Q07014
Gene name |
Lyn |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn |
Names |
V-yes-1 Yamaguchi sarcoma viral related oncogene homolog, p53Lyn, p56Lyn |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:81515 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
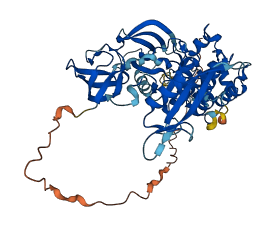
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding, PTM |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
384-408 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
247-501 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Wang Q et al. (2010) "Multicolor monitoring of dysregulated protein kinases in chronic myelogenous leukemia", ACS chemical biology, 5, 887-95
- Sotirellis N et al. (1995) "Autophosphorylation induces autoactivation and a decrease in the Src homology 2 domain accessibility of the Lyn protein kinase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 270, 29773-80
- Williams NK et al. (2009) "Crystal structures of the Lyn protein tyrosine kinase domain in its Apo- and inhibitor-bound state", The Journal of biological chemistry, 284, 284-291
- Saharinen P et al. (2003) "Autoinhibition of Jak2 tyrosine kinase is dependent on specific regions in its pseudokinase domain", Molecular biology of the cell, 14, 1448-59
- Brian BF 4th et al. (2022) "SH3-domain mutations selectively disrupt Csk homodimerization or PTPN22 binding", Scientific reports, 12, 5875
- Boggon TJ et al. (2004) "Structure and regulation of Src family kinases", Oncogene, 23, 7918-27
- Register AC et al. (2014) "SH2-catalytic domain linker heterogeneity influences allosteric coupling across the SFK family", Biochemistry, 53, 6910-23
- Engen JR et al. (2008) "Structure and dynamic regulation of Src-family kinases", Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 65, 3058-73
- Alvarado JJ et al. (2010) "Crystal structure of the Src family kinase Hck SH3-SH2 linker regulatory region supports an SH3-dominant activation mechanism", The Journal of biological chemistry, 285, 35455-61
- Hong E et al. (2004) "Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase-6 Src homology 2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 29700-8
- Ko S et al. (2009) "Structural basis of the auto-inhibition mechanism of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase PTK6", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 384, 236-42
- Qiu H et al. (2002) "Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 34634-41
- Ma W et al. (2009) "Mutation profile of JAK2 transcripts in patients with chronic myeloproliferative neoplasias", The Journal of molecular diagnostics : JMD, 11, 49-53
- Laham LE et al. (2000) "The activation loop in Lck regulates oncogenic potential by inhibiting basal kinase activity and restricting substrate specificity", Oncogene, 19, 3961-70
- Furlan G et al. (2014) "Phosphatase CD45 both positively and negatively regulates T cell receptor phosphorylation in reconstituted membrane protein clusters", The Journal of biological chemistry, 289, 28514-25
- Williams JC et al. (1997) "The 2.35 A crystal structure of the inactivated form of chicken Src: a dynamic molecule with multiple regulatory interactions", Journal of molecular biology, 274, 757-75
- Meng Y et al. (2014) "Locking the active conformation of c-Src kinase through the phosphorylation of the activation loop", Journal of molecular biology, 426, 423-35
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q07014
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q07014-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q07014
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q07014 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q07014
8 regional properties for Q07014
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 247 - 501 | IPR000719 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 127 - 226 | IPR000980 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 63 - 123 | IPR001452 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 363 - 375 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 253 - 275 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 247 - 497 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn, SH3 domain | 67 - 122 | IPR035748 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn, SH2 domain | 125 - 225 | IPR035852 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
17 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction | A cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex. The epithelial cadherins, or E-cadherins, of each interacting cell extend through the plasma membrane into the extracellular space and bind to each other. The E-cadherins bind to catenins on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, where the E-cadherin-catenin complex binds to cytoskeletal components and regulatory and signaling molecules. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integrin alpha2-beta1 complex | An integrin complex that comprises one alpha2 subunit and one beta1 subunit. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| mitochondrial crista | Any of the inward folds of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Their number, extent, and shape differ in mitochondria from different tissues and organisms. They appear to be devices for increasing the surface area of the mitochondrial inner membrane, where the enzymes of electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation are found. Their shape can vary with the respiratory state of the mitochondria. |
| mitochondrial intermembrane space | The region between the inner and outer lipid bilayers of the mitochondrial envelope. |
| mitochondrial membrane | Either of the lipid bilayers that surround the mitochondrion and form the mitochondrial envelope. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| postsynaptic specialization, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane. Its major components include the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
20 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| ephrin receptor binding | Binding to an ephrin receptor. |
| gamma-tubulin binding | Binding to the microtubule constituent protein gamma-tubulin. |
| glycosphingolipid binding | Binding to glycosphingolipid, a compound with residues of sphingoid and at least one monosaccharide. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + protein L-tyrosine = ADP + protein L-tyrosine phosphate by a non-membrane spanning protein. |
| phosphoprotein binding | Binding to a phosphorylated protein. |
| phosphorylation-dependent protein binding | Binding to a protein upon phosphorylation of the target protein. |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a platelet-derived growth factor receptor. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| scaffold protein binding | Binding to a scaffold protein. Scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signaling pathways. Although not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signaling pathway, tethering them into complexes. |
| SH3 domain binding | Binding to a SH3 domain (Src homology 3) of a protein, small protein modules containing approximately 50 amino acid residues found in a great variety of intracellular or membrane-associated proteins. |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
74 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adaptive immune response | An immune response mediated by cells expressing specific receptors for antigen produced through a somatic diversification process, and allowing for an enhanced secondary response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen (immunological memory). |
| B cell homeostasis | The process of regulating the proliferation and elimination of B cells such that the total number of B cells within a whole or part of an organism is stable over time in the absence of an outside stimulus. |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| cellular response to extracellular stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an extracellular stimulus. |
| cellular response to heat | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a heat stimulus, a temperature stimulus above the optimal temperature for that organism. |
| cellular response to retinoic acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a retinoic acid stimulus. |
| dendritic cell differentiation | The process in which a precursor cell type acquires the specialized features of a dendritic cell. A dendritic cell is a leukocyte of dendritic lineage specialized in the uptake, processing, and transport of antigens to lymph nodes for the purpose of stimulating an immune response via T cell activation. |
| erythrocyte differentiation | The process in which a myeloid precursor cell acquires specializes features of an erythrocyte. |
| Fc receptor mediated inhibitory signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of the binding of the Fc portion of an immunoglobulin by an Fc receptor capable of inhibiting an immune effector process contributing to an immune response. The Fc portion of an immunoglobulin is its C-terminal constant region. |
| Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a the binding of the Fc portion of an immunoglobulin by an Fc receptor capable of activating or perpetuating an immune response. The Fc portion of an immunoglobulin is its C-terminal constant region. |
| hemopoiesis | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates. |
| histamine secretion by mast cell | The regulated release of histamine by a mast cell or group of mast cells. |
| immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell capable of activating, perpetuating, or inhibiting an immune response. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. Lipopolysaccharides are major components of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, making them prime targets for recognition by the immune system. |
| negative regulation of B cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of B cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| negative regulation of intracellular signal transduction | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of intracellular signal transduction. |
| negative regulation of MAP kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of MAP kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of mast cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of mast cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of myeloid leukocyte differentiation. |
| negative regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| negative regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| oligodendrocyte development | The process aimed at the progression of an oligodendrocyte over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. An oligodendrocyte is a type of glial cell involved in myelinating the axons in the central nervous system. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| platelet degranulation | The regulated exocytosis of secretory granules containing preformed mediators such as histamine and serotonin by a platelet. |
| positive regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cellular component movement | OBSOLETE. Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the movement of a cellular component. |
| positive regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of dendritic cell apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of the Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of glial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of glial cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of mast cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of mast cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to a molecule. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signaling via the stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade. |
| positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the introduction of a phosphate group to a tyrosine residue of a STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) protein. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of B cell apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of B cell apoptotic process. |
| regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signaling pathways initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a B cell. |
| regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| regulation of cytokine production | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of production of a cytokine. |
| regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| regulation of erythrocyte differentiation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of erythrocyte differentiation. |
| regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response, the immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. |
| regulation of mast cell activation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell activation. |
| regulation of mast cell degranulation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell degranulation. |
| regulation of monocyte chemotaxis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of monocyte chemotaxis. |
| regulation of platelet aggregation | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is the adhesion of one platelet to one or more other platelets via adhesion molecules. |
| regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| response to amino acid | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an amino acid stimulus. An amino acid is a carboxylic acids containing one or more amino groups. |
| response to axon injury | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an axon injury stimulus. |
| response to carbohydrate | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a carbohydrate stimulus. |
| response to hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a hormone stimulus. |
| response to insulin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| response to organic cyclic compound | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an organic cyclic compound stimulus. |
| response to peptide hormone | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a peptide hormone stimulus. A peptide hormone is any of a class of peptides that are secreted into the blood stream and have endocrine functions in living animals. |
| response to sterol depletion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating deprivation of sterols. Sterols are a group of steroids characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl groups and a hydrocarbon side-chain in the molecule. |
| response to toxic substance | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a toxic stimulus. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| tolerance induction to self antigen | Tolerance induction directed at self antigens. |
| toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to toll-like receptor 4. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
84 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V9J3 | Src42A | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q64725 | Syk | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P70600 | Ptk2b | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O35346 | Ptk2 | Focal adhesion kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q5U2X5 | Tnk2 | Activated CDC42 kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09760 | Fer | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fer | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| F4JTP5 | STY46 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22558 | STY8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWL6 | STY17 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY17 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGCIKSKRKD | NLNDDGVDMK | TQPVRNTDRT | IYVRDPTSNK | QQRPVPESQL | LPGQRFQAKD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PEEQGDIVVA | LYPYDGIHPD | DLSFKKGEKM | KVLEEHGEWW | KAKSLSSKRE | GFIPSNYVAK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| VNTLETEEWF | FKDITRKDAE | RQLLAPGNSA | GAFLIRESET | LKGSFSLSVR | DYDPMHGDVI |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KHYKIRSLDN | GGYYISPRIT | FPCISDMIKH | YQKQSDGLCR | RLEKACISPK | PQKPWDKDAW |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EIPRESIKLV | KKLGAGQFGE | VWMGYYNNST | KVAVKTLKPG | TMSAQAFLEE | ANLMKTLQHD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KLVRLYAVVT | KEEPIYIITE | FMAKGSLLDF | LKSDEGSKVL | LPKLIDFSAQ | IAEGMAYIER |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KNYIHRDLRA | ANVLVSESLM | CKIADFGLAR | VIEDNEYTAR | EGAKFPIKWT | APEAINFGCF |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TIKSDVWSFG | ILLYEIVTYG | KIPYPGRTNA | DVMTALSQGY | RMPRMENCPD | ELYDIMKMCW |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | |||
| KESAEERPTF | DYLQSVLDDF | YTATEGQYQQ | QP |