Q5RJI5
Gene name |
Brsk1 (Gm1100, Sadb) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK1 |
Names |
Brain-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 1, BR serine/threonine-protein kinase 1, Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAD-B |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:381979 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
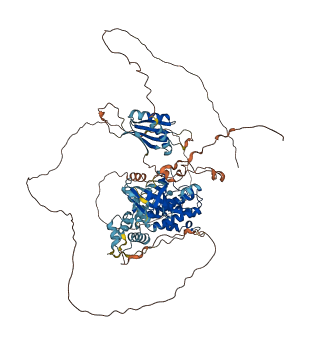
SAD-B is a serine/threonine kinase involved in neuronal development, cell cycle, and energy metabolism. It is highly expressed in the brain and plays a role in axonal arborization, nerve terminal maturation, and neurotransmitter release. SAD-B contains an AIS near the KA1 domain that regulates its activity. This sequence is flexible and solvent-accessible, allowing it to interact with the kinase domain (KD) and ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain to inhibit SAD-B activity. The crystal structure of the mouse SAD-B AIS-KA1 fragment reveals that the AIS is highly flexible in its isolated state, suggesting its readiness to bind to the KD-UBA junction for autoinhibition. Furthermore, the biochemical experiments demonstrate that the AIS of SAD-B non-competitively inhibits the kinase activity of SAD-B, similar to the autoinhibition observed in SAD-A, indicating a conserved mechanism between these kinases.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
34-356 (KD-UBA domains) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
Structural analysis, Split protein assay |
Accessory elements
173-195 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
34-285 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q5RJI5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5IRI | X-ray | 280 A | A/B | 592-719 | PDB |
| AF-Q5RJI5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
30 variants for Q5RJI5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388871397 | 57 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388871446 | 130 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388837984 | 147 | C>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388871436 | 206 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3397575330 | 260 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388881477 | 265 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388859073 | 266 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388859073 | 266 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388876580 | 288 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388876496 | 303 | R>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388859080 | 315 | L>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388868278 | 331 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388874094 | 333 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388867414 | 336 | H>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388876597 | 386 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388875356 | 391 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388867408 | 397 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388876534 | 397 | R>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3388876553 | 432 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388871603 | 434 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388876463 | 555 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388875353 | 562 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388871462 | 598 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388868194 | 622 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388859034 | 647 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388859034 | 647 | E>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3397197597 | 673 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3397604704 | 674 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388868213 | 728 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3397574515 | 748 | P>A | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q5RJI5
6 regional properties for Q5RJI5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Tyrosine-specific protein phosphatase, PTPase domain | 243 - 517 | IPR000242 |
| domain | Tyrosine-specific protein phosphatases domain | 430 - 506 | IPR000387 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 2 - 100 | IPR000980-1 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 108 - 213 | IPR000980-2 |
| domain | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase, catalytic | 408 - 514 | IPR003595 |
| active_site | Protein-tyrosine phosphatase, active site | 451 - 461 | IPR016130 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchoring junction | A cell junction that mechanically attaches a cell (and its cytoskeleton) to neighboring cells or to the extracellular matrix. |
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| distal axon | That part of an axon close to and including the growth cone or the axon terminus. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| presynaptic active zone | A specialized region of the plasma membrane and cell cortex of a presynaptic neuron; encompasses a region of the plasma membrane where synaptic vesicles dock and fuse, and a specialized cortical cytoskeletal matrix. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| gamma-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein gamma-tubulin. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| molecular function inhibitor activity | A molecular function regulator that inhibits or decreases the activity of its target via non-covalent binding that does not result in covalent modification to the target. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + tau-protein = ADP + O-phospho-tau-protein. |
20 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| associative learning | Learning by associating a stimulus (the cause) with a particular outcome (the effect). |
| axonogenesis | De novo generation of a long process of a neuron, including the terminal branched region. Refers to the morphogenesis or creation of shape or form of the developing axon, which carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells. |
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| cellular response to glucose starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of glucose. |
| centrosome duplication | The replication of a centrosome, a structure comprised of a pair of centrioles and peri-centriolar material from which a microtubule spindle apparatus is organized. |
| establishment of cell polarity | The specification and formation of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle | The mitotic cell cycle transition by which a cell in G2 commits to M phase. The process begins when the kinase activity of M cyclin/CDK complex reaches a threshold high enough for the cell cycle to proceed. This is accomplished by activating a positive feedback loop that results in the accumulation of unphosphorylated and active M cyclin/CDK complex. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins and contributes to the establishment of planar polarity. |
| mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling | A mitotic cell cycle checkpoint that detects and negatively regulates progression through the G2/M transition of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. |
| neuron differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a neuron. |
| neuron projection morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites. |
| neurotransmitter secretion | The regulated release of neurotransmitter from the presynapse into the synaptic cleft via calcium-regulated exocytosis during synaptic transmission. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron. |
| regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| regulation of synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| synaptic vesicle cycle | A biological process in which synaptic vesicles are loaded with neurotransmitters, move to the active zone, exocytose and are then recycled via endocytosis, ultimately leading to reloading with neurotransmitters. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8IWQ3 | BRSK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8TDC3 | BRSK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O35280 | Chek1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q69Z98 | Brsk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q61846 | Melk | Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O54863 | Tssk2 | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61241 | Tssk1b | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C0X8 | Sperm motility kinase X | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR | |
| A0AUV4 | Gm7168 | Sperm motility kinase Y | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C0N0 | Gm4922 | Sperm motility kinase Z | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q641K5 | Nuak1 | NUAK family SNF1-like kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5EG47 | Prkaa1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BRK8 | Prkaa2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A2KF29 | Smoktcr | Sperm motility kinase Tcr mutant form | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| D3ZML2 | Brsk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| B2DD29 | Brsk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q19469 | sad-1 | Serine/threonine kinase SAD-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSGSKEGGG | GSPAYHLPHP | HPHPPQHAQY | VGPYRLEKTL | GKGQTGLVKL | GVHCITGQKV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AVKIVNREKL | SESVLMKVER | EIAILKLIEH | PHVLKLHDVY | ENKKYLYLVL | EHVSGGELFD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| YLVKKGRLTP | KEARKFFRQI | VSALDFCHSY | SICHRDLKPE | NLLLDEKNNI | RIADFGMASL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| QVGDSLLETS | CGSPHYACPE | VIKGEKYDGR | RADMWSCGVI | LFALLVGALP | FDDDNLRQLL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EKVKRGVFHM | PHFIPPDCQS | LLRGMIEVEP | EKRLSLEQIQ | KHPWYLGGKH | EPDPCLEPAP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GRRVAMRSLP | SNGELDPDVL | ESMASLGCFR | DRERLHRELR | SEEENQEKMI | YYLLLDRKER |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| YPSCEDQDLP | PRNDVDPPRK | RVDSPMLSRH | GKRRPERKSM | EVLSITDAGS | GGSPVPTRRA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LEMAQHSQRS | RSVSGASTGL | SSSPLSSPRS | PVFSFSPEPG | AGDEARGGGS | PTSKTQTLPS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RGPRGGGAGE | QPPPPSARST | PLPGPPGSPR | SSGGTPLHSP | LHTPRASPTG | TPGTTPPPSP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| GGGVGGAAWR | SRLNSIRNSF | LGSPRFHRRK | MQVPTAEEMS | SLTPESSPEL | AKRSWFGNFI |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| SLDKEEQIFL | VLKDKPLSSI | KADIVHAFLS | IPSLSHSVLS | QTSFRAEYKA | SGGPSVFQKP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| VRFQVDISSS | EGPEPSPRRD | GSSGGGIYSV | TFTLISGPSR | RFKRVVETIQ | AQLLSTHDQP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | |
| SVQALADEKN | GAQTRPAGTP | PRSLQPPPGR | SDPDLSSSPR | RGPPKDKKLL | ATNGTPLP |