Q3UPW2-2
Gene name |
Elf3 |
Protein name |
ETS-related transcription factor Elf-3 |
Names |
E74-like factor 3, Epithelial-restricted with serine box, Epithelium-restricted Ets protein ESX, Epithelium-specific Ets transcription factor 1, ESE-1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:13710 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
ETS (PTHR11849) |
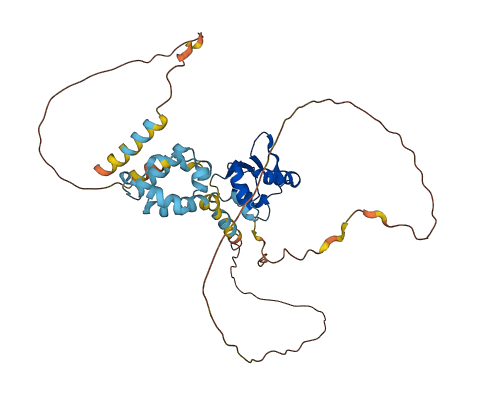
Descriptions
Three regions of Elf3, in addition to its DNA binding domain (ETS domain), influence Elf3 binding to DNA, including the transactivation(TAD) domain that behaves as an autoinhibitory domain. The TAD domain in Elf3 interacts with the DNA-binding Ets domain and thereby inhibits DNA binding. The residues flanking the N- and C-terminal sides of the ETS domain of Elf3 are crucial for its binding to DNA. Deletion of N-terminal region results in enhanced binding compared with the ability of full-length Elf3 to bind to DNA.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
272-354 (Ets domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q3UPW2-2
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3JTG | X-ray | 220 A | A | 289-391 | PDB |
| AF-Q3UPW2-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
21 variants for Q3UPW2-2
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388501462 | 11 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388500888 | 40 | V>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503006 | 55 | P>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388499975 | 77 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388499781 | 83 | P>M | No | EVA | |
| rs31978075 | 95 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388499803 | 97 | Y>N | No | EVA | |
| rs230339373 | 148 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs37603512 | 156 | S>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388502078 | 167 | M>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388503098 | 190 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs31347024 | 231 | D>D | No | EVA | |
| rs31447184 | 233 | G>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3390689569 | 236 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3390689535 | 236 | D>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3390623642 | 241 | L>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388501800 | 301 | D>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3390689494 | 314 | K>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388498409 | 353 | M>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388502710 | 357 | Y>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388499998 | 360 | E>R | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q3UPW2-2
7 regional properties for Q3UPW2-2
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | VHS domain | 5 - 146 | IPR002014 |
| domain | GAT domain | 171 - 299 | IPR004152 |
| domain | Clathrin adaptor, alpha/beta/gamma-adaptin, appendage, Ig-like subdomain | 595 - 719 | IPR008152 |
| domain | Gamma-adaptin ear (GAE) domain | 598 - 719 | IPR008153 |
| domain | N-terminal extension of GAT domain | 169 - 207 | IPR041198 |
| domain | GGA3, GAT domain | 213 - 299 | IPR044111 |
| domain | GGA3, VHS domain | 6 - 146 | IPR046996 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR11849 | ETS |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR11849:SF13 | ETS-RELATED TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR ELF-3 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
DNA-binding transcription factor
helix-turn-helix transcription factor winged helix/forkhead transcription factor |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category |
PDGF signaling pathway Ets |
|
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anatomical structure morphogenesis | The process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. |
| blastocyst development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the blastocyst over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The mammalian blastocyst is a hollow ball of cells containing two cell types, the inner cell mass and the trophectoderm. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| epithelial cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of an epithelial cell, any of the cells making up an epithelium. |
| extracellular matrix organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an extracellular matrix. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| mammary gland involution | The tissue remodeling that removes differentiated mammary epithelia during weaning. |
| negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| transcription by RNA polymerase II | The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II), originating at an RNA polymerase II promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAATCEISNV | FSNYFNAMYS | SEDPTLAPAP | PTTFGTEDLV | LTLNNQQMTL | EGPGPQTRSQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RDRTDPLAVL | HLAEKASWTS | ERPQFWSKTQ | VLEWISYQVE | KNKYDASSID | FSRCDMDGAT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LCSCALEELR | LVFGPLGDQL | HAQLRDLTSN | SSDELSWIIE | LLEKDGMSFQ | ESLGDSGPFD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| QGSPFAQELL | DDGRQASPYY | CSTYGPGAPS | PGSSDVSTAR | TATPQSSHAS | DSGGSDVDLD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LTESKVFPRD | GFPDYKKGEP | KHGKRKRGRP | RKLSKEYWDC | LEGKKSKHAP | RGTHLWEFIR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DILIHPELNE | GLMKWENRHE | GVFKFLRSEA | VAQLWGQKKK | NSNMTYEKLS | RAMRYYYKRE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | |||
| ILERVDGRRL | VYKFGKNSSG | WKEEEVGESR | N |