Q24368
Gene name |
Iswi (CG8625) |
Protein name |
Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain Iswi |
Names |
EC 3.6.4.- , CHRAC 140 kDa subunit , Nucleosome-remodeling factor 140 kDa subunit , NURF-140 , Protein imitation swi |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG8625 |
EC number |
3.6.4.-: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
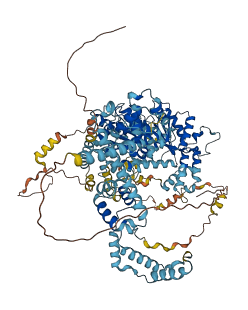
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
131-586 (Helicase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
131-586 (Helicase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

2 structures for Q24368
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1OFC | X-ray | 190 A | X | 691-991 | PDB |
| AF-Q24368-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q24368
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q24368 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q24368
10 regional properties for Q24368
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SNF2, N-terminal | 131 - 410 | IPR000330 |
| domain | SANT/Myb domain | 796 - 845 | IPR001005-1 |
| domain | SANT/Myb domain | 898 - 962 | IPR001005-2 |
| domain | Helicase, C-terminal domain-like | 432 - 586 | IPR001650 |
| domain | Helicase superfamily 1/2, ATP-binding domain | 124 - 316 | IPR014001 |
| domain | ISWI, HAND domain | 697 - 796 | IPR015194 |
| domain | SLIDE domain | 853 - 966 | IPR015195 |
| domain | SANT domain | 795 - 847 | IPR017884 |
| domain | Isw1/2, N-terminal | 125 - 345 | IPR044754 |
| domain | SNF2/RAD5-like, C-terminal helicase domain | 430 - 556 | IPR049730 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.- | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ACF complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2H in mammals, Isw2 in S. cerevisiae), an ACF1 homolog, and generally no other subunits, though Xenopus is an exception with a third non-conserved subunit. ACF plays roles in regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription and in DNA replication and repair. |
| CHRAC | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2H in mammals, Isw2 in S. cerevisiae), an ACF1 homolog, and additional small histone fold subunits (generally two of these, but Xenopus has only one and some additional non-conserved subunits). CHRAC plays roles in the regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription and in DNA replication and repair. |
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| ISWI-type complex | Any nuclear protein complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the imitation switch (ISWI) family. ISWI ATPases are involved in assembling chromatin and in sliding and spacing nucleosomes to regulate transcription of nuclear RNA polymerases I, II, and III and also DNA replication, recombination and repair. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| NURF complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2L in mammals), a NURF301 homolog (BPTF in humans), and additional subunits, though the composition of these additional subunits varies slightly with species. NURF is involved in regulation of transcription from TRNA polymerase II promoters. |
| polytene chromosome | A type of chromosome in a polyploid cell, formed when multiple copies of homologous chromosomes are aligned side by side to give a giant chromosome in which distinct chromosome bands are readily visible. |
| RSF complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2H in mammals) and an RSF1 homolog. It mediates nucleosome deposition and generates regularly spaced nucleosome arrays. In mammals, RSF is involved in regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoters). |
| transcription regulator complex | A protein complex that is capable of associating with DNA by direct binding, or via other DNA-binding proteins or complexes, and regulating transcription. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA | Catalytic activity that acts to modify DNA, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity | An activity, driven by ATP hydrolysis, that modulates the contacts between histones and DNA, resulting in a change in chromosome architecture within the nucleosomal array, leading to chromatin remodeling. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| helicase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| histone binding | Binding to a histone, any of a group of water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic or archaeal chromosomes. They are involved in the condensation and coiling of chromosomes during cell division and have also been implicated in gene regulation and DNA replication. They may be chemically modified (methylated, acetlyated and others) to regulate gene transcription. |
| histone octamer slider activity | A chromatin remodeler activity that slides core histone octamers along chromosomal DNA. |
| nucleosome array spacer activity | A histone octamer slider activity that spaces nucleosomes along chromosomal DNA. This activity is involved in assembling chromatin in uniform nucleosome arrays to regulate transcription by RNA polymerases I, II, and III, as well as DNA replication, recombination and repair. |
| nucleosome binding | Binding to a nucleosome, a complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures. |
| nucleotide binding | Binding to a nucleotide, any compound consisting of a nucleoside that is esterified with (ortho)phosphate or an oligophosphate at any hydroxyl group on the ribose or deoxyribose. |
15 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromatin organization | The assembly or remodeling of chromatin composed of DNA complexed with histones, other associated proteins, and sometimes RNA. |
| chromatin remodeling | A dynamic process of chromatin reorganization resulting in changes to chromatin structure. These changes allow DNA metabolic processes such as transcriptional regulation, DNA recombination, DNA repair, and DNA replication. |
| DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly | The formation of nucleosomes on newly synthesized DNA, coupled to strand elongation. |
| heterochromatin formation | An epigenetic gene silencing mechanism in which chromatin is compacted into heterochromatin, resulting in a chromatin conformation refractory to transcription. This process starts with heterochromatin nucleation, its spreading, and ends with heterochromatin boundary formation. |
| negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| nuclear speck organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of nuclear specks, a class of nuclear body in which splicing factors are localized. |
| nucleosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of one or more nucleosomes. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of circadian rhythm | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a circadian rhythm. A circadian rhythm is a biological process in an organism that recurs with a regularity of approximately 24 hours. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| sperm DNA condensation | The progressive compaction of the spermatid chromatin so that it reaches a level of condensation that is not compatible with nuclear activities such as transcription or DNA replication. |
| sperm DNA decondensation | Unwinding of the condensed nuclear chromatin of an inactive male pronucleus after fertilization. |
| spermatogenesis | The developmental process by which male germ line stem cells self renew or give rise to successive cell types resulting in the development of a spermatozoa. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P38144 | ISW1 | ISWI chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase ISW1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q3B7N1 | CHD1L | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9VL72 | Etl1 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A containing DEAD/H box 1 homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q86WJ1 | CHD1L | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NRZ9 | HELLS | Lymphoid-specific helicase | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60264 | SMARCA5 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P28370 | SMARCA1 | Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q60848 | Hells | Lymphocyte-specific helicase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CXF7 | Chd1l | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P40201 | Chd1 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91ZW3 | Smarca5 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6PGB8 | Smarca1 | Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q7G8Y3 | Os01g0367900 | Probable chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| P41877 | isw-1 | Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain isw-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q22516 | chd-3 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 3 homolog | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9XFH4 | DDM1 | ATP-dependent DNA helicase DDM1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWY3 | CHR11 | ISWI chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase CHR11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSKTDTAAVE | ATEENSNETT | SDAATSSSGE | KEAEFDNKIE | ADRSRRFDFL | LKQTEIFTHF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| MTNSAKSPTK | PKGRPKKIKD | KDKEKDVADH | RHRKTEQEED | EELLAEDSAT | KEIFRFDASP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AYIKSGEMRD | YQIRGLNWMI | SLYENGINGI | LADEMGLGKT | LQTISLLGYL | KHFKNQAGPH |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| IVIVPKSTLQ | NWVNEFKKWC | PSLRAVCLIG | DQDTRNTFIR | DVLMPGEWDV | CVTSYEMCIR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EKSVFKKFNW | RYLVIDEAHR | IKNEKSKLSE | ILREFKTANR | LLITGTPLQN | NLHELWALLN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| FLLPDVFNSS | EDFDEWFNTN | TCLGDDALIT | RLHAVLKPFL | LRRLKAEVEK | RLKPKKEMKI |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| FVGLSKMQRD | WYTKVLLKDI | DVVNGAGKVE | KMRLQNILMQ | LRKCTNHPYL | FDGAEPGPPY |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TTDTHLVYNS | GKMAILDKLL | PKLQEQGSRV | LIFSQMTRML | DILEDYCHWR | NYNYCRLDGQ |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| TPHEDRNRQI | QEFNMDNSAK | FLFMLSTRAG | GLGINLATAD | VVIIYDSDWN | PQMDLQAMDR |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| AHRIGQKKQV | RVFRLITEST | VEEKIVERAE | VKLRLDKMVI | QGGRLVDNRS | NQLNKDEMLN |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| IIRFGANQVF | SSKETDITDE | DIDVILERGE | AKTAEQKAAL | DSLGESSLRT | FTMDTNGEAG |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| TSSVYQFEGE | DWREKQKLNA | LGNWIEPPKR | ERKANYAVDA | YFREALRVSE | PKAPKAPRPP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| KQPIVQDFQF | FPPRLFELLD | QEIYYFRKTV | GYKVPKNTEL | GSDATKVQRE | EQRKIDEAEP |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| LTEEEIQEKE | NLLSQGFTAW | TKRDFNQFIK | ANEKYGRDDI | DNIAKDVEGK | TPEEVIEYNA |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| VFWERCTELQ | DIERIMGQIE | RGEGKIQRRL | SIKKALDQKM | SRYRAPFHQL | RLQYGNNKGK |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| NYTEIEDRFL | VCMLHKLGFD | KENVYEELRA | AIRASPQFRF | DWFIKSRTAL | ELQRRCNTLI |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| TLIERENIEL | EEKERAEKKK | KAPKGSVSAG | SGSASSNTPA | PAPQPKASQK | RKSEVVATSS |
| NSKKKKK |