Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-150 (N-terminal domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
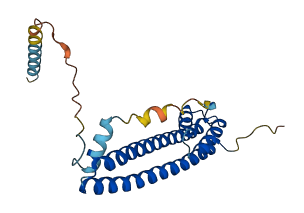
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q4R574
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q4R574-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q4R574
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q4R574 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q4R574
No regional properties for Q4R574
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q4R574 | |||
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| late endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a late endosome. |
No GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for molecular function |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| vacuolar transport | The directed movement of substances into, out of or within a vacuole. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGLFGKTQEK | PPKELVNEWS | LKIRKEMRVV | DRQIRDIQRE | EEKVKRSVKD | AAKKGQKDVC |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VVLAKEMIRS | RKAVSKLYAS | KAHMNSVLMG | MKNQLAVLRV | AGSLQKSTEV | MKAMQSLVKI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PEIRATMREL | SKEMMKAGII | EEMLEDTFES | MDDQEEMEEA | AEMEIDRILF | EITAGALGKA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | ||
| PSKVTDALPE | PEPSGAMAAS | DEEEEEEEAL | EAMQSRLATL | RS |