Q2KI99
Gene name |
STING1 |
Protein name |
Stimulator of interferon genes protein |
Names |
STING, Transmembrane protein 173 |
Species |
Bos taurus (Bovine) |
KEGG Pathway |
bta:533661 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
154-337 (Cytosolic c-di-GMP binding domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
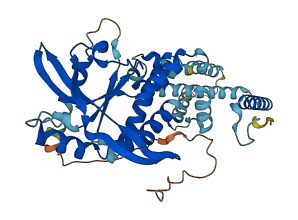
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q2KI99
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q2KI99-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
77 variants for Q2KI99
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs434319677 | 3 | H>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs434319677 | 3 | H>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs467116756 | 3 | H>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs447056038 | 4 | S>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs481765811 | 5 | S>C | No | Ensembl | |
| rs467984374 | 5 | S>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs451062497 | 8 | P>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs445275021 | 10 | I>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs459007312 | 10 | I>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs482409037 | 10 | I>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs479765406 | 14 | R>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs459641099 | 14 | R>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs442738592 | 15 | G>C | No | Ensembl | |
| rs463555315 | 18 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs443393478 | 20 | K>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs471333875 | 21 | A>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs451264538 | 24 | V>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs434350562 | 26 | L>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs472050353 | 29 | C>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs455315460 | 33 | L>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs468069892 | 38 | E>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs451013757 | 38 | E>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs437354419 | 42 | Y>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs445313667 | 47 | L>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs465471198 | 47 | L>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs451643109 | 49 | L>I | No | Ensembl | |
| rs449254328 | 54 | Q>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs463639429 | 60 | I>N | No | Ensembl | |
| rs443413237 | 61 | K>N | No | Ensembl | |
| rs471369642 | 68 | E>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs457776461 | 69 | E>D | No | Ensembl | |
| rs440907209 | 70 | L>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs472087269 | 72 | H>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs455273248 | 73 | V>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs801374840 | 86 | R>W | No | Ensembl | |
| rs480617132 | 139 | L>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs470078737 | 140 | A>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs477897853 | 141 | P>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs457813325 | 157 | H>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs440945702 | 162 | S>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs478531582 | 165 | I>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs433906802 | 176 | P>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs468425829 | 187 | N>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs520476700 | 201 | L>I | No | Ensembl | |
| rs448293302 | 202 | F>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs437752266 | 205 | D>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs469081634 | 247 | L>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs469081634 | 247 | L>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs445716492 | 249 | E>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs477096221 | 249 | E>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs460168453 | 250 | N>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs481556840 | 263 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs461341897 | 272 | S>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs444417140 | 277 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs452382673 | 284 | R>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs473229399 | 286 | E>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs436116660 | 287 | Q>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs473902954 | 288 | A>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs456902714 | 308 | N>Y | No | Ensembl | |
| rs436727997 | 312 | I>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs449172952 | 317 | P>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs480351112 | 325 | L>W | No | Ensembl | |
| rs449800604 | 335 | Q>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs477758776 | 336 | E>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs447379082 | 341 | T>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs461782305 | 342 | M>I | No | Ensembl | |
| rs439835023 | 343 | G>C | No | Ensembl | |
| rs441562968 | 344 | S>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs474510534 | 348 | S>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs464015420 | 349 | V>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs472037752 | 351 | P>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs443847049 | 351 | P>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs434911974 | 357 | S>Y | No | Ensembl | |
| rs472658432 | 360 | P>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs435522271 | 363 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs469911580 | 367 | L>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs449939309 | 377 | V>F | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q2KI99
5 regional properties for Q2KI99
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | 3'5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, catalytic domain | 481 - 814 | IPR002073 |
| domain | GAF domain | 71 - 230 | IPR003018-1 |
| domain | GAF domain | 252 - 439 | IPR003018-2 |
| domain | HD/PDEase domain | 554 - 741 | IPR003607 |
| conserved_site | 3'5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, conserved site | 597 - 608 | IPR023174 |
Functions
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| autophagosome | A double-membrane-bounded compartment that engulfs endogenous cellular material as well as invading microorganisms to target them to the lytic vacuole/lysosome for degradation as part of macroautophagy. |
| autophagosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an autophagosome, a double-membrane-bounded vesicle in which endogenous cellular material is sequestered. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The component of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| integral component of endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) membrane | The component of the ERGIC membrane consisting of the gene products having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| mitochondrial outer membrane | The outer, i.e. cytoplasm-facing, lipid bilayer of the mitochondrial envelope. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| peroxisome | A small organelle enclosed by a single membrane, and found in most eukaryotic cells. Contains peroxidases and other enzymes involved in a variety of metabolic processes including free radical detoxification, lipid catabolism and biosynthesis, and hydrogen peroxide metabolism. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| STING complex | A protein dimer containing two STING monomers. It binds cyclic purine di-nucleotides. Activation of the sting complex by 2',5'-3'-5'-cyclic GMP-AMP activates nuclear transcription factor kB (NF-kB) and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) which then induce transcription of the genes encoding type I IFN and cytokines active in the innate immune response. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP binding | Binding to 2',3' cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) nucleotide, a cyclic purine dinucleotide that consists of AMP and GMP units cyclized via 2',5' and 3',5' linkages. |
| cyclic-di-GMP binding | Binding to cyclic-di-GMP, cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a sequence-specific DNA binding RNA polymerase II transcription factor, any of the factors that interact selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of innate immune response | Any process that initiates an innate immune response. Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. Examples of this process include activation of the hypersensitive response of Arabidopsis thaliana and activation of any NOD or TLR signaling pathway in vertebrate species. |
| autophagosome assembly | The formation of a double membrane-bounded structure, the autophagosome, that occurs when a specialized membrane sac, called the isolation membrane, starts to enclose a portion of the cytoplasm. |
| cellular response to exogenous dsRNA | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an exogenous double-stranded RNA stimulus. |
| cellular response to interferon-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an interferon-beta stimulus. Interferon-beta is a type I interferon. |
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| positive regulation of defense response to virus by host | Any host process that results in the promotion of antiviral immune response mechanisms, thereby limiting viral replication. |
| positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of a transcription factor, any factor involved in the initiation or regulation of transcription. |
| positive regulation of interferon-beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-beta production. |
| positive regulation of macroautophagy | Any process, such as recognition of nutrient depletion, that activates or increases the rate of macroautophagy to bring cytosolic macromolecules to the vacuole/lysosome for degradation. |
| positive regulation of protein binding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of type I interferon production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of type I interferon production. Type I interferons include the interferon-alpha, beta, delta, episilon, zeta, kappa, tau, and omega gene families. |
| positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of a type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway. |
| protein complex oligomerization | The process of creating protein oligomers, compounds composed of a small number, usually between three and ten, of component monomers; protein oligomers may be composed of different or identical monomers. Oligomers may be formed by the polymerization of a number of monomers or the depolymerization of a large protein polymer. |
| regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response, the immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. |
| reticulophagy | The selective autohagy process in which parts of the endoplasmic reticulum are loaded into autophagosomes, delivered to the vacuole, and degraded in response to changing cellular conditions. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1C7U0 | STING1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q86WV6 | STING1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q3TBT3 | Sting1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| B8XX90 | STING1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| F1M391 | Sting1 | Stimulator of interferon genes protein | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPHSSLHPSI | PQPRGLRAQK | AALVLLSACL | VALWGLGEPP | DYTLKWLVLH | LASQQMGLLI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KGICSLAEEL | CHVHSRYHGS | YWRAVRACLC | SSMRCGALLL | LSCYFYCSLP | NMADLPFTWM |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LALLGLSQAL | NILLGLQGLA | PAEVSAICEK | RNFNVAHGLA | WSYYIGYLRL | ILPGLPARIQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| IYNQFHNNTL | QGAGSHRLHI | LFPLDCGVPD | DLNVADPNIR | FLHELPQQSA | DRAGIKGRVY |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TNSIYELLEN | GQRAGVCVLE | YATPLQTLFA | MSQDGRAGFS | REDRLEQAKL | FCRTLEDILA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NAPESQNNCR | LIVYQEPAEG | SSFSLSQEIL | QHLRQEEREV | TMGSTETSVM | PGSSVLSQEP |
| 370 | |||||
| ELLISGLEKP | LPLRSDVF |