Q5EG47
Gene name |
Prkaa1 |
Protein name |
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 |
Names |
AMPK subunit alpha-1, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase, ACACA kinase, Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase, HMGCR kinase, Tau-protein kinase PRKAA1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:105787 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
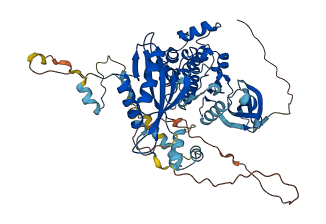
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
27-297 (Catalytic kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
167-189 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
27-279 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Pang T et al. (2007) "Conserved alpha-helix acts as autoinhibitory sequence in AMP-activated protein kinase alpha subunits", The Journal of biological chemistry, 282, 495-506
- Hardie DG et al. (2012) "AMP-activated protein kinase: a target for drugs both ancient and modern", Chemistry & biology, 19, 1222-36
- Chen L et al. (2009) "Structural insight into the autoinhibition mechanism of AMP-activated protein kinase", Nature, 459, 1146-9
- Mitchelhill KI et al. (1997) "Posttranslational modifications of the 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase beta1 subunit", The Journal of biological chemistry, 272, 24475-9
- Crute BE et al. (1998) "Functional domains of the alpha1 catalytic subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 273, 35347-54
- Li YY et al. (2013) "Novel small-molecule AMPK activator orally exerts beneficial effects on diabetic db/db mice", Toxicology and applied pharmacology, 273, 325-34
- Oakhill JS et al. (2009) "Structure and function of AMP-activated protein kinase", Acta physiologica (Oxford, England), 196, 3-14
- Pang T et al. (2008) "Small molecule antagonizes autoinhibition and activates AMP-activated protein kinase in cells", The Journal of biological chemistry, 283, 16051-60
- Scott JW et al. (2014) "ATP sensitive bi-quinoline activator of the AMP-activated protein kinase", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 443, 435-40
- Handa N et al. (2011) "Structural basis for compound C inhibition of the human AMP-activated protein kinase α2 subunit kinase domain", Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography, 67, 480-7
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q5EG47
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5UFU | X-ray | 345 A | PDB | ||
| AF-Q5EG47-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q5EG47
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q5EG47 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q5EG47
6 regional properties for Q5EG47
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 27 - 279 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 146 - 158 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 33 - 56 | IPR017441 |
| domain | PRKAA1, UBA-like autoinhibitory domain | 296 - 360 | IPR028797 |
| domain | AMPK, C-terminal adenylate sensor domain | 406 - 480 | IPR032270 |
| domain | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase alpha 1 catalytic subunit, C-terminal | 404 - 557 | IPR039137 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nuclear speck | A discrete extra-nucleolar subnuclear domain, 20-50 in number, in which splicing factors are seen to be localized by immunofluorescence microscopy. |
| nucleotide-activated protein kinase complex | A protein complex that possesses nucleotide-dependent protein kinase activity. The nucleotide can be AMP (in S. pombe and human) or ADP (in S. cerevisiae). |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
15 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| [acetyl-CoA carboxylase] kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP |
| [hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH)] kinase activity | +Catalysis of the reaction: [3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH)] + ATP = [3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH)] phosphate + ADP. |
| AMP-activated protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. This reaction requires the presence of AMP. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| histone serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group to a serine residue of a histone. |
| kinase binding | Binding to a kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + tau-protein = ADP + O-phospho-tau-protein. |
60 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| bile acid and bile salt transport | The directed movement of bile acid and bile salts into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| bile acid signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by bile acid binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade | The series of molecular signals in which calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity enabled by a CAMKK directly activates an AMPK. The cascade begins with calmodulin binding calcium which in turn binds CAMKK enabling its calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity. The cascade ends with AMP-activated protein kinase activity. |
| cellular response to calcium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a calcium ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| cellular response to glucose starvation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of deprivation of glucose. |
| cellular response to glucose stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a glucose stimulus. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| cellular response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| cellular response to nutrient levels | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus reflecting the presence, absence, or concentration of nutrients. |
| cellular response to organonitrogen compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organonitrogen stimulus. An organonitrogen compound is formally a compound containing at least one carbon-nitrogen bond. |
| cellular response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a prostagladin E stimulus. |
| cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organism exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| cholesterol biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| chromatin organization | The assembly or remodeling of chromatin composed of DNA complexed with histones, other associated proteins, and sometimes RNA. |
| cold acclimation | Any process that increases freezing tolerance of an organism in response to low, nonfreezing temperatures. |
| energy homeostasis | Any process involved in the balance between food intake (energy input) and energy expenditure. |
| fatty acid biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a fatty acid, any of the aliphatic monocarboxylic acids that can be liberated by hydrolysis from naturally occurring fats and oils. Fatty acids are predominantly straight-chain acids of 4 to 24 carbon atoms, which may be saturated or unsaturated; branched fatty acids and hydroxy fatty acids also occur, and very long chain acids of over 30 carbons are found in waxes. |
| fatty acid homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of fatty acid within an organism or cell. |
| fatty acid oxidation | The removal of one or more electrons from a fatty acid, with or without the concomitant removal of a proton or protons, by reaction with an electron-accepting substance, by addition of oxygen or by removal of hydrogen. |
| glucose homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of glucose within an organism or cell. |
| glucose metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving glucose, the aldohexose gluco-hexose. D-glucose is dextrorotatory and is sometimes known as dextrose; it is an important source of energy for living organisms and is found free as well as combined in homo- and hetero-oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| lipid biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids, compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. |
| motor behavior | The specific neuromuscular movement of a single organism in response to external or internal stimuli. |
| negative regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of hepatocyte apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of insulin receptor signaling. |
| negative regulation of lipid catabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids. |
| negative regulation of TOR signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TOR signaling. |
| negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of tubulin deacetylation. |
| neuron cellular homeostasis | The cellular homeostatic process that preserves a neuron in a stable, differentiated functional and structural state. |
| positive regulation of autophagy | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of glycolytic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glycolysis. |
| positive regulation of mitochondrial transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription occuring in the mitochondrion. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-lysine acetylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of peptidyl-lysine acetylation. |
| positive regulation of protein localization | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a protein localization. |
| positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein targeting to mitochondrion. |
| positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of skeletal muscle tissue development. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of bile acid secretion | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the controlled release of bile acid from a cell or a tissue. |
| regulation of circadian rhythm | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a circadian rhythm. A circadian rhythm is a biological process in an organism that recurs with a regularity of approximately 24 hours. |
| regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| regulation of stress granule assembly | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of stress granule assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of proteins and RNA molecules to form a stress granule. |
| regulation of vesicle-mediated transport | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of vesicle-mediated transport, the directed movement of substances, either within a vesicle or in the vesicle membrane, into, out of or within a cell. |
| response to 17alpha-ethynylestradiol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a 17alpha-ethynylestradiol stimulus. |
| response to activity | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an activity stimulus. |
| response to caffeine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a caffeine stimulus. Caffeine is an alkaloid found in numerous plant species, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding upon them. |
| response to camptothecin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a camptothecin stimulus. |
| response to gamma radiation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a gamma radiation stimulus. Gamma radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) or light emission of a specific frequency produced from sub-atomic particle interaction, such as electron-positron annihilation and radioactive decay. Gamma rays are generally characterized as EMR having the highest frequency and energy, and also the shortest wavelength, within the electromagnetic radiation spectrum. |
| response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| rhythmic process | Any process pertinent to the generation and maintenance of rhythms in the physiology of an organism. |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
75 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q02066 | Abscisic acid-inducible protein kinase | Triticum aestivum (Wheat) | PR | |
| P06782 | SNF1 | Carbon catabolite-derepressing protein kinase | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | EV |
| Q5GLH2 | TRIB2 | Tribbles homolog 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0VCE3 | TRIB3 | Tribbles homolog 3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3SZW1 | TSSK1B | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q92519 | TRIB2 | Tribbles homolog 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96RU7 | TRIB3 | Tribbles homolog 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96RU8 | TRIB1 | Tribbles homolog 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q15831 | STK11 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96RG2 | PASK | PAS domain-containing serine/threonine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9BXA7 | TSSK1B | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q14680 | MELK | Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P54646 | PRKAA2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P27448 | MARK3 | MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q13131 | PRKAA1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8K4K3 | Trib2 | Tribbles homolog 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K4K2 | Trib3 | Tribbles homolog 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K4K4 | Trib1 | Tribbles homolog 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O54863 | Tssk2 | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61241 | Tssk1b | Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61846 | Melk | Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BRK8 | Prkaa2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O35280 | Chek1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q69Z98 | Brsk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q5RJI5 | Brsk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase BRSK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q8C0X8 | Sperm motility kinase X | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR | |
| A0AUV4 | Gm7168 | Sperm motility kinase Y | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C0N0 | Gm4922 | Sperm motility kinase Z | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q641K5 | Nuak1 | NUAK family SNF1-like kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A2KF29 | Smoktcr | Sperm motility kinase Tcr mutant form | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q28948 | PRKAA2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q09136 | PRKAA1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q9WTQ6 | Trib3 | Tribbles homolog 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q09137 | Prkaa2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | EV |
| P54645 | Prkaa1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | EV |
| Q5QNM6 | CIPK13 | Putative CBL-interacting protein kinase 13 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q5JLQ9 | CIPK30 | CBL-interacting protein kinase 30 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q5N942 | SAPK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK4 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q852Q0 | OSK3 | Serine/threonine protein kinase OSK3 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q75LR7 | SAPK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK1 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q75H77 | SAPK10 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK10 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q7Y0B9 | SAPK8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK8 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q7XQP4 | SAPK7 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK7 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q0D4J7 | SAPK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6ERS4 | CIPK16 | CBL-interacting protein kinase 16 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| P0C5D6 | SAPK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q75V57 | SAPK9 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SAPK9 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q852Q1 | OSK4 | Serine/threonine protein kinase OSK4 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q852Q2 | OSK1 | Serine/threonine protein kinase OSK1 | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| Q8LIG4 | CIPK3 | CBL-interacting protein kinase 3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6ZLP5 | CIPK23 | CBL-interacting protein kinase 23 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2RAX3 | CIPK33 | CBL-interacting protein kinase 33 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2QY53 | CIPK32 | CBL-interacting protein kinase 32 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q21017 | kin-29 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase kin-29 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q95ZQ4 | aak-2 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P45894 | aak-1 | 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P43291 | SRK2A | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2A | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C958 | SRK2B | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2B | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M9E9 | SRK2C | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2C | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64812 | SRK2J | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2J | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2V452 | CIPK3 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O22971 | CIPK13 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q39192 | SRK2D | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2D | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O65554 | CIPK6 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q940H6 | SRK2E | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2E | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P43292 | SRK2G | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2G | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FJ54 | CIPK20 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 20 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FFP9 | SRK2H | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2H | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q39193 | SRK2I | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SRK2I | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q93VD3 | CIPK23 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 23 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q94CG0 | CIPK21 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 21 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FLZ3 | KIN12 | SNF1-related protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha KIN12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9LDI3 | CIPK24 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 24 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P92958 | KIN11 | SNF1-related protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha KIN11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q38997 | KIN10 | SNF1-related protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha KIN10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MRRLSSWRKM | ATAEKQKHDG | RVKIGHYILG | DTLGVGTFGK | VKVGKHELTG | HKVAVKILNR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QKIRSLDVVG | KIRREIQNLK | LFRHPHIIKL | YQVISTPSDI | FMVMEYVSGG | ELFDYICKNG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RLDEKESRRL | FQQILSGVDY | CHRHMVVHRD | LKPENVLLDA | HMNAKIADFG | LSNMMSDGEF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LRTSCGSPNY | AAPEVISGRL | YAGPEVDIWS | SGVILYALLC | GTLPFDDDHV | PTLFKKICDG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IFYTPQYLNP | SVISLLKHML | QVDPMKRAAI | KDIREHEWFK | QDLPKYLFPE | DPSYSSTMID |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DEALKEVCEK | FECSEEEVLS | CLYNRNHQDP | LAVAYHLIID | NRRIMNEAKD | FYLATSPPDS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| FLDDHHLTRP | HPERVPFLVA | ETPRARHTLD | ELNPQKSKHQ | GVRKAKWHLG | IRSQSRPNDI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| MAEVCRAIKQ | LDYEWKVVNP | YYLRVRRKNP | VTSTFSKMSL | QLYQVDSRTY | LLDFRSIDDE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| ITEAKSGTAT | PQRSGSISNY | RSCQRSDSDA | EAQGKPSDVS | LTSSVTSLDS | SPVDVAPRPG |
| 550 | |||||
| SHTIEFFEMC | ANLIKILAQ |