Q39253
Gene name |
CAX1 |
Protein name |
Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 1 |
Names |
Ca(2+)/H(+) antiporter CAX1, Ca(2+)/H(+) exchanger 1, Protein CATION EXCHANGER 1, Protein RARE COLD INDUCIBLE 4 |
Species |
Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) |
KEGG Pathway |
ath:AT2G38170 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
VACUOLAR CALCIUM ION TRANSPORTER (PTHR31503) |
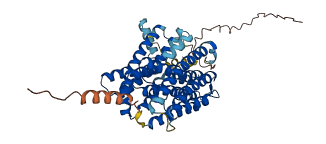
Descriptions
CAX1 plays a key role in determining cytosolic Ca2+ levels. A 36-amino acid N-terminal region on lCAX1 acts as an autoinhibitory domain for Ca2+/H+ transport activity. A synthetic peptide designed against the CAX1 36 amino acids inhibits Ca2+/H+ transport mediated by an N-terminal-truncated CAX1. The CAX1 N-terminal regulatory region physically interacts with the 7-amino acid region (residues 56-62) within CAX1.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
56-62 (7 amino acids within the first quarter of CAX1) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM, Partner binding |
Assay |
Peptide inhibitor test, Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Pittman JK et al. (2002) "Mechanism of N-terminal autoinhibition in the Arabidopsis Ca(2+)/H(+) antiporter CAX1", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 26452-9
- Pittman JK et al. (2001) "Regulation of CAX1, an Arabidopsis Ca(2+)/H+ antiporter. Identification of an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain", Plant physiology, 127, 1020-9
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q39253
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q39253-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
22 variants for Q39253
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSVATH01963991 | 6 | T>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH13569575 | 13 | E>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676139 | 26 | R>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15993098_T_G | 27 | E>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15993031_C_A | 50 | V>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15992999_T_A | 60 | K>N | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15992926_C_T | 85 | A>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15992904_C_T | 92 | G>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676127 | 96 | P>H | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676111 | 187 | R>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676103 | 224 | A>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH00264345 | 290 | A>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15990992_C_T | 295 | M>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH13569495 | 318 | N>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14595205 | 371 | L>M | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676085 | 376 | A>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH01963943 | 412 | H>Y | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_2_15990258_A_T | 428 | I>N | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676048 | 441 | A>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH13569431 | 447 | Q>P | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH15231846 | 460 | V>F | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH05676047 | 461 | F>L | No | 1000Genomes |
No associated diseases with Q39253
40 regional properties for Q39253
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 1606 - 1859 | IPR000719-1 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 2958 - 3210 | IPR000719-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 57 - 117 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 739 - 806 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 886 - 954 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 985 - 1053 | IPR003598-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 1081 - 1148 | IPR003598-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 1205 - 1272 | IPR003598-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 1502 - 1569 | IPR003598-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 2596 - 2664 | IPR003598-8 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 51 - 128 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 733 - 817 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 880 - 965 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 979 - 1064 | IPR003599-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1075 - 1159 | IPR003599-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1199 - 1283 | IPR003599-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1401 - 1487 | IPR003599-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1496 - 1580 | IPR003599-8 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 2590 - 2675 | IPR003599-9 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 1287 - 1387 | IPR003961-1 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 2678 - 2774 | IPR003961-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 45 - 126 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 727 - 817 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 874 - 963 | IPR007110-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 968 - 1056 | IPR007110-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1069 - 1157 | IPR007110-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1193 - 1283 | IPR007110-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1490 - 1578 | IPR007110-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 2583 - 2673 | IPR007110-8 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 1720 - 1732 | IPR008271-1 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 3073 - 3085 | IPR008271-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 45 - 127 | IPR013098-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 727 - 816 | IPR013098-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 874 - 964 | IPR013098-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 976 - 1063 | IPR013098-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 1070 - 1158 | IPR013098-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 1193 - 1282 | IPR013098-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 1490 - 1579 | IPR013098-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 2584 - 2674 | IPR013098-8 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 1612 - 1635 | IPR017441 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR31503 | VACUOLAR CALCIUM ION TRANSPORTER |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR31503:SF43 | VACUOLAR CATION_PROTON EXCHANGER 1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | transporter | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| calcium:proton antiporter complex | A protein complex that enables the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: Ca2+(in) + H+(out) = Ca2+(out) + H+(in). |
| plant-type vacuole | A closed structure that is completely surrounded by a unit membrane, contains liquid, and retains the same shape regardless of cell cycle phase. An example of this structure is found in Arabidopsis thaliana. |
| plant-type vacuole membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a vacuole that retains the same shape regardless of cell cycle phase. The membrane separates its contents from the cytoplasm of the cell. An example of this component is found in Arabidopsis thaliana. |
| vacuole | A closed structure, found only in eukaryotic cells, that is completely surrounded by unit membrane and contains liquid material. Cells contain one or several vacuoles, that may have different functions from each other. Vacuoles have a diverse array of functions. They can act as a storage organelle for nutrients or waste products, as a degradative compartment, as a cost-effective way of increasing cell size, and as a homeostatic regulator controlling both turgor pressure and pH of the cytosol. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| calcium:proton antiporter activity | Enables the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: Ca2+(in) + H+(out) = Ca2+(out) + H+(in). |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| calcium ion transmembrane transport | A process in which a calcium ion is transported from one side of a membrane to the other by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| calcium ion transport | The directed movement of calcium (Ca) ions into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| cation transport | The directed movement of cations, atoms or small molecules with a net positive charge, into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| cellular calcium ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of calcium ions at the level of a cell. |
| cellular manganese ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of manganese ions at the level of a cell. |
| cellular zinc ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of zinc ions at the level of a cell. |
| cold acclimation | Any process that increases freezing tolerance of an organism in response to low, nonfreezing temperatures. |
| lithium ion transport | The directed movement of lithium ion into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| phosphate ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of phosphate ions within an organism or cell. |
| regulation of stomatal movement | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of stomatal movement. |
| response to salt stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating an increase or decrease in the concentration of salt (particularly but not exclusively sodium and chloride ions) in the environment. |
1 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q93Z81 | CAX3 | Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAGIVTEPWS | VAENGNPSIT | AKGSSRELRL | GRTAHNMSSS | SLRKKSDLRV | IQKVPYKGLK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DFLSNLQEVI | LGTKLAILFP | AIPAAIICTY | CGVSQPWIFG | LSLLGLTPLA | ERVSFLTEQL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AFYTGPTLGG | LLNATCGNAT | ELIIAILALT | NNKVAVVKYS | LLGSILSNLL | LVLGTSLFCG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GIANIRREQR | FDRKQADVNF | FLLLLGFLCH | LLPLLVGYLK | NGEASAAVLS | DMQLSISRGF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SIVMLISYIA | YLVFQLWTHR | QLFDAQEQED | EYDDDVEQET | AVISFWSGFA | WLVGMTLVIA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LLSEYVVATI | EEASDKWNLS | VSFISIILLP | IVGNAAEHAG | AVIFAFKNKL | DISLGVALGS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ATQIGLFVVP | LTIIVAWILG | INMDLNFGPL | ETGCLAVSII | ITAFTLQDGS | SHYMKGLVLL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | ||
| LCYFIIAICF | FVDKLPQKQN | AIHLGHQAMN | NVVTATGGGV | FSS |