Q24592
Gene name |
hop (HD-160, CG1594) |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch |
Names |
|
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG1594 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
1034-1059 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
892-1164 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
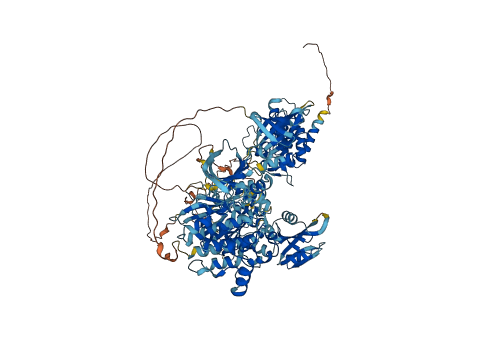
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q24592
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q24592-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q24592
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q24592 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q24592
9 regional properties for Q24592
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | FERM domain | 46 - 414 | IPR000299 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 582 - 843 | IPR000719-1 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 892 - 1164 | IPR000719-2 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 598 - 834 | IPR001245-1 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 894 - 1149 | IPR001245-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 1010 - 1022 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 898 - 926 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Band 4.1 domain | 33 - 259 | IPR019749 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 892 - 1151 | IPR020635 |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The leaflet the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endomembrane system | A collection of membranous structures involved in transport within the cell. The main components of the endomembrane system are endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, vesicles, cell membrane and nuclear envelope. Members of the endomembrane system pass materials through each other or though the use of vesicles. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cytokine receptor binding | Binding to a cytokine receptor. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
37 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| blastoderm segmentation | The hierarchical steps resulting in the progressive subdivision of the anterior/posterior axis of the embryo. |
| border follicle cell migration | The directed movement of a border cell through the nurse cells to reach the oocyte. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| compound eye development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the compound eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The compound eye is an organ of sight that contains multiple repeating units, often arranged hexagonally. Each unit has its own lens and photoreceptor cell(s) and can generate either a single pixelated image or multiple images, per eye. |
| compound eye morphogenesis | The morphogenetic process in which the anatomical structures of the compound eye are generated and organized. The adult compound eye is a precise assembly of 700-800 ommatidia. Each ommatidium is composed of 20 cells, identified by cell type and position. An example of compound eye morphogenesis is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| compound eye photoreceptor cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the specialized features of an eye photoreceptor cell. |
| cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a cytokine to a receptor on the surface of a cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| equator specification | The formation and development of the equator that forms the boundary between the photoreceptors in the dorsal sector of the eye and those in the ventral sector, dividing the eye into dorsal and ventral halves. |
| establishment of ommatidial planar polarity | The specification of polarized ommatidia. Ommatidia occur in two chiral forms. The trapezoidal arrangement of photoreceptors in the dorsal part of the eye is the mirror image of that in the ventral part. |
| eye-antennal disc morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures derived from the eye-antennal disc are generated and organized. This includes the transformation of an eye-antennal imaginal disc from a monolayered epithelium in the larvae of holometabolous insects into recognizable adult structures including the eye, antenna, head capsule and maxillary palps. |
| haltere disc morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures derived from the haltere disc are generated and organized. This includes the transformation of a haltere imaginal disc from a monolayered epithelium in the larvae of holometabolous insects into the recognizable adult capitellum, pedicel, haltere sclerite, metathoracic spiracle and metanotum. |
| hemocyte differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires the characteristics of a mature hemocyte. Hemocytes are blood cells associated with a hemocoel (the cavity containing most of the major organs of the arthropod body) which are involved in defense and clotting of hemolymph, but not involved in transport of oxygen. |
| hindgut morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the hindgut are generated and organized. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| larval lymph gland hemopoiesis | The production of blood cells from the larval lymph gland. The lymph gland consists of three to six bilaterally paired lobes that are attached to the cardioblasts during larval stages, and it degenerates during pupal stages. |
| leg disc morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures derived from the leg disc are generated and organized. This includes the transformation of a leg imaginal disc from a monolayered epithelium in the larvae of holometabolous insects into recognizable adult structures including the leg, coxa and ventral thoracic pleura. |
| locomotor rhythm | The rhythm of the locomotor activity of an organism during its 24 hour activity cycle. |
| long-term memory | The memory process that deals with the storage, retrieval and modification of information a long time (typically weeks, months or years) after receiving that information. This type of memory is typically dependent on gene transcription regulated by second messenger activation. |
| male germ-line sex determination | The determination of sex and sexual phenotype in a male organism's germ line. |
| mediolateral intercalation | The interdigitation of cells along the mediolateral axis during gastrulation. |
| nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state. |
| ommatidial rotation | The process in which photoreceptors are arranged in ommatidia in the dorsal and ventral fields to be mirror images. The polarity is established in the imaginal discs concurrently with cell fate specification. |
| open tracheal system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an open tracheal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. An open tracheal system is a respiratory system, a branched network of epithelial tubes that supplies oxygen to target tissues via spiracles. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| ovarian follicle cell development | The process that occurs during oogenesis involving the ovarian follicle cells, somatic cells which surround the germ cells of an ovary. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| ovarian follicle cell stalk formation | Development of ovarian follicle cells to create the interfollicular stalks that connect the egg chambers of progressive developmental stages. An example of this process is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own tyrosine amino acid residues, or a tyrosine residue on an identical protein. |
| periodic partitioning | The regionalization process that divides the spatial regions of an embryo into serially repeated regions. |
| positive regulation of heterochromatin assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of heterochromatin formation. |
| primary sex determination | The sex determination process that results in the initial specification of sexual status of an individual organism. |
| receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT | Any process in which STAT proteins (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) and JAK (Janus Activated Kinase) proteins convey a signal to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. The receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT begins with activation of a receptor and proceeeds through STAT protein activation by members of the JAK family of tyrosine kinases. STAT proteins dimerize and subsequently translocate to the nucleus. The pathway ends with regulation of target gene expression by STAT proteins. |
| regulation of biological quality | Any process that modulates a qualitative or quantitative trait of a biological quality. A biological quality is a measurable attribute of an organism or part of an organism, such as size, mass, shape, color, etc. |
| regulation of embryonic cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of an embryonic cell. |
| regulation of hemocyte proliferation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of hemocyte proliferation. Hemocytes are blood cells associated with a hemocoel (the cavity containing most of the major organs of the arthropod body) which are involved in defense and clotting of hemolymph, but not involved in transport of oxygen. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| stem cell population maintenance | The process by which an organism or tissue maintains a population of stem cells of a single type. This can be achieved by a number of mechanisms: stem cell asymmetric division maintains stem cell numbers; stem cell symmetric division increases them; maintenance of a stem cell niche maintains the conditions for commitment to the stem cell fate for some types of stem cell; stem cells may arise de novo from other cell types. |
| tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | The process of introducing a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| wing disc morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures derived from the wing disc are generated and organized. This includes the transformation of a wing imaginal disc from a monolayered epithelium in the larvae of holometabolous insects into recognizable adult structures including the wing hinge, wing blade and pleura. |
76 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MALANGGEDR | MDDSSSGRTS | LADSASLTNS | SLRSGTSSQS | IHTNDGTIRV | FNFTTGEFER |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FHPNMLCEEI | CNTMCRQLGI | APIAQLLYGI | REHSTSRRPS | PLVRLDLTWC | LPGERLNCQL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VYCFRMRFRV | PELDSQLELI | DGRSHKFLYR | QMRYDMRTEQ | IPEIRYPEHK | DKSTGLAVMD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| MLIDDQEQSE | DQQAMRSIEK | LYKLYLPPSL | WRAHSFFVGS | KIREVFRSLK | ANSLSVERLK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| WHYVHQVSHL | APTYMTEQFT | CTVQYLPNEE | VARGSGPIGT | SLAHSTSTLA | SSGSTNTLST |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LTTNTNSVAL | GGSGKKAKRR | STSGGIDVYV | RVFPHDSLEP | GLKVARVTSE | ATLKWILVGA |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VEGIFMISKI | NDTSVRLEIV | GLPKGYEMQF | QTEKEMKSFI | SYLGIYIRLS | SKWMQDLCHS |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YRTPSLEELS | SLHCHGPIGG | AYSLMKLHEN | GDKCGSYIVR | ECDREYNIYY | IDINTKIMAK |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| KTDQERCKTE | TFRIVRKDSQ | WKLSYNNGEH | VLNSLHEVAH | IIQADSPDRY | RIPASKYDKP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| PLLLLLLPKN | LKAKKTDLQL | SEAELQRRNP | QIFNPRTDLQ | WYPDSISLSD | DGMMFTMRGD |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| WIQQSPVKDV | SVTMKMLKSD | GNFMEFFRLA | QTWSLIQSPQ | FLKLYGLTLA | DPYTMVMEYS |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| RYGPLNKFLH | SMPNVTLHCL | LDLMHGLVRG | MHYLEDNKII | HNYIRCSNLY | VTKYDPNSYV |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| LDAKISDPGY | PRPYRESDSP | WIPVKYYRNL | QAAKTDQFAQ | LWAFATTIYE | IFSRCKEDLS |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| TLRQEQLLRQ | KNLDGNILKM | LDQDICPAPI | FETIMDGWSD | DETKRFSHHD | IFSRLNTIKA |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| EILPNYMPPP | EIATNGTGDE | TVIDRSDIPF | LPFPRSNMLM | VIPLTSECRV | IYNMENMIGR |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| GHYGTVYKGH | LEFNDKDQPR | EQVAIKMLNT | MQVSTDFHRE | IGIMRTLSHP | NIVKFKYWAE |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| KSHCIIMEYL | QSGSFDIYLR | FTAPNLNNPR | LVSFALDIAN | GMKYLSDMGL | IHRDLAARNI |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| LVDHNGDGDC | VKISDFGLAQ | FANSDGYYYA | KSKRDIPIRW | YSPEAISTCR | FSSYSDVWSY |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| GVTLFEMFSR | GEEPNLVPIQ | TSQEDFLNRL | QSGERLNRPA | SCPDFIYDLM | QLCWHATPRS |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | |||
| RPSFATIVDI | ITREVATKVT | HPTDGHQSPP | NQPTDAE |