Q2LKW6
Gene name |
Nlrp1b |
Protein name |
NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1b allele 1 |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
NACHT, LRR AND PYD DOMAINS-CONTAINING PROTEIN 1 (PTHR46985) |
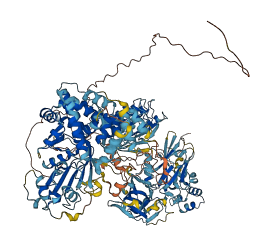
Descriptions
Nlrp1b is a receptor that detects the reduction of cellular ATP. Upon activation, this receptor recruits procaspase-1, which promotes cytokine processing and a proinflammatory form of cell death termed pyroptosis. The leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain in Nlrp1b, interacting with NACHT domain within the same protein, is involved in autoinhibition and mutations within the LRR domain activates the protein.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
126-435 (NACHT domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Deletion assay |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q2LKW6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q2LKW6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q2LKW6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q2LKW6 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q2LKW6
6 regional properties for Q2LKW6
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CARD domain | 1143 - 1226 | IPR001315 |
| domain | NACHT nucleoside triphosphatase | 126 - 435 | IPR007111 |
| domain | FIIND domain | 850 - 1133 | IPR025307 |
| domain | CARD8/ASC/NALP1, CARD domain | 1143 - 1223 | IPR033516 |
| domain | NOD2, winged helix domain | 365 - 419 | IPR041075 |
| domain | NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein, helical domain HD2 | 421 - 532 | IPR041267 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR46985 | NACHT, LRR AND PYD DOMAINS-CONTAINING PROTEIN 1 |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR46985:SF5 | NACHT, LRR AND PYD DOMAINS-CONTAINING PROTEIN 1B ALLELE 2 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | defense/immunity protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| inflammasome complex | A cytosolic protein complex that is capable of activating caspase-1. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| NLRP1 inflammasome complex | An inflammasome complex that consists of two components, NLRP1 (NALP1) and caspase-1 or caspase-5. The exact mechanisms of NLRP1 activation remain obscure, but potassium ion efflux appears to be essential. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a cysteine-type endopeptidase. |
| double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA. |
| double-stranded RNA binding | Binding to double-stranded RNA. |
| endopeptidase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of internal, alpha-peptide bonds in a polypeptide chain. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| peptidase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed when the carbon atom from the carboxyl group of one amino acid shares electrons with the nitrogen atom from the amino group of a second amino acid. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| protein self-association | Binding to a domain within the same polypeptide. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase in the context of an apoptotic process. |
| antiviral innate immune response | A defense response against viruses mediated through an innate immune response. An innate immune response is mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a neuron, the basic cellular unit of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. |
| NLRP1 inflammasome complex assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a NLRP1 inflammasome complex. |
| positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interleukin-1 beta production. |
| protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
| protein homooligomerization | The process of creating protein oligomers, compounds composed of a small number, usually between three and ten, of identical component monomers. Oligomers may be formed by the polymerization of a number of monomers or the depolymerization of a large protein polymer. |
| pyroptosis | A caspase-1-dependent cell death subroutine that is associated with the generation of pyrogenic mediators such as IL-1beta and IL-18. |
| regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| self proteolysis | The hydrolysis of proteins into smaller polypeptides and/or amino acids by cleavage of their own peptide bonds. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEESPPKQKS | NTKVAQHEGQ | QDLNTTRHMN | VELKHRPKLE | RHLKLGMIPV | VYMKQGEEIL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YPAQSLREEN | LIQNFTSLLL | LQKLCPKDPE | NMIRKSWASC | VPEEGGHMIN | IQDLFGPNIG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TQKEPQLVII | EGAAGIGKST | LARLVKRAWK | EGQLYRDHFQ | HVFFFSCREL | AQCKKLSLAE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LIAQGQEVPT | APINQILSHP | EKLLFILDGI | DEPAWVLADQ | NPELCLHWSQ | RQPVHTLLGS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LLGKSILPEA | FFLLTTRTTA | LQKFIPSLPM | PCQVEVLGFS | GIERENYFYK | YFANQRHAIT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| AFMMVESNPV | LLTLCEVPWV | CWLVCTCLKK | QMEQGRVLSL | KSQTTTALCL | KYLSLTIPDK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| HRRTQVKALC | SLAAEGIWKR | RTLFSESDLC | KQGLDEDAVA | TFLKTGVLQK | QASSLSYSFA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| HLCLQEFFAA | ISCILEDSEE | RHGNMEMDRI | VETLVERYGR | QNLFEAPTVR | FLFGLLGKEG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VKGMEKLFSC | SLHGKTNLKL | LWHILVKSQP | HQPPCLGLLH | CLYENQDMEL | LTHVMHDLQG |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| TIVPGPNDTA | HTVLQTNVKH | LVVQTDMELM | VATFCIQFYC | HVRTLQLNME | KQQGYALISP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| RMVLYRWTPI | TNASWEILFY | NLKFTRNLEG | LDLSGNSLRY | SVVQSLCNTL | RYPGCQLKTL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| WLVKCGLTSR | YCSLLASVLS | AHSSLTELYL | QLNDLGDDGV | RMLCEGLRNP | VCNLSILWLD |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| LSSLSAQVIT | ELRTLEEKNP | KLYIRSIWMP | HMMVPTENMD | EEAILTTLKQ | QRQESGDKPM |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| EILGTEEDFW | GPTGPVATEL | VDRVRNLYRM | PQMMVPTENM | DEEDILTSFK | QQRQQSGANP |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| MEILGTEEDF | WGPIGPVATE | VVYRERNLYR | VQLPMAGSYH | CPSTRLHFVV | TRAVTIEIEF |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| CAWSQFLDKT | PLQQSHMVVG | PLFDIKAEQG | AVTAVYLPHF | VSLKDTKAST | FDFKVAHFQE |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| HGMVLETPDR | VKPGYTVLKN | PSFSPMGVVL | RIIPAARHFI | PITSITLIYY | RVNQEEVTLH |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| LYLVPNDCTI | QKAIDDEEMK | FQFVRINKPP | PVDNLFIGSR | YIVSGSENLE | ITPKELELCY |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| RSSKEFQLFS | EIYVGNMGSE | IKLQIKNKKH | MKLIWEALLK | PGDLRPALPR | IAQALKDAPS |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| LLHFMDQHRE | QLVARVTSVD | PLLDKLHGLV | LNEESYEAVR | AENTNQDKMR | KLFNLSRSWS |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | |||
| RACKDLFYQA | LKETHPHLVM | DLLEKSGGVS | LGS |