Q570Y9
Gene name |
Deptor (Depdc6, Kiaa4200) |
Protein name |
DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein |
Names |
DEP domain-containing protein 6 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:97998 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
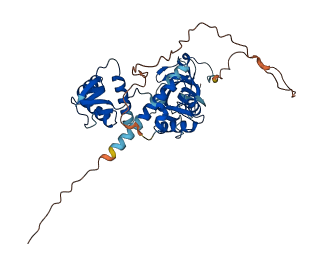
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q570Y9
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q570Y9-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
19 variants for Q570Y9
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs238761121 | 7 | G>V | No | EVA | |
| rs45948680 | 11 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389354449 | 63 | C>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389358903 | 96 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs254664020 | 125 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs48423113 | 128 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3405608463 | 144 | M>R | No | EVA | |
| rs47338588 | 149 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3406009221 | 172 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389358921 | 203 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3404606617 | 218 | R>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3406085318 | 218 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3406009253 | 219 | M>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3406174216 | 222 | R>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389367129 | 224 | R>M | No | EVA | |
| rs258587596 | 234 | T>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389355553 | 293 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371487 | 348 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389363011 | 408 | D>E | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q570Y9
5 regional properties for Q570Y9
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | DEP domain | 36 - 119 | IPR000591-1 |
| domain | DEP domain | 146 - 219 | IPR000591-2 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 330 - 407 | IPR001478 |
| domain | DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein, DEP domain 1 | 36 - 117 | IPR037335 |
| domain | DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein, DEP domain 2 | 133 - 217 | IPR037336 |
No GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for cellular component |
No GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for molecular function |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of cell size | Any process that reduces cell size. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of TOR signaling | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TOR signaling. |
| negative regulation of TORC1 signaling | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TORC1 signaling. |
| negative regulation of TORC2 signaling | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of TORC2 signaling. |
| regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
2 homologous proteins in AiPD
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEEGSSGGSG | SSDSNAGGSG | GVQQRELERM | AEVLVTGEQL | RLRLHEEKVI | KDRRHHLKTY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PNCFVAKELI | DWLIEHKEAS | DRETAIKLMQ | KLADRGIIHH | VCDEHKEFKD | VKLFYRFRKD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DGTFALDSEV | KAFMRGQRLY | EKLMSPETTL | LQPREEEGVK | YERTFMASEF | LDWLVQEGEA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TTRKEAEQLC | HRLMDHGIIQ | HVSNKHPFVD | SNLLYQFRMN | FRRRRRLMEL | LNETSPSSQE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| THDSPFCLRK | QSHDSRKSTS | FMSVSPSKEI | KIVSAVRRSS | MSSCGSSGYF | SSSPTLSSSP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PVLCNPKSVL | KRPVTSEELL | TPGAPYARKT | FTIVGDAVGW | GFVVRGSKPC | HIQAVDPSGP |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | ||
| AAAAGMKVCQ | FVVSVNGLNV | LNVDYRTVSN | LILTGPRTIV | MEVMEELDC |