Q19266
Gene name |
pkc-3 (aPKC, F09E5.1) |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C-like 3 |
Names |
EC 2.7.11.13 , Atypical protein kinase C-3 , aPKC3 |
Species |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
KEGG Pathway |
cel:CELE_F09E5.1 |
EC number |
2.7.11.13: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
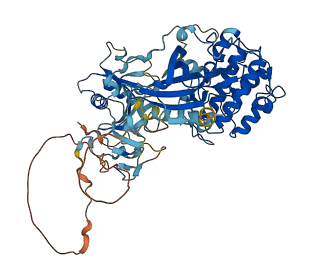
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
230-597 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Atypical Protein Kinase C iota) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
394-417 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
257-586 (Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, Atypical Protein Kinase C) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
394-417 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
253-586 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Ivey RA et al. (2014) "Requirements for pseudosubstrate arginine residues during autoinhibition and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-(PO₄)₃-dependent activation of atypical PKC", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 25021-30
- Huang X et al. (2003) "Crystal structure of an inactive Akt2 kinase domain", Structure (London, England : 1993), 11, 21-30
- Truebestein L et al. (2021) "Structure of autoinhibited Akt1 reveals mechanism of PIP(3)-mediated activation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118,
- Lučić I et al. (2018) "Conformational sampling of membranes by Akt controls its activation and inactivation", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115, E3940-E3949
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q19266
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q19266-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q19266
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q19266 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q19266
14 regional properties for Q19266
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | PB1 domain | 12 - 95 | IPR000270 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 253 - 522 | IPR000719 |
| domain | AGC-kinase, C-terminal | 524 - 595 | IPR000961 |
| domain | Protein kinase C-like, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding domain | 127 - 179 | IPR002219 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 373 - 385 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 259 - 286 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Protein kinase, C-terminal | 544 - 585 | IPR017892 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 125 - 139 | IPR020454-1 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 141 - 150 | IPR020454-2 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 154 - 165 | IPR020454-3 |
| domain | Diacylglycerol/phorbol-ester binding | 166 - 178 | IPR020454-4 |
| domain | Atypical protein kinase C, catalytic domain | 257 - 586 | IPR034659 |
| domain | Protein kinase C, PB1 domain | 13 - 95 | IPR034877 |
| domain | PB1-like domain | 12 - 95 | IPR053793 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.13 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| cell cortex | The region of a cell that lies just beneath the plasma membrane and often, but not always, contains a network of actin filaments and associated proteins. |
| cortical actin cytoskeleton | The portion of the actin cytoskeleton, comprising filamentous actin and associated proteins, that lies just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| diacylglycerol-dependent serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell differentiation | The cellular developmental process in which a relatively unspecialized cell, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cell, acquires specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize a specific cell. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| defense response to fungus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a fungus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an embryo over time, from zygote formation until the end of the embryonic life stage. The end of the embryonic life stage is organism-specific and may be somewhat arbitrary; for mammals it is usually considered to be birth, for insects the hatching of the first instar larva from the eggshell. |
| establishment or maintenance of cell polarity | Any cellular process that results in the specification, formation or maintenance of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| gastrulation | A complex and coordinated series of cellular movements that occurs at the end of cleavage during embryonic development of most animals. The details of gastrulation vary from species to species, but usually result in the formation of the three primary germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. |
| gonad development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the gonad over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The gonad is an animal organ that produces gametes; in some species it also produces hormones. |
| gonadal mesoderm development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the gonadal mesoderm over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The gonadal mesoderm is the middle layer of the three primary germ layers of the embryo which will go on to form the gonads of the organism. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| response to wounding | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to the organism. |
| single fertilization | The union of male and female gametes to form a zygote. |
15 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P24583 | PKC1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| A1Z9X0 | aPKC | Atypical protein kinase C | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P41743 | PRKCI | Protein kinase C iota type | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q05513 | PRKCZ | Protein kinase C zeta type | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q62074 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q02956 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| F1M7Y5 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09217 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q17941 | akt-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase akt-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9XTG7 | akt-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase akt-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9Y1J3 | pdk-1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| P34722 | tpa-1 | Protein kinase C-like 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P90980 | pkc-2 | Protein kinase C-like 2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q2L6W9 | sax-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase sax-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q90XF2 | prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSPTSLEED | GDIKLKTRFQ | GQVVVLYARP | PLILDDFFAL | LKDACKQHKK | QDITVKWIDE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DGDPISIDSQ | MELDEAVRCL | NSSQEAELNI | HVFVGKPELP | GLPCQGEDKT | VYRRGARRWK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KIYLYNGHRF | QAKRLNRRIQ | CFICHDYIWG | IGRQGFRCVD | CRLCVHKKCH | RHVRTHCGQA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LQGPNIIPMA | PASGSLKGAR | SNTSSSTTRS | GGGIDNGAFH | EHEIESPGST | SHDASRAMNG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NGSSKWAVSL | NDFRLLTVIG | RGSYAKVVQA | EHVSTRQIYA | IKIIKKEMFN | EDEDIDWVQT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| EKSVFEAASN | YPFLVGLHSC | FQTESRLFFV | IEFVPGGDLM | FHMQQQRKLP | EEHARFYSGE |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| IILALHFLHS | RGIIYRDLKL | DNVLIDAEGH | IKLTDYGMCK | ENIKDGDLTS | TFCGTPNYIA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PEILRGDEYG | FSVDWWALGV | LMFEMMAGRS | PFDIVGMQNS | EENTEDYLFQ | IILERQIRIP |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| RSLSVRASGI | LKGFLNKDPT | ERLGCKLDIN | EGLRDMKEHQ | FFRGFIDWEA | LEQKAVAPPY |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | |
| HPAVESDRDL | THFDHQFTDE | LPQLSPDNPD | VIARIDQSEF | DGFEYVNPLQ | MSREDSV |