Q5RB23
Gene name |
JAK2 |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 |
Names |
Janus kinase 2, JAK-2 |
Species |
Pongo abelii (Sumatran orangutan) (Pongo pygmaeus abelii) |
KEGG Pathway |
pon:100172517 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
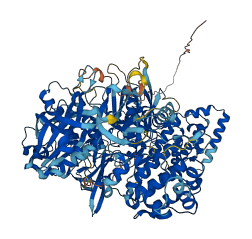
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
849-1126 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
698-717 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
545-809 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
993-1019 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
849-1126 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q5RB23
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q5RB23-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q5RB23
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q5RB23 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q5RB23
19 regional properties for Q5RB23
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | FERM domain | 37 - 380 | IPR000299 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 545 - 809 | IPR000719-1 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 849 - 1126 | IPR000719-2 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 397 - 487 | IPR000980 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 546 - 805 | IPR001245-1 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 849 - 1120 | IPR001245-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 972 - 984 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 855 - 883 | IPR017441 |
| domain | FERM central domain | 152 - 261 | IPR019748 |
| domain | Band 4.1 domain | 33 - 270 | IPR019749 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 545 - 805 | IPR020635-1 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 849 - 1123 | IPR020635-2 |
| domain | Janus kinase 2, pseudokinase domain | 545 - 806 | IPR035588 |
| domain | Janus kinase 2, catalytic domain | 844 - 1127 | IPR035589 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2, SH2 domain | 386 - 482 | IPR035860 |
| domain | JAK2, FERM domain C-lobe | 266 - 386 | IPR037838 |
| domain | JAK, FERM F2 lobe domain | 143 - 261 | IPR041046 |
| domain | FERM F1 lobe ubiquitin-like domain | 40 - 134 | IPR041155 |
| domain | JAK1-3/TYK2, pleckstrin homology-like domain | 302 - 381 | IPR041381 |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| endomembrane system | A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| heme binding | Binding to a heme, a compound composed of iron complexed in a porphyrin (tetrapyrrole) ring. |
| histone binding | Binding to a histone, any of a group of water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic or archaeal chromosomes. They are involved in the condensation and coiling of chromosomes during cell division and have also been implicated in gene regulation and DNA replication. They may be chemically modified (methylated, acetlyated and others) to regulate gene transcription. |
| histone kinase activity (H3-Y41 specific) | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group to the tyrosine-41 residue of histone H3. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of Janus kinase activity | The process of introducing a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a JAK (Janus Activated Kinase) protein, thereby activating it. |
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| chromatin organization | The assembly or remodeling of chromatin composed of DNA complexed with histones, other associated proteins, and sometimes RNA. |
| cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a cytokine to a receptor on the surface of a cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| erythrocyte differentiation | The process in which a myeloid precursor cell acquires specializes features of an erythrocyte. |
| growth hormone receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | The process in which STAT proteins (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) are activated by members of the JAK (janus activated kinase) family of tyrosine kinases, following the binding of physiological ligands to the growth hormone receptor. Once activated, STATs dimerize and translocate to the nucleus and modulate the expression of target genes. |
| histone H3-Y41 phosphorylation | OBSOLETE. The modification of histone H3 by the addition of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue at position 41 of the histone. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGMACLTMTE | MEGTSTSSIY | QNGDISGNAN | SMKQIDPVLL | VYLYHSLGKS | EADYLTFPSG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EYVAEEICIA | ASKACGITPV | YHNMFALMSE | TERIWYPPNH | VFHIDESTRH | NVLYRIRFYF |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PRWYCSGSNR | AYRHGISRGA | EAPLLDDFVM | SYLFAQWRHD | FVHGWIKVPV | THETQEECLG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| MAVLDMMRIA | KENDQTPLAI | YNSISYKTFL | PKCIRAKIQD | YHILTRKRIR | YRFRRFIQQF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SQCKATARNL | KLKYLINLET | LQSAFYTEKF | EVKEPGSGPS | GEEIFATIII | TGNGGIQWSR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GKHKESETLT | EQDLQLYCDF | PNIIDVSIKQ | ANQEGSNESR | VVTIHKQDGK | NLEIELSSLR |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EALSFVSLID | GYYRLTADAH | HYLCKEVAPP | TVLENIQSNC | HGPISMDFAI | SKLKKAGNQT |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GLYVLRCSPK | DFNKYFLTFA | VERENVIEYK | HCLITKNENE | EYNLSGTKKN | FSSLKDLLNC |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| YQMETVRSDN | IIFQFTKCCP | PKPKDKSNLL | VFRTNGVSDV | PTSPTLQRPT | HMNQMVFHKI |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| RNEDLIFNES | LGQGTFTKIF | KGVRREVGDY | GQLHETEVLL | KVLDKAHRNY | SESFFEAASM |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| MSKLSHKHLV | LNYGVCVCGD | ENILVQEFVK | FGSLDTYLKK | NKNCINILWK | LEVAKQLAWA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| MHFLEENTLI | HGNVCAKNIL | LIREEDRKTG | NPPFIKLSDP | GISITVLPKD | ILQERIPWVP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| PECIENPKNL | NLATDKWSFG | TTLWEICSGG | DKPLSALDSQ | RKLQFYEDRH | QLPAPKWAEL |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| ANLINNCMDY | EPDFRPSFRA | IIRDLNSLFT | PDYELLTEND | MLPNMRIGAL | GFSGAFEDRD |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| PTQFEERHLK | FLQQLGKGNF | GSVEMCRYDP | LQDNTGEVVA | VKKLQHSTEE | HLRDFEREIE |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| ILKSLQHDNI | VKYKGVCYSA | GRRNLKLIME | YLPYGSLRDY | LQKHKERIDH | KKLLQYTSQI |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| CKGMEYLGTK | RYIHRDLATR | NILVENENRV | KIGDFGLTKV | LPQDKEYYKV | KEPGESPIFW |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| YAPESLTESK | FSVASDVWSF | GVVLYELFTY | IEKSKSPPAE | FMRMIGNDKQ | GQMIVFHLIE |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | |
| LLKNNGRLPR | PDGCPDEIYM | IMTECWNNNV | NQRPSFRDLA | LRVDQIRDNM | AG |