Q2HWD6
Gene name |
KIT |
Protein name |
Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit |
Names |
SCFR , EC 2.7.10.1 , Proto-oncogene c-Kit , Tyrosine-protein kinase Kit , CD antigen CD117 |
Species |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
KEGG Pathway |
ssc:396810 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
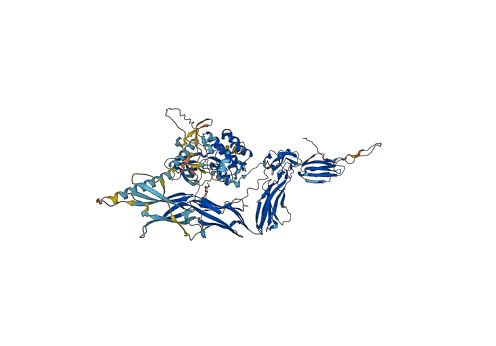
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
585-920 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM, Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
805-830 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
585-933 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
805-830 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
585-933 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Griffith J et al. (2004) "The structural basis for autoinhibition of FLT3 by the juxtamembrane domain", Molecular cell, 13, 169-78
- Reindl C et al. (2006) "From kinases to cancer: leakiness, loss of autoinhibition and leukemia", Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.), 5, 599-602
- Jiang J et al. (2004) "Identifying and characterizing a novel activating mutation of the FLT3 tyrosine kinase in AML", Blood, 104, 1855-8
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Juxtamembrane autoinhibition in receptor tyrosine kinases", Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 5, 464-71
- Mol CD et al. (2004) "Structural basis for the autoinhibition and STI-571 inhibition of c-Kit tyrosine kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 31655-63
- Liang L et al. (2016) "Structural and biochemical studies of the PDGFRA kinase domain", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 477, 667-672
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q2HWD6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q2HWD6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q2HWD6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q2HWD6 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q2HWD6
15 regional properties for Q2HWD6
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 585 - 933 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 586 - 918 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class III, conserved site | 644 - 657 | IPR001824 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 49 - 104 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 224 - 297 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 43 - 112 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 121 - 205 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 218 - 308 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 320 - 410 | IPR003599-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 37 - 98 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 212 - 308 | IPR007110-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 784 - 796 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich domain | 220 - 302 | IPR013151 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 591 - 619 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 585 - 920 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cytokine binding | Binding to a cytokine, any of a group of proteins that function to control the survival, growth and differentiation of tissues and cells, and which have autocrine and paracrine activity. |
| growth factor binding | Binding to a growth factor, proteins or polypeptides that stimulate a cell or organism to grow or proliferate. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction |
32 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| B cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a B cell. A B cell is a lymphocyte of B lineage with the phenotype CD19-positive and capable of B cell mediated immunity. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a cytokine to a receptor on the surface of a cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound | The series of events involved in the perception of sound vibration in which the vibration is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| digestive tract development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the digestive tract over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The digestive tract is the anatomical structure through which food passes and is processed. |
| embryonic hemopoiesis | The stages of blood cell formation that take place within the embryo. |
| erythrocyte differentiation | The process in which a myeloid precursor cell acquires specializes features of an erythrocyte. |
| erythropoietin-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by erythropoietin (EPO) binding to the erythropoietin receptor (EPO-R) on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| Fc receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of the Fc portion of an immunoglobulin to an Fc receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. The Fc portion of an immunoglobulin is its C-terminal constant region. |
| hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation | The process in which precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a hematopoietic progenitor cell, a class of cell types including myeloid progenitor cells and lymphoid progenitor cells. |
| immature B cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of an immature B cell. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| Kit signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of stem cell factor to the tyrosine kinase receptor KIT on the surface of a target cell, and ending with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. Stem cell factor (KIT ligand) binding to the receptor Kit mediates receptor dimerization, activation of its intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation. The activated receptor then phosphorylates various substrates, thereby activating distinct signaling cascades within the cell that trigger a change in state or activity of the cell. |
| lamellipodium assembly | Formation of a lamellipodium, a thin sheetlike extension of the surface of a migrating cell. |
| mast cell degranulation | The regulated exocytosis of secretory granules containing preformed mediators such as histamine, serotonin, and neutral proteases by a mast cell. |
| mast cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized myeloid precursor cell acquires the specialized features of a mast cell. A mast cell is a cell that is found in almost all tissues containing numerous basophilic granules and capable of releasing large amounts of histamine and heparin upon activation. |
| megakaryocyte development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a megakaryocyte cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Megakaryocyte development does not include the steps involved in committing a cell to a megakaryocyte fate. A megakaryocyte is a giant cell 50 to 100 micron in diameter, with a greatly lobulated nucleus, found in the bone marrow. |
| melanocyte adhesion | The attachment of a melanocyte to another cell via adhesion molecules. |
| melanocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a melanocyte. |
| melanocyte migration | The orderly movement of melanocytes from one site to another, often during the development of a multicellular organism. A melanocyte is a pigment cell derived from the neural crest. It contains melanin-filled pigment granules, which give a brown to black appearance. |
| ovarian follicle development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the ovarian follicle over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| pigmentation | The accumulation of pigment in an organism, tissue or cell, either by increased deposition or by increased number of cells. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of dendritic cell cytokine production. |
| positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell cytokine production. |
| positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway activity. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| spermatogenesis | The developmental process by which male germ line stem cells self renew or give rise to successive cell types resulting in the development of a spermatozoa. |
| stem cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a stem cell. A stem cell is a cell that retains the ability to divide and proliferate throughout life to provide progenitor cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. |
| T cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires characteristics of a more mature T-cell. A T cell is a type of lymphocyte whose definin characteristic is the expression of a T cell receptor complex. |
74 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q06805 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q06807 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P43481 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P13369 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| Q28889 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Felis catus (Cat) (Felis silvestris catus) | SS |
| P18460 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P21804 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q9PUF6 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8QHL3 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18461 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q08156 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| O97799 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| Q07407 | htl | Fibroblast growth factor receptor homolog 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q6J9G0 | STYK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P36888 | FLT3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P16234 | PDGFRA | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09619 | PDGFRB | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35916 | FLT4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35968 | KDR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P17948 | FLT1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07333 | CSF1R | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P22455 | FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P22607 | FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07949 | RET | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P35590 | TIE1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02763 | TEK | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P11362 | FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P21802 | FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P10721 | KIT | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91V87 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6J9G1 | Styk1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase STYK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P24786 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q2QLE0 | MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q7TQM3 | Fgfrl1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P53767 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P20786 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q91ZT1 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q04589 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G3V9H8 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q498D6 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q05030 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08775 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17833 | old-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor old-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q19238 | F09A5.2 | Putative tyrosine-protein kinase F09A5.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q10656 | egl-15 | Myoblast growth factor receptor egl-15 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P34892 | kin-16 | Receptor-like tyrosine-protein kinase kin-16 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| G5ED65 | ver-1 | Protein ver-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9LMN7 | WAK5 | Wall-associated receptor kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LSV3 | WAKL16 | Putative wall-associated receptor kinase-like 16 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8AXB3 | kdrl | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor kdr-like | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5GIT4 | kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73791 | tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90Z00 | fgfr1a | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JG38 | fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9I8N6 | csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q90413 | fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q9DE49 | pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q5MD89 | flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q8JFR5 | kita | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kita | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MRGARRAWDF | LFVLQLLLRV | QTGSSQPSVS | PEELSPPSIH | PAKSELIVSA | GDEIRLFCTD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PGSVKWTFET | LGQLSENTHA | EWIVEKAEAM | NTGNYTCTNE | GGLSSSIYVF | VRDPEKLFLV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DPPLYGKEDN | DALVRCPLTD | PEVTNYSLTG | CEGKPLPKDL | TFVADPKAGI | TIKNVKREYH |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RLCLHCSANQ | GGKSVLSKKF | TLKVRAAIRA | VPVVAVSKAS | YLLREGEEFA | VMCLIKDVSS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SVDSMWIREN | SQTKAQVKRN | SWHQGDFNFL | RQEKLTISSA | RVNDSGVFMC | YANNTFGSAN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| VTTTLEVVDK | GFINIFPMMN | TTVFVNDGED | VDLIVEYEAY | PKPEHRQWIY | MNRTATDKWE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DYPKSENESN | IRYVSELHLT | RLKGTEGGTY | TFLVSNADVN | SSVTFNVYVN | TKPEILTHDR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LMNGMLQCVA | AGFPEPTIDW | YFCPGTEQRC | SVPVGPVDVQ | IQNSSVSPFG | KLVIHSSIDY |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SAFKHNGTVE | CRAYNDVGKS | SAFFNFAFKE | QIHAHTLFTP | LLIGFVIAAG | MMCIIVMILT |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| YKYLQKPMYE | VQWKVVEEIN | GNNYVYIDPT | QLPYDHKWEF | PRNRLSFGKT | LGAGAFGKVV |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| EATAYGLIKS | DAAMTVAVKM | LKPSAHLTER | EALMSELKVL | SYLGNHMNIV | NLLGACTIGG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| PTLVITEYCC | YGDLLNFLRR | KRDSFICSKQ | EDHAEAALYK | NLLHSKESSC | SDSTNEYMDM |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| KPGVSYVVPT | KADKRRSARI | GSYIERDVTP | AIMEDDELAL | DLEDLLSFSY | QVAKGMAFLA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SKNCIHRDLA | ARNILLTHGR | ITKICDFGLA | RDIKNDSNYV | VKGNARLPVK | WMAPESIFNC |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| VYTFESDVWS | YGIFLWELFS | LGSSPYPGMP | VDSKFYKMIK | EGFRMLSPEH | APAEMYDIMK |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| TCWDADPLKR | PTFKQIVQLI | EKQISESTNH | IYSNLANCSP | HRENPAVDHS | VRINSVGSSA |
| 970 | |||||
| SSTQPLLVHE | DV |