Q09014
Gene name |
Ncf1 |
Protein name |
Neutrophil cytosol factor 1 |
Names |
NCF-1, 47 kDa neutrophil oxidase factor, NCF-47K, Neutrophil NADPH oxidase factor 1, p47-phox |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:17969 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
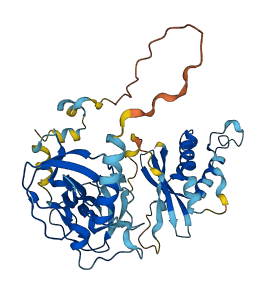
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
156-215 (N-SH3); 226-285 (C-SH3) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yuzawa S et al. (2004) "A molecular mechanism for autoinhibition of the tandem SH3 domains of p47phox, the regulatory subunit of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase", Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms, 9, 443-56
- Yuzawa S et al. (2003) "Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the autoinhibited form of the tandem SH3 domain of p47(phox)", Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography, 59, 1479-80
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q09014
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q09014-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
4 variants for Q09014
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs251450768 | 10 | A>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs230192078 | 19 | I>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs51100936 | 345 | L>Q | No | Ensembl | |
| rs223656911 | 350 | T>A | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q09014
8 regional properties for Q09014
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | SH3 domain | 156 - 215 | IPR001452-1 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 226 - 285 | IPR001452-2 |
| domain | Phox homology | 4 - 125 | IPR001683 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1, C-terminal | 359 - 390 | IPR015039 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1, PBR/AIR | 282 - 331 | IPR032136 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1, PX domain | 6 - 123 | IPR034909 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1, first SH3 domain | 160 - 212 | IPR035756 |
| domain | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1, second SH3 domain | 230 - 282 | IPR035757 |
10 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| extrinsic component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to one of its surfaces, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| NADPH oxidase complex | A enzyme complex of which the core is a heterodimer composed of a light (alpha) and heavy (beta) chain, and requires several other water-soluble proteins of cytosolic origin for activity. Functions in superoxide generation by the NADPH-dependent reduction of O2. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| rough endoplasmic reticulum | The rough (or granular) endoplasmic reticulum (ER) has ribosomes adhering to the outer surface; the ribosomes are the site of translation of the mRNA for those proteins which are either to be retained within the cisternae (ER-resident proteins), the proteins of the lysosomes, or the proteins destined for export from the cell. Glycoproteins undergo their initial glycosylation within the cisternae. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| phosphatidylinositol binding | Binding to an inositol-containing glycerophospholipid, i.e. phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) and its phosphorylated derivatives. |
| phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 3' and 4' positions. |
| SH3 domain binding | Binding to a SH3 domain (Src homology 3) of a protein, small protein modules containing approximately 50 amino acid residues found in a great variety of intracellular or membrane-associated proteins. |
| superoxide-generating NAD(P)H oxidase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: NAD(P)H + O2 = NAD(P)H + O2-. |
| superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity | Increases the activity of the enzyme superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase. |
21 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| cell population proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| cellular defense response | A defense response that is mediated by cells. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| defense response to fungus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a fungus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| defense response to Gram-positive bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-positive bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a potentially harmful byproduct of aerobic cellular respiration which can cause damage to DNA. |
| inflammatory response | The immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The process is characterized by local vasodilation, extravasation of plasma into intercellular spaces and accumulation of white blood cells and macrophages. |
| leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity | The directed killing of a target cell by a leukocyte. |
| leukotriene metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving leukotriene, a pharmacologically active substance derived from a polyunsaturated fatty acid, such as arachidonic acid. |
| NADP catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate, a coenzyme involved in many redox and biosynthetic reactions; catabolism may be of either the oxidized form, NADP, or the reduced form, NADPH. |
| neutrophil-mediated killing of fungus | The directed killing of a fungal cell by a neutrophil. |
| neutrophil-mediated killing of gram-positive bacterium | The directed killing of a gram-positive bacterium by a neutrophil. |
| protein targeting to membrane | The process of directing proteins towards a membrane, usually using signals contained within the protein. |
| reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of reactive oxygen species, any molecules or ions formed by the incomplete one-electron reduction of oxygen. |
| regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of a phase of elevated metabolic activity, during which oxygen consumption increases made as a defense response ; this leads to the production, by an NADH dependent system, of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anions and hydroxyl radicals. |
| respiratory burst | A phase of elevated metabolic activity, during which oxygen consumption increases; this leads to the production, by an NADH dependent system, of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anions and hydroxyl radicals. |
| respiratory burst involved in defense response | A phase of elevated metabolic activity, during which oxygen consumption increases made as part of a defense response ; this leads to the production, by an NADH dependent system, of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anions and hydroxyl radicals. |
| response to bacterium | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a bacterium. |
| response to yeast | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a yeast species. |
| superoxide anion generation | The enzymatic generation of superoxide, the superoxide anion O2- (superoxide free radical), or any compound containing this species, by a cell in response to environmental stress, thereby mediating the activation of various stress-inducible signaling pathways. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O77774 | NCF1 | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P14598 | NCF1 | Neutrophil cytosol factor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| A6NI72 | NCF1B | Putative neutrophil cytosol factor 1B | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| A8MVU1 | NCF1C | Putative neutrophil cytosol factor 1C | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P97369 | Ncf4 | Neutrophil cytosol factor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A2AAY5 | Sh3pxd2b | SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 2B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O89032 | Sh3pxd2a | SH3 and PX domain-containing protein 2A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| F1M707 | Ncf1 | Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGDTFIRHIA | LLGFEKRFIP | SQHYVYMFLV | KWQDLSEKVV | YRKFTEIYEF | HKMLKEMFPI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EAGEIHTENR | VIPHLPAPRW | FDGQRAAESR | QGTLTEYFNG | LMGLPVKISR | CPHLLDFFKV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RPDDLKLPTD | SQAKKPETYL | VPKDGKNNVA | DITGPIILQT | YRAIADYEKS | SGTEMTVATG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DVVDVVEKSE | SGWWFCQMKT | KRGWVPASYL | EPLDSPDEAE | DPDPNYAGEP | YVTIKAYAAV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EEDEMSLSEG | EAIEVIHKLL | DGWWVVRKGD | ITGYFPSMYL | QKAGEEITQA | QRQIRGRGAP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PRRSTIRNAQ | SIHQRSRKRL | SQDTYRRNSV | RFLQQRRRPG | RPGPLSTDGT | KDNPSTPRVK |
| 370 | 380 | ||||
| PQPAVPPRPS | SDLILHRCTE | STKRKLTSAV |