Q3SZJ2
Gene name |
RIPK2 |
Protein name |
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 |
Names |
Tyrosine-protein kinase RIPK2 |
Species |
Bos taurus (Bovine) |
KEGG Pathway |
bta:534407 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
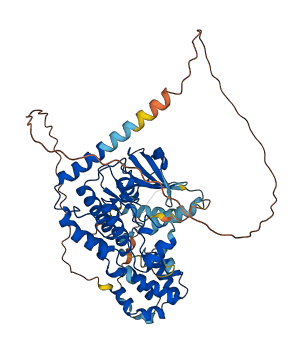
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q3SZJ2
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q3SZJ2-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
77 variants for Q3SZJ2
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs478328721 | 4 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs462980643 | 5 | P>A | No | EVA | |
| rs482846209 | 6 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs133399549 | 7 | C>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs478699276 | 13 | I>L | No | EVA | |
| rs438335586 | 15 | Y>D | No | EVA | |
| rs471521861 | 19 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs471521861 | 19 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs456128206 | 20 | D>A | No | EVA | |
| rs444631159 | 20 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs456128206 | 20 | D>G | No | EVA | |
| rs474461713 | 21 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs455906175 | 21 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs433116382 | 23 | Y>S | No | EVA | |
| rs469509183 | 24 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs469509183 | 24 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs467579694 | 25 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs480746302 | 25 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs467579694 | 25 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs448977154 | 26 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs448977154 | 26 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs460244897 | 27 | G>A | No | EVA | |
| rs478738057 | 27 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs1116411151 | 28 | A>E | No | EVA | |
| rs477810989 | 29 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs473910914 | 30 | G>A | No | EVA | |
| rs444135315 | 30 | G>C | No | EVA | |
| rs444135315 | 30 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs455955225 | 31 | T>P | No | EVA | |
| rs455955225 | 31 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs473708043 | 32 | V>E | No | EVA | |
| rs473708043 | 32 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs433170670 | 33 | S>A | No | EVA | |
| rs433170670 | 33 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs457320402 | 34 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs468673144 | 35 | A>D | No | EVA | |
| rs445334669 | 35 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs449015864 | 40 | W>C | No | EVA | |
| rs478572177 | 41 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs478572177 | 41 | R>P | No | EVA | |
| rs445147137 | 44 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs478140314 | 47 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs462556555 | 48 | H>P | No | EVA | |
| rs450441101 | 49 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs450441101 | 49 | L>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs461805214 | 50 | H>L | No | EVA | |
| rs440648769 | 56 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs440648769 | 56 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs461343367 | 58 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs449441616 | 65 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs520708291 | 112 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs516857166 | 118 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs470615166 | 236 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs452066420 | 277 | P>A | No | EVA | |
| rs476083653 | 283 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs482707959 | 289 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs460809055 | 290 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs448838960 | 293 | V>F | No | EVA | |
| rs478757438 | 298 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs460206396 | 302 | F>I | No | EVA | |
| rs472029706 | 305 | A>S | No | EVA | |
| rs518520600 | 310 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs463138509 | 311 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs444776754 | 313 | K>R | No | EVA | |
| rs437709644 | 319 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs437470748 | 355 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs453514726 | 379 | D>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs461004784 | 405 | C>W | No | EVA | |
| rs482799278 | 405 | C>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs442491093 | 406 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs479300344 | 406 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs460716390 | 407 | H>D | No | EVA | |
| rs385794205 | 423 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs478762800 | 482 | T>P | No | EVA | |
| rs480380296 | 484 | K>T | No | EVA | |
| rs466621125 | 525 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs444943162 | 531 | N>H | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q3SZJ2
5 regional properties for Q3SZJ2
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 18 - 294 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 22 - 287 | IPR001245 |
| domain | CARD domain | 430 - 522 | IPR001315 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 142 - 154 | IPR008271 |
| domain | RIP2, CARD domain | 436 - 522 | IPR042149 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| vesicle | Any small, fluid-filled, spherical organelle enclosed by membrane. |
10 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| CARD domain binding | Binding to a CARD (N-terminal caspase recruitment) domain, a protein-protein interaction domain that belongs to the death domain-fold superfamily. These protein molecule families are similar in structure with each consisting of six or seven anti-parallel alpha-helices that form highly specific homophilic interactions between signaling partners. CARD exists in the N-terminal prodomains of several caspases and in apoptosis-regulatory proteins and mediates the assembly of CARD-containing proteins that participate in activation or suppression of CARD carrying members of the caspase family. |
| caspase binding | Binding to a caspase family protein. |
| JUN kinase kinase kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: JNKK + ATP = JNKK phosphate + ADP. This reaction is the phosphorylation and activation of JUN kinase kinases (JNKKs). |
| LIM domain binding | Binding to a LIM domain (for Lin-11 Isl-1 Mec-3) of a protein, a domain with seven conserved cysteine residues and a histidine, that binds two zinc ions and acts as an interface for protein-protein interactions. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
48 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase. |
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation | The expansion of a CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell population by cell division. |
| cellular response to lipoteichoic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lipoteichoic acid stimulus; lipoteichoic acid is a major component of the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria and typically consists of a chain of glycerol-phosphate repeating units linked to a glycolipid anchor. |
| cellular response to muramyl dipeptide | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a muramyl dipeptide stimulus. Muramyl dipeptide is derived from peptidoglycan. |
| cellular response to peptidoglycan | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptidoglycan stimulus. Peptidoglycan is a bacterial cell wall macromolecule. |
| cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a cytokine to a receptor on the surface of a cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| defense response to Gram-positive bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-positive bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least ERK1 or ERK2 (MAPKs), a MEK (a MAPKK) and a MAP3K. The cascade may involve 4 different kinases, as it can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinase in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell through the I-kappaB-kinase (IKK)-dependent activation of NF-kappaB. The cascade begins with activation of a trimeric IKK complex (consisting of catalytic kinase subunits IKKalpha and/or IKKbeta, and the regulatory scaffold protein NEMO) and ends with the regulation of transcription of target genes by NF-kappaB. In a resting state, NF-kappaB dimers are bound to I-kappaB proteins, sequestering NF-kappaB in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of I-kappaB targets I-kappaB for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, thus releasing the NF-kappaB dimers, which can translocate to the nucleus to bind DNA and regulate transcription. |
| immature T cell proliferation in thymus | The expansion of an immature T cell population by cell division in the thymus. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| JNK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a JNK (a MAPK), a JNKK (a MAPKK) and a JUN3K (a MAP3K). The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. Lipopolysaccharides are major components of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, making them prime targets for recognition by the immune system. |
| nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a ligand (such as a bacterial peptidoglycan) to a cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 (NOD1) protein receptor, and ending with regulation of a downstream cellular process. |
| nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a ligand (such as a bacterial peptidoglycan) to a cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 (NOD2) protein receptor, and ending with regulation of a downstream cellular process. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of chemokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of chemokine production. |
| positive regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of a cytokine mediated signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of immature T cell proliferation in the thymus. |
| positive regulation of interferon-gamma production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-gamma production. Interferon-gamma is also known as type II interferon. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-1 beta production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-2 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-2 production. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-6 production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-6 production. |
| positive regulation of JNK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the JNK cascade. |
| positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of macrophage cytokine production. Macrophage cytokine production is the appearance of a chemokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels. |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation. Peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation is the phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of protein binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| positive regulation of protein ubiquitination | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of ubiquitin groups to a protein. |
| positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of T-helper 1 cell differentiation. |
| positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of a T-helper 1 type immune response. |
| positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of tumor necrosis factor production. |
| positive regulation of xenophagy | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of xenophagy. |
| response to exogenous dsRNA | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an exogenous double-stranded RNA stimulus. |
| response to interleukin-1 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-1 stimulus. |
| response to interleukin-12 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-12 stimulus. |
| response to interleukin-18 | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interleukin-18 stimulus. |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
| toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to toll-like receptor 2. |
| toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to toll-like receptor 4. |
| xenophagy | The selective autophagy process in which a region of cytoplasm containing an intracellular pathogen or some part of an intracellular pathogen (e.g. viral capsid) is enclosed in a double membrane bound autophagosome, which then fuses with the lysosome leading to degradation of the contents. |
37 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2VDU3 | MAP3K7 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q4TVR5 | DSTYK | Dual serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q6XUX0 | DSTYK | Dual serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P83104 | Takl1 | Putative mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7-like | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q95UN8 | slpr | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| Q02779 | MAP3K10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8NB16 | MLKL | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q16584 | MAP3K11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P00540 | MOS | Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase mos | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5TCX8 | MAP3K21 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 21 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6XUX3 | DSTYK | Dual serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O43318 | MAP3K7 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9NYL2 | MAP3K20 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 20 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q38SD2 | LRRK1 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P80192 | MAP3K9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O43353 | RIPK2 | Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q80XI6 | Map3k11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VDG6 | Map3k21 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 21 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62073 | Map3k7 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q3U1V8 | Map3k9 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9D2Y4 | Mlkl | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9ESL4 | Map3k20 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 20 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P00536 | Mos | Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase mos | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q66L42 | Map3k10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P58801 | Ripk2 | Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P0C8E4 | Map3k7 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q66HA1 | Map3k11 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| D3ZG83 | Map3k10 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P00539 | Mos | Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase mos | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9TZM3 | lrk-1 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9FPR3 | EDR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase EDR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q05609 | CTR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase CTR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q67E00 | dstyk | Dual serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinase | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSAEPVCSAL | PAIPYHKLAD | LRYLSRGASG | TVSSARHADW | RVQVAVKHLH | IHSPLLDSER |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NDVLREAEIL | HKARFSYILP | ILGICNEPEF | LGIVTEYMPN | GSLNELLHRK | IEYPDVPWPL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RFRILHEIAL | GVNYLHNMNP | PLLHHDLKTQ | NILLDNEFHV | KIADFGLSKW | RMMSLSQSRS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SKSAPEGGTI | VYMPPENYEP | GQKARASVKH | DIYSYAIIIW | EVLSRKQPFE | DVTNPLQIMY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SVSQGHRPDT | NEESLPFDIP | HRALMISLIE | SGWAQNPDER | PSFLKCLIEL | EPVLRTFEEI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TFLEAVIQLK | KTKLQNASRT | VHLSDKKKRE | LSPNIPVNSG | PREESCGSSQ | LHKTSGSPGT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SRSLSAPQDK | DFLSAKTQDF | SALHQCSVNH | SRNSDFCVDC | QVAFCDHRTA | PCSLAIVNPL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SAEGNSGRFQ | PGIAQQWIQS | KREDIVSQMT | EACLNQSLDA | LLSRDLIMKE | DYELISTKPT |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | |
| RTSKVRQLLD | TTDIQGEEFA | RVIVQKLKDN | KQMGLQPYPE | ILVLSQSPSL | NFFHNKSHKK |