Q3UP24
Gene name |
Nlrc4 (Card12, Ipaf) |
Protein name |
NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 |
Names |
Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 12, Ice protease-activating factor, Ipaf |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:268973 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
NLR FAMILY CARD DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 4 (PTHR47688) |
Descriptions
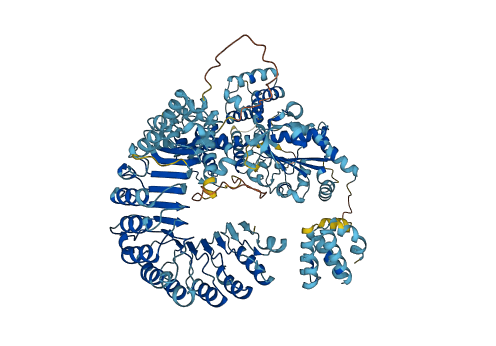
Nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) proteins oligomerize into multiprotein complexes termed inflammasomes when activated. NLRs constitute a crucial component of the cytosolic immunosurveillance system of mammals by detecting the signature components of pathogens and consequently triggering immune responses. The adenosine diphosphate-mediated interaction between the central nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) and the winged-helix domain (WHD) is critical for stabilizing the closed conformation. In addition, the helical domain HD2 repressively contacts a conserved and functionally important α-helix of the NBD. The C-terminal leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain is positioned to sterically occlude one side of the NBD domain and consequently sequester NLRC4 in monomeric state. Disruption of ADP-mediated NBD-WHD or NBD-HD2/NBD-LRR interactions resulted in constitutive activation of NLRC4.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
95-298 (Nucleotide-binding domain, NBD) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Deletion assay |
Target domain |
95-298 (Nucleotide-binding domain, NBD) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Target domain |
95-298 (Nucleotide-binding domain, NBD) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis, Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

5 structures for Q3UP24
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3JBL | EM | 450 A | A/B/C/D/E/F/G/H/I/J/K | 93-1024 | PDB |
| 4KXF | X-ray | 320 A | B/D/F/H/K/L/N/P | 1-1024 | PDB |
| 5AJ2 | EM | 4000 A | PDB | ||
| 6B5B | EM | 520 A | B/C | 1-1024 | PDB |
| AF-Q3UP24-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
22 variants for Q3UP24
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs260110611 | 30 | L>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs50842374 | 99 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs242419320 | 206 | R>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs224088761 | 295 | A>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs218687347 | 348 | Q>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs236103197 | 351 | R>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs49937915 | 385 | D>N | No | Ensembl | |
| rs231646020 | 387 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs238764373 | 628 | E>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs255864832 | 639 | P>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs108159529 | 670 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs250835686 | 737 | G>D | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29502769 | 756 | I>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs46190029 | 782 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs224857287 | 788 | R>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs264573917 | 796 | L>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs108684273 | 799 | T>I | No | Ensembl | |
| rs233690887 | 819 | S>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs108575465 | 908 | G>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs50053453 | 920 | R>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs50575999 | 948 | C>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs51771173 | 1013 | S>N | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q3UP24
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR47688 | NLR FAMILY CARD DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 4 |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR47688:SF1 | NLR FAMILY CARD DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 4 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| IPAF inflammasome complex | An inflammasome complex that consists of three components, IPAF, NAIP and caspase-1, and includes among its functions the sensing of flagellin derived from Legionella pneumophila, Salmonella typhimurium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Shigella flexneri. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| caspase binding | Binding to a caspase family protein. |
| endopeptidase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of an endopeptidase, any enzyme that hydrolyzes nonterminal peptide bonds in polypeptides. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
16 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase. |
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase in the context of an apoptotic process. |
| activation of innate immune response | Any process that initiates an innate immune response. Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. Examples of this process include activation of the hypersensitive response of Arabidopsis thaliana and activation of any NOD or TLR signaling pathway in vertebrate species. |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| detection of bacterium | The series of events in which a stimulus from a bacterium is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-1 beta production. |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| positive regulation of protein processing | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of protein maturation by peptide bond cleavage. |
| protein homooligomerization | The process of creating protein oligomers, compounds composed of a small number, usually between three and ten, of identical component monomers. Oligomers may be formed by the polymerization of a number of monomers or the depolymerization of a large protein polymer. |
| pyroptosis | A caspase-1-dependent cell death subroutine that is associated with the generation of pyrogenic mediators such as IL-1beta and IL-18. |
| regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the activity of a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in apoptosis. |
22 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1MHT9 | NLRC4 | NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9NPP4 | NLRC4 | NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| F1M649 | Nlrc4 | NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9LRR4 | RPPL1 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8W3K3 | At1g58400 | Putative disease resistance protein At1g58400 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q39214 | RPM1 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FJB5 | RPP8L3 | Disease resistance RPP8-like protein 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9T048 | At4g27190 | Disease resistance protein At4g27190 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9XIF0 | At1g59780 | Putative disease resistance protein At1g59780 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22727 | At1g61190 | Probable disease resistance protein At1g61190 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P0C8S1 | RPP8L2 | Probable disease resistance RPP8-like protein 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C646 | RXW24L | Probable disease resistance protein RXW24L | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64790 | At1g61300 | Probable disease resistance protein At1g61300 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9FKZ0 | At5g66910 | Probable disease resistance protein At5g66910 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P60838 | SUMM2 | Disease resistance protein SUMM2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| F4J339 | RPP1 | Probable disease resistance protein RPP1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q38834 | RPP13L4 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64973 | RPS5 | Disease resistance protein RPS5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q940K0 | UNI | Disease resistance protein UNI | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64789 | At1g61310 | Probable disease resistance protein At1g61310 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9XGM3 | RPS4 | Disease resistance protein RPS4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O23317 | At4g14610 | Probable disease resistance protein At4g14610 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNFIRNNRRA | LIQRMGLTVT | KQICDDLFAL | NVLNNQEANV | IYCEPLEQEA | ARKIIHMTMQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KGSAACNLFL | KSLENWDYFV | YQDLTGQNLS | YQVTEEDLNV | LAQNLKDLYN | SPAFLNFYPL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| GEDIDIIFNL | EKTFTEPIMW | KKDHRHHRVE | QLTLGSLLEA | LKSPCLIEGE | SGKGKSTLLQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RIAMLWASGG | CRALKGFRLV | FFIHLRSARG | GLFETLYDQL | LNIPDFISKP | TFKALLLKLH |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KEVLFLLDGY | NEFHPQNCPE | IEALIKENHR | FKNMVIVTTT | TECLRHIRHV | GALTAEVGDM |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TEDSAKDLIE | AVLVPDQVER | LWAQIQESRC | LRNLMKTPLF | VVITCAIQMG | RQEFQAHTQT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| MLFQTFYDLL | IQKNSHRYRG | GASGDFARSL | DYCGDLALEG | VFAHKFDFEP | EHGSSMNEDV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LVTIGLLCKY | TAQRLKPTYK | FFHKSFQEYT | AGRRLSSLLT | SKEPEEVSKG | NSYLNKMVSI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SDITSLYGNL | LLYTCGSSTE | ATRAVMRHLA | MVYQHGSLQG | LSVTKRPLWR | QESIQSLRNT |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| TEQDVLKAIN | VNSFVECGIN | LFSESMSKSD | LSQEFEAFFQ | GKSLYINSEN | IPDYLFDFFE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| YLPNCASALD | FVKLDFYERA | TESQDKAEEN | VPGVHTEGPS | ETYIPPRAVS | LFFNWKQEFK |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| TLEVTLRDIN | KLNKQDIKYL | GKIFSSATNL | RLHIKRCAAM | AGRLSSVLRT | CKNMHTLMVE |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ASPLTTDDEQ | YITSVTGLQN | LSIHRLHTQQ | LPGGLIDSLG | NLKNLERLIL | DDIRMNEEDA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| KNLAEGLRSL | KKMRLLHLTH | LSDIGEGMDY | IVKSLSEESC | DLQEMKLVAC | CLTANSVKVL |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| AQNLHNLIKL | SILDISENYL | EKDGNEALQE | LIGRLGVLGE | LTTLMLPWCW | DVHTSLPKLL |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| KQLEGTPGLA | KLGLKNWRLR | DEEIKSLGEF | LEMNPLRDLQ | QLDLAGHCVS | SDGWLYFMNV |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| FENLKQLVFF | DFSTEEFLPD | AALVRKLSQV | LSKLTLLQEV | KLTGWEFDDY | DISAIKGTFK |
| LVTA |