | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8TAX9 | GSDMB | Gasdermin-B | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8CB12 | Gsdmc3 | Gasdermin-C3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q2KHK6 | Gsdmc2 | Gasdermin-C2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3TR54 | Gsdmc4 | Gasdermin-C4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99NB5 | Gsdmc | Gasdermin-C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9D8T2 | Gsdmd | Gasdermin-D | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9EST1 | Gsdma | Gasdermin-A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q32M21 | Gsdma2 | Gasdermin-A2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P85967 | Gsdmc | Gasdermin-C | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPVFEDVTRA | LVRELNPRGD | LTPLDSLIDF | KHFRPFCLVL | RKRKSTLFWG | ARYVRTDYTL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LDLLEPGSSP | SDLTDSGNFS | FKNMLDVQVQ | GLVEVPKTVK | VKGTAGLSQS | STLEVQTLSV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| APSALENLKK | ERKLSADHSF | LNEMRYHEKN | LYVVMEAVEA | KQEVTVEQTG | NANAIFSLPS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LALLGLQGSL | NNNKAVTIPK | GCVLAYRVRL | LRVFLFNLWD | IPYICNDSMQ | TFPKIRRVPC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SAFISPTQMI | SEEPEEEKLI | GEMHEDFKTL | KEEVQRETQE | VEKLSPVGRS | SLLTSLSHLL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GKKKELQDLE | QKLEGALDKG | QKVTLEALPK | DVLLSKDAMD | AILYFLGALT | ELTEEQLKIL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VKSLEKKILP | VQLKLVESTL | EQNFLQDKEG | VFPLQPDLLS | SLGEEELTLT | EALVGLSGLE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | ||
| VQRSGPQYAW | DPDTRHNLCA | LYAGLSLLHL | LSRKSNALTY | CALS |