Q5R411
Gene name |
Pacsin1 |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 |
Names |
|
Species |
Pongo abelii (Sumatran orangutan) (Pongo pygmaeus abelii) |
KEGG Pathway |
pon:100172814 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
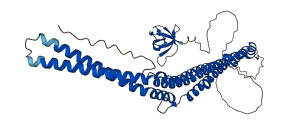
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
19-276 (F-BAR domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q5R411
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q5R411-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q5R411
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q5R411 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q5R411
Functions
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon terminus | Terminal inflated portion of the axon, containing the specialized apparatus necessary to release neurotransmitters. The axon terminus is considered to be the whole region of thickening and the terminal button is a specialized region of it. |
| COPI-coated vesicle | A vesicle with a coat formed of the COPI coat complex proteins. COPI-coated vesicles are found associated with Golgi membranes at steady state, are involved in Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum (retrograde) vesicle transport, and possibly also in intra-Golgi transport. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| photoreceptor ribbon synapse | A ribbon synapse between a retinal photoreceptor cell (rod or cone) and a retinal bipolar cell. These contain a plate-like synaptic ribbon. |
| presynaptic endocytic zone | A specialized region of the plasma membrane and underlying cytoplasm which surround the the active zone, into which synaptic vesicle membranes are recycled following exocytosis. It is especially enriched in endocytic proteins following intense activity. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoskeletal protein binding | Binding to a protein component of a cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton). |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| phospholipid binding | Binding to a phospholipid, a class of lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments. Includes processes that control the spatial distribution of actin filaments, such as organizing filaments into meshworks, bundles, or other structures, as by cross-linking. |
| negative regulation of endocytosis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of endocytosis. |
| neuron projection morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a neuron projection are generated and organized. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites. |
| plasma membrane tubulation | A membrane tubulation process occurring in a plasma membrane. |
| protein localization to membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in a membrane. |
| synaptic vesicle endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process, in which the synaptic vesicle membrane constituents are retrieved from the presynaptic membrane on the axon terminal after neurotransmitter secretion by exocytosis. Synaptic vesicle endocytosis can occur via clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent mechanisms. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSSYDEASL | APEETTDSFW | EVGNYKRTVK | RIDDGHRLCN | DLMNCVQERA | KIEKAYGQQL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TDWAKRWRQL | IEKGPQYGSL | ERAWGAIMTE | ADKVSELHQE | VKNNLLNEDL | EKVKNWQKDA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| YHKQIMGGFK | ETKEAEDGFR | KAQKPWAKKM | KELEAAKKAY | HLACKEEKLA | MTREMNSKSE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| QSVTPEQQKK | LQDKVDKCKQ | DVQKTQEKYE | KVLEDVGKTT | PQYMENMEQV | FEQCQQFEEK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RLVFLKEVLL | DIKRHLNLAE | NSSYIHVYRE | LEQAIRGADA | QEDLRWFRST | SGPGMPMNWP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QFEEWNPDLP | HTTTKKEKQP | KKAEGVALTN | ATGAVESTSQ | AGDRGSVSSY | DRGQPYATEW |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SDDESGNPFG | GSEANGGANP | FEDDSKGVRV | RALYDYDGQE | QDELSFKAGD | ELTKLGEEDE |
| 430 | 440 | ||||
| QGWCRGRLDS | GQLGLYPANY | VEAI |