Q17850
Gene name |
pak-1 (C09B8.7) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase pak-1 |
Names |
CePAK, p21-activated kinase 1, PAK1 |
Species |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
KEGG Pathway |
cel:CELE_C09B8.7 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
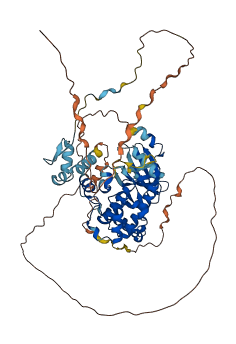
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q17850
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q17850-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q17850
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q17850 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q17850
5 regional properties for Q17850
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CRIB domain | 67 - 123 | IPR000095 |
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 295 - 546 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 410 - 422 | IPR008271 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 301 - 324 | IPR017441 |
| domain | p21 activated kinase binding domain | 65 - 110 | IPR033923 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| hemidesmosome | A cell-substrate junction (attachment structure) found in epithelial cells that links intermediate filaments to extracellular matrices via transmembrane complexes. In vertebrates, hemidesmosomes mediate contact between the basal side of epithelial cells and the basal lamina. In C. elegans, hemidesmosomes connect epithelial cells to distinct extracellular matrices on both the apical and basal cell surfaces. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| embryonic body morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the embryonic soma are generated and organized. |
| embryonic morphogenesis | The process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized during the embryonic phase. The embryonic phase begins with zygote formation. The end of the embryonic phase is organism-specific. For example, it would be at birth for mammals, larval hatching for insects and seed dormancy in plants. |
| gonad morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the gonads are generated and organized. A gonad is an animal organ producing gametes, e.g. the testes or the ovary in mammals. |
| hemidesmosome assembly | Assembly of hemidesmosomes, integrin-containing protein complexes that bind to laminin in the basal lamina. Hemidesmosomes form the contact between the basal surface of epithelial cells and the underlying basal lamina. |
| inductive cell migration | Migration of a cell in a multicellular organism that, having changed its location, is required to induce normal properties in one or more cells at its new location. An example of this would be the distal tip cells of Caenorhabditis elegans. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| motor neuron axon guidance | The process in which the migration of an axon growth cone of a motor neuron is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| nematode larval development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the nematode larva over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Nematode larval development begins with the newly hatched first-stage larva (L1) and ends with the end of the last larval stage (for example the fourth larval stage (L4) in C. elegans). Each stage of nematode larval development is characterized by proliferation of specific cell lineages and an increase in body size without alteration of the basic body plan. Nematode larval stages are separated by molts in which each stage-specific exoskeleton, or cuticle, is shed and replaced anew. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of axonogenesis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of axonogenesis, the generation of an axon, the long process of a neuron. |
| regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAP kinase (MAPK) cascade. |
22 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q12469 | SKM1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase SKM1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q08E52 | PAK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q7YQL4 | PAK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| Q9VXE5 | mbt | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK mbt | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q9P286 | PAK5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NQU5 | PAK6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O96013 | PAK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13177 | PAK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O75914 | PAK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q13153 | PAK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8C015 | Pak5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3ULB5 | Pak6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8CIN4 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61036 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O88643 | Pak1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| D4A280 | Pak5 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64303 | Pak2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35465 | Pak1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62829 | Pak3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5EGQ3 | max-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase max-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EFU0 | pak-2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase pak-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9NB31 | cst-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase cst-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MKAFSSYDEK | PPAPPIRFSS | SATRENQVVG | LKPLPKEPEA | TKKKKTMPNP | FMKKNKDKKE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ASEKPVISRP | SNFEHTIHVG | YDPKTGEFTG | MPEAWARLLT | DSQISKQEQQ | QNPQAVLDAL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KYYTQGESSG | QKWLQYDMMF | IDDAPSRTPS | YGLKPQPYST | SSLPYHGNKI | QDPRKMNPMT |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TSTSSAGYNS | KQGVPPTTFS | VNENRSSMPP | SYAPPPVPHG | ETPADIVPPA | IPDRPARTLS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IYTKPKEEEE | KIPDLSKGQF | GVQARGQKAK | KKMTDAEVLT | KLRTIVSIGN | PDRKYRKVDK |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IGSGASGSVY | TAIEISTEAE | VAIKQMNLKD | QPKKELIINE | ILVMRENKHA | NIVNYLDSYL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VCDELWVVME | YLAGGSLTDV | VTECQMEDGI | IAAVCREVLQ | ALEFLHSRHV | IHRDIKSDNI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LLGMDGSVKL | TDFGFCAQLS | PEQRKRTTMV | GTPYWMAPEV | VTRKQYGPKV | DVWSLGIMAI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EMVEGEPPYL | NENPLRAIYL | IATNGKPDFP | GRDSMTLLFK | DFVDSALEVQ | VENRWSASQL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | |||
| LTHPFLRCAK | PLASLYYLIV | AAKKSIAEAS | NS |