Q32PA5
Gene name |
UBE2C (UBCH10) |
Protein name |
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C |
Names |
(E3-independent) E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme C, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme C, Ubiquitin carrier protein C, Ubiquitin-protein ligase C |
Species |
Bos taurus (Bovine) |
KEGG Pathway |
bta:506962 |
EC number |
2.3.2.23: Aminoacyltransferases |
Protein Class |
|
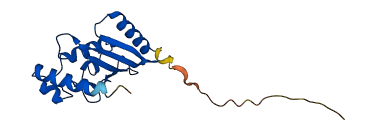
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q32PA5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q32PA5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
60 variants for Q32PA5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs448048240 | 2 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs460086621 | 3 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs478846741 | 5 | N>T | No | EVA | |
| rs445840466 | 7 | D>A | No | EVA | |
| rs464441554 | 10 | A>P | No | EVA | |
| rs450018867 | 20 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs437921708 | 20 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs450625592 | 79 | Y>D | No | EVA | |
| rs436215236 | 84 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs454763188 | 85 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs434822363 | 87 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs474187030 | 87 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs471922621 | 91 | Y>H | No | EVA | |
| rs476025096 | 96 | V>E | No | EVA | |
| rs476025096 | 96 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs463918062 | 96 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs438511663 | 98 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs438511663 | 98 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs461619719 | 99 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs479449663 | 100 | T>P | No | EVA | |
| rs458627370 | 102 | C>W | No | EVA | |
| rs450511426 | 103 | Y>* | No | EVA | |
| rs476939196 | 103 | Y>S | No | EVA | |
| rs468976482 | 105 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs448361207 | 106 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs466878225 | 108 | D>A | No | EVA | |
| rs466878225 | 108 | D>G | No | EVA | |
| rs434758863 | 109 | T>N | No | EVA | |
| rs453274366 | 110 | Q>P | No | EVA | |
| rs471809528 | 111 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs457431918 | 112 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs475961796 | 114 | C>G | No | EVA | |
| rs443035058 | 116 | D>G | No | EVA | |
| rs455221432 | 117 | I>M | No | EVA | |
| rs473728317 | 118 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs439973236 | 119 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs476826708 | 121 | K>R | No | EVA | |
| rs444049955 | 122 | W>G | No | EVA | |
| rs481019670 | 124 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs448216227 | 125 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs478914653 | 127 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs445949489 | 129 | R>T | No | EVA | |
| rs432357850 | 135 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs457417459 | 137 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs469520706 | 139 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs481467027 | 141 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs467129311 | 149 | N>H | No | EVA | |
| rs434155013 | 151 | H>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs438231653 | 156 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs456678956 | 156 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs456678956 | 156 | W>C | No | EVA | |
| rs474571925 | 159 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs474571925 | 159 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs474413445 | 166 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs441438401 | 169 | T>P | No | EVA | |
| rs460012092 | 170 | Y>* | No | EVA | |
| rs478537124 | 173 | Q>K | No | EVA | |
| rs445585615 | 173 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs463304018 | 178 | D>A | No | EVA | |
| rs481886454 | 180 | P>S | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q32PA5
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.2.23 | Aminoacyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anaphase-promoting complex | A ubiquitin ligase complex that degrades mitotic cyclins and anaphase inhibitory protein, thereby triggering sister chromatid separation and exit from mitosis. Substrate recognition by APC occurs through degradation signals, the most common of which is termed the Dbox degradation motif, originally discovered in cyclin B. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity | Isoenergetic transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-ubiquitin + Y -> Y-ubiquitin + X, where both the X-ubiquitin and Y-ubiquitin linkages are thioester bonds between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and a sulfhydryl side group of a cysteine residue. |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-Ub + Y --> Y-Ub + X, where both X-Ub and Y-Ub are covalent linkages. |
9 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, with ubiquitin-protein ligation catalyzed by the anaphase-promoting complex, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| exit from mitosis | The cell cycle transition where a cell leaves M phase and enters a new G1 phase. M phase is the part of the mitotic cell cycle during which mitosis and cytokinesis take place. |
| free ubiquitin chain polymerization | The process of creating free ubiquitin chains, compounds composed of a large number of ubiquitin monomers. These chains are not conjugated to a protein. |
| protein K11-linked ubiquitination | A protein ubiquitination process in which ubiquitin monomers are attached to a protein, and then ubiquitin polymers are formed by linkages between lysine residues at position 11 of the ubiquitin monomers. K11-linked polyubiquitination targets the substrate protein for degradation. The anaphase-promoting complex promotes the degradation of mitotic regulators by assembling K11-linked polyubiquitin chains. |
| protein K48-linked ubiquitination | A protein ubiquitination process in which a polymer of ubiquitin, formed by linkages between lysine residues at position 48 of the ubiquitin monomers, is added to a protein. K48-linked ubiquitination targets the substrate protein for degradation. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the cell cycle process in which a cell progresses from metaphase to anaphase during mitosis, triggered by the activation of the anaphase promoting complex by Cdc20/Sleepy homolog which results in the degradation of Securin. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of a ubiquitin group, or multiple ubiquitin groups, to the protein. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1RML1 | UBE2S | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 S | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P61085 | UBE2K | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q32LD2 | UBE2T | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 T | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q32L27 | UBE2Q2 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 Q2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| O00762 | UBE2C | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9D1C1 | Ube2c | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MASQNRDPVA | ASVAAARKGA | EPSGGAARGP | VGKRLQQELM | TLMMSGDKGI | SAFPESDNLF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KWVGTIHGAA | GTVYEDLRYK | LSLEFPSGYP | YNAPTVKFLT | PCYHPNVDTQ | GNICLDILKD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | |
| KWSALYDVRT | ILLSIQSLLG | EPNIDSPLNT | HAAELWKNPT | AFKKYLQETY | SKQVSSQDP |