Q2PKF4
Gene name |
GNAQ |
Protein name |
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha |
Names |
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-q |
Species |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
KEGG Pathway |
ssc:654405 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
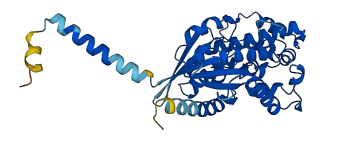
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q2PKF4
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q2PKF4-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for Q2PKF4
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs704695037 | 288 | L>I | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q2PKF4
No regional properties for Q2PKF4
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q2PKF4 | |||
Functions
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| heterotrimeric G-protein complex | Any of a family of heterotrimeric GTP-binding and hydrolyzing proteins; they belong to a superfamily of GTPases that includes monomeric proteins such as EF-Tu and RAS. Heterotrimeric G-proteins consist of three subunits; the alpha subunit contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and possesses GTPase activity; the beta and gamma subunits are tightly associated and function as a beta-gamma heterodimer; extrinsic plasma membrane proteins (cytoplasmic face) that function as a complex to transduce signals from G protein-coupled receptors to an effector protein. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nuclear membrane | Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the nucleus and form the nuclear envelope; excludes the intermembrane space. |
| photoreceptor outer segment | The outer segment of a vertebrate photoreceptor that contains a stack of membrane discs embedded with photoreceptor proteins. |
| synapse | The junction between an axon of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron, a muscle fiber or a glial cell. As the axon approaches the synapse it enlarges into a specialized structure, the presynaptic terminal bouton, which contains mitochondria and synaptic vesicles. At the tip of the terminal bouton is the presynaptic membrane; facing it, and separated from it by a minute cleft (the synaptic cleft) is a specialized area of membrane on the receiving cell, known as the postsynaptic membrane. In response to the arrival of nerve impulses, the presynaptic terminal bouton secretes molecules of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic membrane. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein-coupled receptor binding | Binding to a G protein-coupled receptor. |
| G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding | Binding to a complex of G-protein beta/gamma subunits. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a GTPase, an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of GTP. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
11 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| action potential | A process in which membrane potential cycles through a depolarizing spike, triggered in response to depolarization above some threshold, followed by repolarization. This cycle is driven by the flow of ions through various voltage gated channels with different thresholds and ion specificities. |
| adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway in which the signal is transmitted via the activation or inhibition of adenylyl cyclase activity and a subsequent change in the intracellular concentration of cyclic AMP (cAMP). |
| entrainment of circadian clock | The synchronization of a circadian rhythm to environmental time cues such as light. |
| G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway | A G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by a ligand binding to an acetylcholine receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| glutamate receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of glutamate to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| phototransduction, visible light | The sequence of reactions within a cell required to convert absorbed photons from visible light into a molecular signal. A visible light stimulus is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived visually by an organism; for organisms lacking a visual system, this can be defined as light with a wavelength within the range 380 to 780 nm. |
| protein stabilization | Any process involved in maintaining the structure and integrity of a protein and preventing it from degradation or aggregation. |
| regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| regulation of platelet activation | Any process that modulates the rate or frequency of platelet activation. Platelet activation is a series of progressive, overlapping events triggered by exposure of the platelets to subendothelial tissue. |
20 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P38408 | GNA14 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-14 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q28294 | GNAQ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P23625 | Galphaq | G protein alpha q subunit | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P29992 | GNA11 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P30679 | GNA15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O95837 | GNA14 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-14 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P50148 | GNAQ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P30678 | Gna15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P21279 | Gnaq | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P29797 | GNAS | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P93564 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | SS |
| O88302 | Gna15 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-15 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9JID2 | Gna11 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-11 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P82471 | Gnaq | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q0DJ33 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Oryza sativa subsp. japonica (Rice) | SS |
| P49084 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| P93163 | GPA2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-2 subunit | Glycine max (Soybean) (Glycine hispida) | SS |
| O80462 | XLG1 | Extra-large guanine nucleotide-binding protein 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P18064 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| P26981 | GPA1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-1 subunit | Solanum lycopersicum (Tomato) (Lycopersicon esculentum) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MTLESIMACC | LSEEAKEARR | INDEIERQLR | RDKRDARREL | KLLLLGTGES | GKSTFIKQMR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IIHGSGYSDE | DKRGFTKLVY | QNIFTAMQAM | IRAMDTLKIP | YKYEHNKAHA | QLVREVDVEK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VSAFENPYVD | AIKSLWNDPG | IQECYDRRRE | YQLSDSTKYY | LNDLDRVADP | AYLPTQQDVL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RVRVPTTGII | EYPFDLQSVI | FRMVDVGGQR | SERRKWIHCF | ENVTSIMFLV | ALSEYDQVLV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ESDNENRMEE | SKALFRTIIT | YPWFQNSSVI | LFLNKKDLLE | EKIMYSHLVD | YFPEYDGPQR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | |
| DAQAAREFIL | KMFVDLNPDS | DKIIYSHFTC | ATDTENIRFV | FAAVKDTILQ | LNLKEYNLV |