Q3UYH7
Gene name |
Adrbk2 |
Protein name |
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 |
Names |
Beta-ARK-2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:320129 |
EC number |
2.7.11.15: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
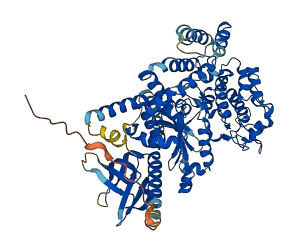
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q3UYH7
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q3UYH7-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
31 variants for Q3UYH7
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388773846 | 51 | N>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3395799772 | 66 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388777419 | 123 | Q>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388766561 | 147 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388787094 | 158 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388782139 | 159 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388781038 | 199 | R>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388779781 | 216 | M>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388769252 | 220 | K>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388766487 | 245 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3395799390 | 250 | D>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388772193 | 269 | F>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388772193 | 269 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3395667030 | 291 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388773851 | 326 | D>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs29565070 | 350 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3388779761 | 364 | K>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388780811 | 365 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388785862 | 367 | C>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388777397 | 521 | V>SDG* | No | EVA | |
| rs48260081 | 540 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388773887 | 548 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388776930 | 576 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388781022 | 587 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388766503 | 588 | L>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388782121 | 590 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388766497 | 593 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388762982 | 595 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388782124 | 603 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388777409 | 643 | W>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388769279 | 660 | R>C | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q3UYH7
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.15 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
13 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cilium | A specialized eukaryotic organelle that consists of a filiform extrusion of the cell surface and of some cytoplasmic parts. Each cilium is largely bounded by an extrusion of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane, and contains a regular longitudinal array of microtubules, anchored to a basal body. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite terminus | A structure at the distal end of a dendrite adapted to carry out a specific function, e.g. dendriole. |
| dendritic shaft | Cylindric portion of the dendrite, directly stemming from the perikaryon, and carrying the dendritic spines. |
| dendritic spine | A small, membranous protrusion from a dendrite that forms a postsynaptic compartment, typically receiving input from a single presynapse. They function as partially isolated biochemical and an electrical compartments. Spine morphology is variable:they can be thin, stubby, mushroom, or branched, with a continuum of intermediate morphologies. They typically terminate in a bulb shape, linked to the dendritic shaft by a restriction. Spine remodeling is though to be involved in synaptic plasticity. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| sperm midpiece | The highly organized segment of the sperm flagellum which begins at the connecting piece and is characterized by the presence of 9 outer dense fibers (ODFs) that lie outside each of the 9 outer axonemal microtubule doublets and by a sheath of mitochondria that encloses the ODFs and the axoneme; the midpiece terminates about one-fourth of the way down the sperm flagellum at the annulus, which marks the beginning of the principal piece. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
| Z disc | Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| beta-adrenergic receptor kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + beta-adrenergic receptor = ADP + phospho-beta-adrenergic receptor. |
| D1 dopamine receptor binding | Binding to a D1 dopamine receptor. |
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| G protein-coupled receptor kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + G protein-coupled receptor = ADP + G protein-coupled receptor phosphate. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
9 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway after prolonged stimulation with an agonist of the pathway. |
| G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to its receptor, in which the activated receptor promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP on the alpha-subunit of an associated heterotrimeric G-protein complex. The GTP-bound activated alpha-G-protein then dissociates from the beta- and gamma-subunits to further transmit the signal within the cell. The pathway begins with receptor-ligand interaction, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process. The pathway can start from the plasma membrane, Golgi or nuclear membrane. |
| inositol phosphate metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving inositol phosphate, 1,2,3,4,5,6-cyclohexanehexol, with one or more phosphate groups attached. |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| receptor internalization | A receptor-mediated endocytosis process that results in the movement of receptors from the plasma membrane to the inside of the cell. The process begins when cell surface receptors are monoubiquitinated following ligand-induced activation. Receptors are subsequently taken up into endocytic vesicles from where they are either targeted to the lysosome or vacuole for degradation or recycled back to the plasma membrane. |
| regulation of signal transduction | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction. |
| rhodopsin metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving rhodopsin, a brilliant purplish-red, light-sensitive visual pigment found in the rod cells of the retinas. |
19 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P43249 | GRK5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P21146 | GRK2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P26818 | GRK3 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P32865 | Gprk1 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P25098 | GRK2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q15835 | GRK1 | Rhodopsin kinase GRK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P34947 | GRK5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P32298 | GRK4 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P43250 | GRK6 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35626 | GRK3 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8VEB1 | Grk5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99MK8 | Grk2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O70293 | Grk6 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WVL4 | Grk1 | Rhodopsin kinase GRK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62833 | Grk5 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P26817 | Grk2 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P97711 | Grk6 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P26819 | Grk3 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q09639 | grk-2 | G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MADLEAVLAD | VSYLMAMEKS | KTAPAARASK | KVVLPEPSIR | SVMQRYLAER | NEITFDKIFN |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QKIGFLLFKD | FCLNEIGEAV | PQVKFYEEIK | EYEKLDNEED | RLRRSRQMYD | AYIMRELLSS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| THQFSKQAVE | HVQSHLSKKQ | VTATLFQPYI | EEICESLRGD | IFQKFMESDK | FTRFCQWKNV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ELNIHLSMND | FSVHRIIGRG | GFGEVYGCRK | ADTGKMYAMK | CLDKKRVKMK | QGETLALNER |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IMLSLVSTGD | CPFIVCMTYA | FHTPDKLCFI | LDLMNGGDMH | YHLSQHGVFS | EKEMRFYASE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IILGLEHMHT | CFVVYRDLKP | ANILLDEYGH | VRISDLGLAC | DFSKKKPHAS | VGTHGYMAPE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VLQKGTCYDS | SADWFSLGCM | LFKLLRGHSP | FRQHKTKDKH | EIDRMTLTVN | VQLPDAFSPE |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LRSLLEGLLQ | RDVSQRLGCG | GGGARELKEH | IFFKGIDWQH | VYLRKYPPPL | IPPRGEVNAA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| DAFDIGSFDE | EDTKGIKLLD | CDQDLYKNFP | LVISERWQQE | VVETIYDAVN | ADTDKIEARR |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KAKNKQLGQE | EDYAMGKDCI | MHGYMLKLGN | PFLTQWQRRY | FYLFPNRLEW | RGEGESRQSL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LTMEQIMSVE | ETQIKDRKCI | LLRIKGGKQF | VLQCESDPEF | AQWLKELTCT | FNEAQRLLRR |
| 670 | 680 | ||||
| APKFLNKPRA | AILEFSKPPL | CHRNSSGL |