Q29502
Gene name |
PAK2 |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 |
Names |
Gamma-PAK, p21-activated kinase 2, PAK-2, p21-activated protein kinase I, PAKI |
Species |
Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit) |
KEGG Pathway |
ocu:100009535 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
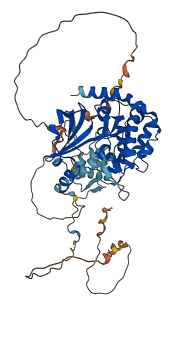
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
249-500 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
385-408 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
229-524 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p21-activated kinase 2) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q29502
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q29502-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q29502
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q29502 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q29502
6 regional properties for Q29502
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CRIB domain | 73 - 130 | IPR000095 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 249 - 500 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 364 - 376 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 255 - 278 | IPR017441 |
| domain | p21 activated kinase binding domain | 72 - 117 | IPR033923 |
| domain | p21-activated kinase 2, catalytic domain | 229 - 524 | IPR035064 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activator activity | Increases the activity of a protein tyrosine kinase, an enzyme which phosphorylates a tyrosyl phenolic group on a protein. |
| small GTPase binding | Binding to a small monomeric GTPase. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form an adherens junction. An adherens junction is a cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex at which the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane is attached to actin filaments. |
| bicellular tight junction assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a tight junction, an occluding cell-cell junction that is composed of a branching network of sealing strands that completely encircles the apical end of each cell in an epithelial sheet. |
| cellular response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| dendritic spine development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| execution phase of apoptosis | A stage of the apoptotic process that starts with the controlled breakdown of the cell through the action of effector caspases or other effector molecules (e.g. cathepsins, calpains etc.). Key steps of the execution phase are rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis. |
| negative regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein localization to cell-cell junction | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained, in a location within a cell-cell junction. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSDNGELEDK | PPAPPVRMSS | TIFSTGGKDP | LSANHSLKPL | PSVPEEKKPR | NKIISIFSGT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EKGSKKKEKE | RPEISPPSDF | EHTIHVGFDA | VTGEFTGMPE | QWARLLQTSN | ITKLEQKKNP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QAVLDVLKFY | DSNTVKQKYL | SFTPPEKDGF | PSGAPALNTK | VSETSAVVTE | EDDDDEEAAP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PVIAPRPDHT | KSIYTRSVID | PIPAPVGDSH | VDSGAKSSDK | QKKKTKMTDE | EIMEKLRTIV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SIGDPKKKYT | RYEKIGQGAS | GTVFTATDVA | LGQEVAIKQI | NLQKQPKKEL | IINEILVMKE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LKNPNIVNFL | DSYLVGDELF | VVMEYLAGGS | LTDVVTETCM | DEAQIAAVCR | ECLQALEFLH |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ANQVIHRDIK | SDNVLLGMEG | SVKLTDFGFC | AQITPEQSKR | STMVGTPYWM | APEVVTRKAY |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GPKVDIWSLG | IMAIEMVEGE | PPYLNENPLR | ALYLIATNGT | PELQNPEKLS | PIFRDFLNRC |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | ||
| LEMDVEKRGS | AKELLQHPFL | KLAKPLSSLT | PLIMAAKEAM | KSNR |