Q4KM47
Gene name |
Cdk10 |
Protein name |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 10 |
Names |
Cell division protein kinase 10 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:361434 |
EC number |
2.7.11.22: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
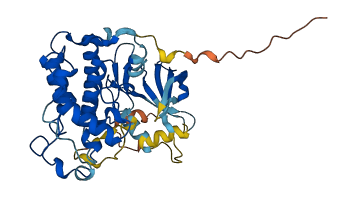
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
178-201 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
29-337 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Cyclin-Dependent protein Kinase 10) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q4KM47
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q4KM47-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q4KM47
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q4KM47 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q4KM47
4 regional properties for Q4KM47
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.22 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ciliary basal body | A membrane-tethered, short cylindrical array of microtubules and associated proteins found at the base of a eukaryotic cilium (also called flagellum) that is similar in structure to a centriole and derives from it. The cilium basal body is the site of assembly and remodelling of the cilium and serves as a nucleation site for axoneme growth. As well as anchoring the cilium, it is thought to provide a selective gateway regulating the entry of ciliary proteins and vesicles by intraflagellar transport. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity | Cyclin-dependent catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Cyclin-dependent catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
8 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell projection organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| negative regulation of cilium assembly | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cilium assembly. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the formation, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| regulation of cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle. |
| regulation of mitotic cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progress through the mitotic cell cycle. |
12 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2TBL8 | CDK10 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 10 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P21127 | CDK11B | Cyclin-dependent kinase 11B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q15131 | CDK10 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q3UMM4 | Cdk10 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q641Z4 | Cdk9 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q66HE7 | Cdkl1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q5XIT0 | Cdkl2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q4KM34 | Cdk20 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 20 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O35831 | Cdk17 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 17 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9JM01 | Cdkl3 | Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q09437 | cdk-11.1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 11.1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9FGW5 | CDKG1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase G1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSQCQIWVRH | HLCCSFQIPT | LAASLFQLGR | CRSVKEFEKL | NRIGEGTYGI | VYRARDTQTD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EIVALKKVRM | DKEKDGIPIS | SLREITLLLR | LRHPNIVELK | EVVVGNHLES | IFLVMGYCEQ |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DLASLLENMP | TPFSEAQVKC | ILLQVLRGLQ | YLHRSFIIHR | DLKVSNLLMT | DKGCVKTADF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GLARAYGVPV | KPMTPKVVTL | WYRAPELLLG | TTTQTTSIDM | WAVGCILAEL | LAHKPLLPGT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SEIHQIDLIV | QLLGTPSENI | WPGFSKLPLA | GQYSLRKQPY | NNLKHKFPWL | SEAGLRLLNF |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| LFMYDPKKRA | TAGDCLESSY | FKEKPLPCEP | ELMPTFPHHR | NKRAAPAATE | GQSKRCRP |