Q5U820
Gene name |
CFTR (ABCC7) |
Protein name |
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
Names |
CFTR, ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 7, Channel conductance-controlling ATPase, cAMP-dependent chloride channel |
Species |
Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) |
KEGG Pathway |
cfa:492302 |
EC number |
5.6.1.6: Enzymes altering polypeptide conformation or assembly |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
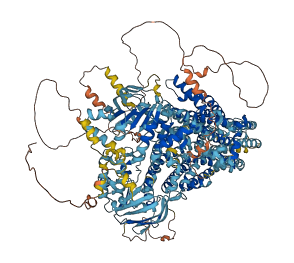
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q5U820
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q5U820-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q5U820
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q5U820 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q5U820
9 regional properties for Q5U820
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | ABC transporter-like, ATP-binding domain | 423 - 646 | IPR003439-1 |
| domain | ABC transporter-like, ATP-binding domain | 1213 - 1446 | IPR003439-2 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 450 - 623 | IPR003593-1 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 1239 - 1448 | IPR003593-2 |
| domain | ABC transporter type 1, transmembrane domain | 82 - 350 | IPR011527-1 |
| domain | ABC transporter type 1, transmembrane domain | 861 - 1156 | IPR011527-2 |
| conserved_site | ABC transporter-like, conserved site | 548 - 562 | IPR017871 |
| domain | CFTR regulator domain | 639 - 850 | IPR025837 |
| domain | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, ATP-binding cassette domain 1 | 389 - 670 | IPR047082 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 5.6.1.6 | Enzymes altering polypeptide conformation or assembly |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
13 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| chloride channel complex | An ion channel complex through which chloride ions pass. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| early endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an early endosome. |
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| recycling endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a recycling endosome. |
14 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ABC-type transporter activity | Primary active transporter characterized by two nucleotide-binding domains and two transmembrane domains. Uses the energy generated from ATP hydrolysis to drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity | Primary active transporter of a solute across a membrane, via the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate, to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. The transport protein may be transiently phosphorylated (P-type transporters), or not (ABC-type transporters and other families of transporters). Primary active transport occurs up the solute's concentration gradient and is driven by a primary energy source. |
| bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of bicarbonate from one side of a membrane to the other. Bicarbonate is the hydrogencarbonate ion, HCO3-. |
| chaperone binding | Binding to a chaperone protein, a class of proteins that bind to nascent or unfolded polypeptides and ensure correct folding or transport. |
| chloride channel activity | Enables the facilitated diffusion of a chloride (by an energy-independent process) involving passage through a transmembrane aqueous pore or channel without evidence for a carrier-mediated mechanism. |
| chloride channel inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents, or reduces the activity of a chloride channel. |
| chloride transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of chloride ions from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| intracellularly ATP-gated chloride channel activity | Enables passage of a chloride ion through a transmembrane channel that opens when ATP is bound by the channel complex or one of its constituent parts on the intracellular side of the plasma membrane. |
| isomerase activity | Catalysis of the geometric or structural changes within one molecule. Isomerase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 5. |
| PDZ domain binding | Binding to a PDZ domain of a protein, a domain found in diverse signaling proteins. |
| Sec61 translocon complex binding | Binding to a Sec61 translocon complex. |
21 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amelogenesis | The process whose specific outcome is the formation of tooth enamel, occurring in two stages: secretory stage and maturation stage. |
| bicarbonate transport | The directed movement of bicarbonate into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| cellular response to cAMP | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a cAMP (cyclic AMP, adenosine 3',5'-cyclophosphate) stimulus. |
| cellular response to forskolin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a forskolin stimulus. |
| chloride transmembrane transport | The process in which chloride is transported across a membrane. |
| cholesterol biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| cholesterol transport | The directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| establishment of localization in cell | Any process, occuring in a cell, that localizes a substance or cellular component. This may occur via movement, tethering or selective degradation. |
| intracellular pH elevation | Any process that increases the internal pH of a cell, measured by the concentration of the hydrogen ion. |
| membrane hyperpolarization | The process in which membrane potential increases with respect to its steady-state potential, usually from negative potential to a more negative potential. For example, during the repolarization phase of an action potential the membrane potential often becomes more negative or hyperpolarized before returning to the steady-state resting potential. |
| multicellular organismal water homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of water within a tissue, organ, or a multicellular organism. |
| positive regulation of cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel activity. |
| positive regulation of enamel mineralization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of enamel mineralization, the deposition of calcium salts in tooth enamel. |
| positive regulation of exocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of the regulated release of insulin that contributes to the response of a cell to glucose. |
| positive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of voltage-gated chloride channel activity. |
| response to endoplasmic reticulum stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stress acting at the endoplasmic reticulum. ER stress usually results from the accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the ER lumen. |
| sperm capacitation | A process required for sperm to reach fertilization competence. Sperm undergo an incompletely understood series of morphological and molecular maturational processes, termed capacitation, involving, among other processes, protein tyrosine phosphorylation and increased intracellular calcium. |
| transepithelial water transport | The directed movement of water (H2O) from one side of an epithelium to the other. |
| transmembrane transport | The process in which a solute is transported across a lipid bilayer, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| vesicle docking involved in exocytosis | The initial attachment of a vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the vesicle and the target membrane, that contributes to exocytosis. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2QLE5 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q6UR05 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P91660 | Rh5 | Probable multidrug resistance-associated protein lethal(2)03659 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q2QLA3 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Equus caballus (Horse) | PR |
| P13569 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P26361 | Cftr | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6PQZ2 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q00553 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MQRSPLEKAS | VLSKLFFSWT | RPILIKGYRQ | RLELSDIYQV | PSTDSADHLS | EKLEREWDRE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LASKKNPKLI | NALRRCFFWR | FAFYGILLYL | GEVTKAVQPL | LLGRIIASYD | PDNKQERSIA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IYLAIGLCLL | FIMRPLLLHP | AIFGLHHIGM | QIRIAMFSLI | YKKTLKLSSR | VLDKISIGQL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VSLLSNNLNK | FDEGLALAHF | VWIAPLQVTL | LMGLLWDLLQ | ASAFCGLAFL | IVLALVQAGL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GRMIMKYRDQ | RAGKINERLV | ITSEVIENIQ | SVKAYCWEEA | MEKIIENIRQ | TELKLTRKAA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| HVRYFNSSAF | FFSGFFVVSL | SVLPYALIKT | IILRKIFTTI | SFCIVLRMAV | TRQFPWAVQT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| WYDSLGAINK | IQDFLQKQEY | KTLEYNLTTT | EVMMENVTAF | WEEGFGELLE | KAKENSNDRK |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| ISNGDNSLFF | SNFSLLGTPV | LKDINFKIER | GQLLAVAGST | GAGKTSLLMM | IMGELEPSEG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| KIKHSGRISF | CSQFSWIMPG | TIKENIIFGV | SYDEYRYRSV | IKACQLEEDI | SKFAEKDNIV |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LGEGGVTLSG | GQRARISLAR | AVYKDADLYL | LDSPFGYLDV | LTEKEIFESC | VCKLMANKTR |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| ILVTSKMEHL | KKADKVLILH | EGSCYFYGTF | SELQSLRPDF | SSKLMGYDSF | DQFSPERRNS |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| IITETLRRFS | LEGDAAVPWN | ETKKQSFKQT | GEFGEKRKNS | ILNPINSIRK | FSIVQKTPLP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| MNGIEGESEV | PVERRLSLFP | DCEQGEAILP | RSNMINTGPT | LRRQRRQSVL | NLMTRSSVNQ |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| GQSIHRRTTA | STRKMSLAPQ | ANLTEMDIYS | RRLSQDSGLE | ISEEINEEDL | KECFFDDVES |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| IPPVTTWNTY | LRYITVHKNL | IFVLIWCLVI | FLAEVAVSLV | VLWILRNLSS | QDKGNSTQSV |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| NSSYAVIFTS | TSAYYIFYIY | VGVADTLLAL | GLFRGLPLVH | TLITVSKILH | HKMLHSVLQA |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| PMSTLNTLKA | GGILNRFSKD | IAILDDLLPL | TIFDFIQLLL | IVIGAVAVVS | VLQPYIFLAT |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| VPVIAAFIIL | RAYFLHTSQQ | LKQLESEGRS | PIFTHLLTSL | KGLWTLRAFG | RQPYFETLFH |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| KALNLHTANW | FLYLSTLRWF | QMRMEIIFVI | FFIAVTFISI | LTTGEGEGTV | GIILTLAMNI |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| MGTLQWAVNS | SIEVDSLMRS | VSRVFKFIDM | PTEESKPPTK | SFKPSKDAQL | SKVTITENRH |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| VREDDIWPSG | GQMTVKDLTA | KYIDGGNAIL | ENISFSISPG | QRVGLLGRTG | SGKSTLLSAL |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| LRLVNTEGEI | QIDGVSWDSI | PLQEWRRAFG | VIPQKVFIFS | GTFRKNLDPY | GQWNDQEIWK |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| VADEVGLRSV | IEQFPGKLDF | VLVDGGYVLS | HGHKQLMCLA | RSVLRKAKIL | LLDEPSAHLD |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| PITYQIIRRT | LKQAFADCTV | ILSEHRIEAM | LECQRFLVIE | DSRLRQFESI | QRLLSERSAF |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | ||
| RQAIGPPERP | GLLPHRLSSR | QRSPSRIAAL | KEETEDEVQD | TRL |