Q3ZBW5
Gene name |
RHOB |
Protein name |
Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB |
Names |
|
Species |
Bos taurus (Bovine) |
KEGG Pathway |
bta:515118 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
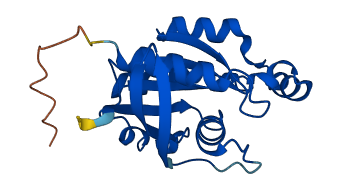
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q3ZBW5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q3ZBW5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q3ZBW5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q3ZBW5 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q3ZBW5
6 regional properties for Q3ZBW5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 345 - 624 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 349 - 614 | IPR001245 |
| domain | Gnk2-homologous domain | 20 - 123 | IPR002902-1 |
| domain | Gnk2-homologous domain | 133 - 246 | IPR002902-2 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 466 - 478 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 351 - 373 | IPR017441 |
Functions
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cleavage furrow | The cleavage furrow is a plasma membrane invagination at the cell division site. The cleavage furrow begins as a shallow groove and eventually deepens to divide the cytoplasm. |
| late endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a late endosome. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| cell adhesion | The attachment of a cell, either to another cell or to an underlying substrate such as the extracellular matrix, via cell adhesion molecules. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to hydrogen peroxide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) stimulus. |
| cellular response to ionizing radiation | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a ionizing radiation stimulus. Ionizing radiation is radiation with sufficient energy to remove electrons from atoms and may arise from spontaneous decay of unstable isotopes, resulting in alpha and beta particles and gamma rays. Ionizing radiation also includes X-rays. |
| mitotic cytokinesis | A cell cycle process that results in the division of the cytoplasm of a cell after mitosis, resulting in the separation of the original cell into two daughter cells. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| small GTPase mediated signal transduction | The series of molecular signals in which a small monomeric GTPase relays a signal. |
37 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q00246 | RHO4 | GTP-binding protein RHO4 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P61585 | RHOA | Transforming protein RhoA | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1RMJ6 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q17QI8 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2HJ68 | RND1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9PSX7 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P48148 | Rho1 | Ras-like GTP-binding protein Rho1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q96L33 | RHOV | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92730 | RND1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O94844 | RHOBTB1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61587 | RND3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O94955 | RHOBTB3 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08134 | RHOC | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61586 | RHOA | Transforming protein RhoA | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P62745 | RHOB | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8BLR7 | Rnd1 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein Rho6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61588 | Rnd3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9DAK3 | Rhobtb1 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CTN4 | Rhobtb3 | Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8VDU1 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62159 | Rhoc | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoC | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9QUI0 | Rhoa | Transforming protein RhoA | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P62746 | Rhob | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O77683 | RND3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q6SA80 | Rnd3 | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoE | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9Z1Y0 | Rhov | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoV | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P61589 | Rhoa | Transforming protein RhoA | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P62747 | Rhob | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9SSX0 | RAC1 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 1 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6Z808 | RAC3 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q68Y52 | RAC2 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q67VP4 | RAC4 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein 4 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q22038 | rho-1 | Ras-like GTP-binding protein rhoA | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9SU67 | ARAC8 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O82480 | ARAC7 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q38903 | ARAC2 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O82481 | ARAC10 | Rac-like GTP-binding protein ARAC10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAIRKKLVV | VGDGACGKTC | LLIVFSKDEF | PEVYVPTVFE | NYVADIEVDG | KQVELALWDT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AGQEDYDRLR | PLSYPDTDVI | LMCFSVDSPD | SLENIPEKWV | PEVKHFCPNV | PIILVANKKD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LRSDEHVRTE | LARMKQEPVR | TDDGRAMAVR | IQAYDYLECS | AKTKEGVREV | FETATRAALQ |
| 190 | |||||
| KRYGSQNGCI | NCCKVL |