Q5EGY4
Gene name |
Ykt6 |
Protein name |
Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 |
Names |
|
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:64351 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
SYNAPTOBREVIN HOMOLOG YKT6 (PTHR45806) |
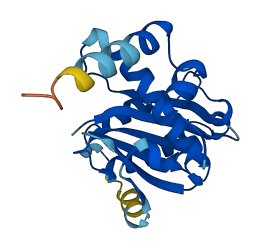
Descriptions
Most SNAREs are permanently anchored to membranes, but the SNARE Ykt6 is found both on intracellular membranes and in the cytoplasm. The SNARE core is autoinhibited by the N-terminal longin domain.
The dynamics of Ykt6 are believed to be governed by the reversible palmitoylation of the protein, which cycles Ykt6 between intracellular membranes and the cytoplasm. Palmitoylation of Ykt6 increases the partition coefficient of Ykt6 to membranes, thereby shifting some populations of the protein from the cytosol to cellular membranes. Palmitoylation-mediated membrane insertion will further shift the conformational equilibrium of Ykt6 to the open state. The specific membrane localization and the amount of membrane-associated Ykt6 are predicted to be affected by its reversible palmitoylation machinery in cells, as the majority of Ykt6 exists in the unpalmitoylated cytosolic form
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
125-185 (v-SNARE coiled-coil homology) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

2 structures for Q5EGY4
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3KYQ | X-ray | 244 A | A | 1-198 | PDB |
| AF-Q5EGY4-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for Q5EGY4
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs8155272 | 107 | R>T | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q5EGY4
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR45806 | SYNAPTOBREVIN HOMOLOG YKT6 |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR45806:SF1 | SYNAPTOBREVIN HOMOLOG YKT6 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
14 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical dendrite | A dendrite that emerges near the apical pole of a neuron. In bipolar neurons, apical dendrites are located on the opposite side of the soma from the axon. |
| basal dendrite | A dendrite that emerges near the basal pole of a neuron. In bipolar neurons, basal dendrites are either on the same side of the soma as the axon, or project toward the axon. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| SNARE complex | A protein complex involved in membrane fusion; a stable ternary complex consisting of a four-helix bundle, usually formed from one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs with an ionic layer sandwiched between hydrophobic layers. One well-characterized example is the neuronal SNARE complex formed of synaptobrevin 2, syntaxin 1a, and SNAP-25. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a palmitoyl (systematic name, hexadecanoyl) group to a sulfur atom on the cysteine of a protein molecule, in the reaction hexadecanoyl-CoA + L-cysteinyl- |
| SNAP receptor activity | Acting as a marker to identify a membrane and interacting selectively with one or more SNAREs on another membrane to mediate membrane fusion. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi, mediated by COP II vesicles. Small COP II coated vesicles form from the ER and then fuse directly with the cis-Golgi. Larger structures are transported along microtubules to the cis-Golgi. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi | The directed movement of membrane-bounded vesicles from endosomes back to the trans-Golgi network where they are recycled for further rounds of transport. |
| vesicle docking involved in exocytosis | The initial attachment of a vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the vesicle and the target membrane, that contributes to exocytosis. |
| vesicle targeting | The process in which vesicles are directed to specific destination membranes. Targeting involves coordinated interactions among cytoskeletal elements (microtubules or actin filaments), motor proteins, molecules at the vesicle membrane and target membrane surfaces, and vesicle cargo. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P36015 | YKT6 | Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | EV |
| Q3T000 | YKT6 | Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| O15498 | YKT6 | Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9CQW1 | Ykt6 | Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9LVM9 | YKT62 | VAMP-like protein YKT62 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9ZRD6 | YKT61 | VAMP-like protein YKT61 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q6P816 | ykt6 | Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q7ZUN8 | ykt6 | Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKLYSLSVFY | KGEPKAVLLK | AAYDVSSFSF | FQRSSVQEFM | TFTSQLIVER | SAKGSRASVK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EQEYLCHVYV | RSDSLAGVVI | ADSEYPSRVA | FTLLEKVLDE | FSKQVDRIDW | PVGSPATIHY |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TALDGHLSRY | QNPREADPMS | KVQAELDETK | IILHNTMESL | LERGEKLDDL | VSKSEVLGTQ |
| 190 | |||||
| SKAFYKTARK | QNSCCAIM |